The Bantu peoples are a diverse group of over 100 million people, spanning across central, eastern, and southern Africa. Their history, culture, and traditions are a rich tapestry, woven from the threads of various linguistic, ethnic, and geographical influences. To delve into the fascinating world of the Bantu peoples, let's explore five key facts that highlight their significance and contributions to the African continent.
Key Points
- The Bantu peoples originated from the Cameroon region, migrating to various parts of Africa over 2,000 years ago.
- They possess a distinct linguistic heritage, with over 500 languages belonging to the Bantu language family.
- Bantu cultures are known for their rich tradition of storytelling, music, and art, which play a vital role in their spiritual and social practices.
- The Bantu peoples have made significant contributions to African agriculture, introducing crops like bananas, yams, and cassava to various regions.
- Despite facing numerous challenges, including colonization and urbanization, the Bantu peoples continue to maintain their cultural identity and traditional practices.
Origin and Migration of the Bantu Peoples

The Bantu peoples are believed to have originated from the Cameroon region, specifically from the area around the Sanaga River. Around 2000 BCE, they began a gradual migration to various parts of Africa, driven by factors such as climate change, population growth, and the search for new resources. This migration, which spanned over 1,000 years, had a profound impact on the linguistic, cultural, and genetic landscape of Africa. Today, the Bantu peoples can be found in countries such as the Democratic Republic of Congo, Angola, Zambia, Tanzania, Kenya, and South Africa, among others.
Bantu Languages and Linguistic Diversity
The Bantu languages are a branch of the Niger-Congo language family, which is the largest language family in Africa. With over 500 languages, the Bantu language family is incredibly diverse, ranging from languages like Swahili and Zulu, which have millions of speakers, to smaller languages like Fang and Duala, which have fewer than 100,000 speakers. Despite this linguistic diversity, the Bantu languages share a common grammatical structure and vocabulary, reflecting their shared ancestry and cultural heritage. For instance, the Bantu languages are known for their complex system of noun classes, which are used to categorize nouns into different categories based on their semantic properties.
| Language | Number of Speakers |
|---|---|
| Swahili | over 100 million |
| Zulu | over 10 million |
| Fang | around 1 million |
| Duala | around 100,000 |

Bantu Cultures and Traditions
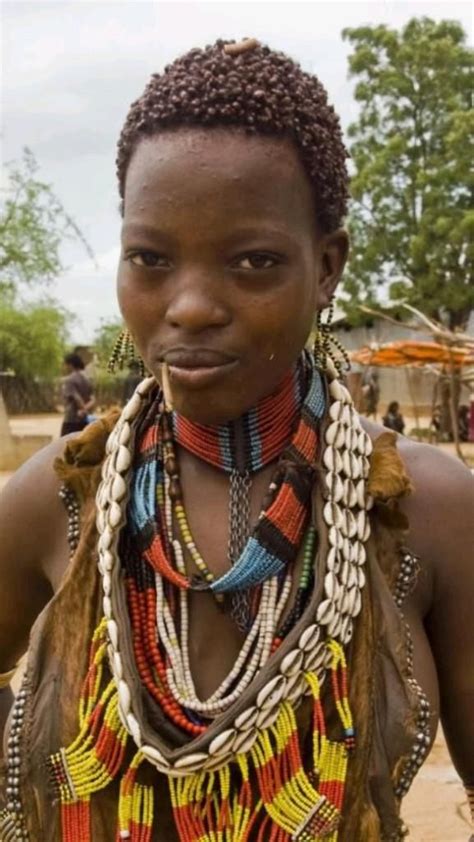

Bantu cultures are known for their rich tradition of storytelling, music, and art, which play a vital role in their spiritual and social practices. In many Bantu societies, storytelling is used to pass down cultural values, historical events, and moral lessons from one generation to the next. Music and dance are also essential components of Bantu cultures, with many communities using them to communicate with their ancestors, celebrate important events, and express their emotions. The Bantu peoples are also skilled artisans, producing intricate wood carvings, baskets, and textiles that reflect their cultural heritage and aesthetic sensibilities.
Agricultural Contributions of the Bantu Peoples
The Bantu peoples have made significant contributions to African agriculture, introducing crops like bananas, yams, and cassava to various regions. These crops have become staples in many African societies, providing a reliable source of food and income for millions of people. The Bantu peoples have also developed innovative farming techniques, such as crop rotation and irrigation, which have helped to increase agricultural productivity and reduce the risk of famine. Additionally, the Bantu peoples have played a crucial role in the development of African animal husbandry, introducing cattle, goats, and sheep to various regions and developing unique breeds that are well adapted to local environments.
In conclusion, the Bantu peoples are a vibrant and diverse group, with a rich cultural heritage and a significant impact on the African continent. From their origins in the Cameroon region to their migrations to various parts of Africa, the Bantu peoples have left an indelible mark on the linguistic, cultural, and agricultural landscape of Africa. As we continue to learn more about the Bantu peoples and their traditions, we are reminded of the importance of preserving cultural diversity and promoting cross-cultural understanding in our increasingly globalized world.
What is the significance of the Bantu migration in African history?
+The Bantu migration had a profound impact on the linguistic, cultural, and genetic landscape of Africa, shaping the course of African history and leaving a lasting legacy that can still be seen today.
What are some of the common characteristics of Bantu languages?
+Bantu languages are known for their complex system of noun classes, which are used to categorize nouns into different categories based on their semantic properties. They also have a distinctive grammatical structure and vocabulary, reflecting their shared ancestry and cultural heritage.
What is the role of storytelling in Bantu cultures?
+Storytelling plays a vital role in Bantu cultures, serving as a means of passing down cultural values, historical events, and moral lessons from one generation to the next. It is also used to entertain, educate, and socