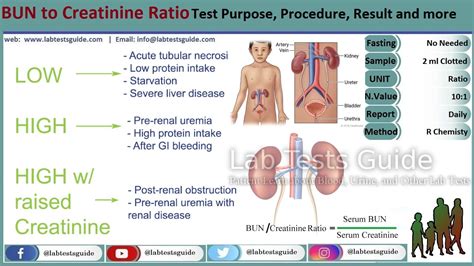
The concept of bun creat ratio, also known as the bun-to-creatinine ratio, is a critical metric in clinical diagnostics, particularly in the realm of renal function assessment. This ratio is calculated by dividing the blood urea nitrogen (BUN) level by the creatinine level, both of which are waste products that are filtered out by the kidneys. Understanding the bun creat ratio is essential for healthcare professionals to diagnose and manage conditions affecting kidney function.
Introduction to Bun Creat Ratio
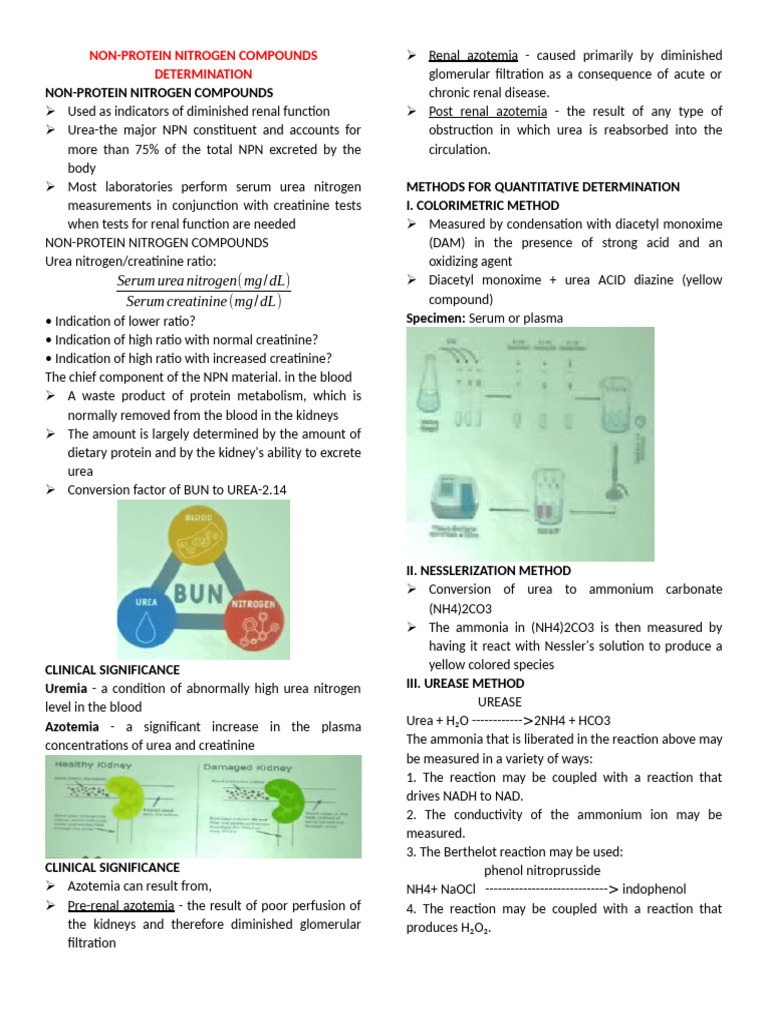
The bun creat ratio is significant because it helps differentiate between prerenal, renal, and postrenal causes of acute kidney injury (AKI) or chronic kidney disease (CKD). Prerenal causes are related to decreased blood flow to the kidneys, such as dehydration or heart failure. Renal causes involve direct damage to the kidney tissues, as seen in diseases like glomerulonephritis. Postrenal causes are related to obstruction of urine flow, such as kidney stones or bladder outlet obstruction. A normal bun creat ratio typically ranges from 10:1 to 20:1, though this can vary slightly between laboratories.
Calculating the Bun Creat Ratio
To calculate the bun creat ratio, one simply divides the BUN level (in mg/dL) by the creatinine level (in mg/dL). For example, if a patient’s BUN level is 20 mg/dL and their creatinine level is 1 mg/dL, the bun creat ratio would be 20:1. This calculation is straightforward but provides valuable information about the patient’s kidney function and potential underlying causes of renal impairment.
| Condition | BUN Level (mg/dL) | Creatinine Level (mg/dL) | Bun Creat Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 10-20 | 0.6-1.2 | 10:1 to 20:1 |
| Prerenal AKI | 40 | 1.5 | 26.67:1 |
| Renal AKI | 20 | 2.0 | 10:1 |
| Postrenal AKI | 15 | 1.0 | 15:1 |
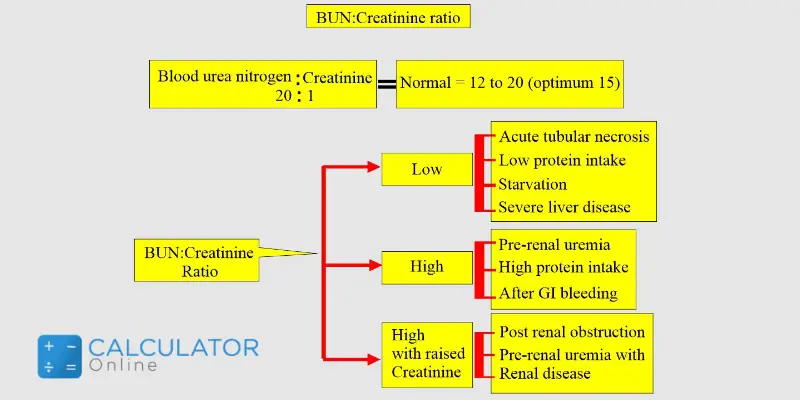
Key Points
- The bun creat ratio is a diagnostic tool used to assess kidney function and differentiate between prerenal, renal, and postrenal causes of acute kidney injury or chronic kidney disease.
- A normal bun creat ratio ranges from 10:1 to 20:1, though this can vary slightly between laboratories.
- Prerenal causes of AKI often result in a higher bun creat ratio, typically above 20:1, due to increased BUN reabsorption in the setting of decreased renal perfusion.
- Renal causes, which directly damage the kidney tissues, usually result in a ratio within the normal range or slightly elevated, as both BUN and creatinine are elevated but to a similar extent.
- Postrenal causes, involving obstruction of urine flow, may present with a variety of bun creat ratios, depending on the severity and duration of the obstruction, as well as the presence of any underlying renal dysfunction.
Clinical Interpretation of the Bun Creat Ratio
Clinical interpretation of the bun creat ratio must consider the patient’s volume status, as dehydration or volume depletion can increase the BUN level, thus elevating the ratio. Conversely, overhydration can dilute the BUN level, potentially lowering the ratio. It’s also essential to consider other factors that can influence BUN and creatinine levels independently, such as high-protein diets, gastrointestinal bleeding (which can increase BUN), and muscle mass (which affects creatinine levels).
Limitations and Considerations
While the bun creat ratio is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has limitations. For instance, it may not accurately reflect the severity of kidney dysfunction in certain conditions, such as early stages of kidney disease or in patients with significant muscle wasting, where creatinine levels may be artificially low. Moreover, the ratio can be influenced by factors unrelated to kidney function, such as liver disease, which can affect urea production, or certain medications that alter creatinine secretion or reabsorption in the kidneys.
What does a high bun creat ratio indicate?
+A high bun creat ratio, typically above 20:1, often suggests prerenal causes of acute kidney injury, such as dehydration or heart failure, where there's increased reabsorption of urea in the kidneys due to decreased blood flow.
Can the bun creat ratio be used to diagnose chronic kidney disease?
+While the bun creat ratio can provide insights into kidney function, it is not used in isolation to diagnose chronic kidney disease (CKD). Diagnosis of CKD involves assessment of kidney damage (usually indicated by the presence of protein in the urine) and decreased kidney function (measured by the glomerular filtration rate, GFR), among other factors.
How does muscle mass affect the bun creat ratio?
+Muscle mass affects the creatinine level, as creatinine is a byproduct of muscle metabolism. Individuals with less muscle mass, such as the elderly or those with muscle wasting diseases, will have lower creatinine levels, potentially altering the bun creat ratio. This must be considered when interpreting the ratio, especially in patients with significant variations in muscle mass.
In conclusion, the bun creat ratio is a valuable tool in the assessment of kidney function, offering insights into the potential causes of acute kidney injury or chronic kidney disease. However, its interpretation must be nuanced, considering the patient’s overall clinical context, including volume status, muscle mass, and the presence of other conditions that could influence BUN and creatinine levels. By understanding the strengths and limitations of the bun creat ratio, healthcare professionals can more effectively diagnose and manage renal disorders, ultimately improving patient outcomes.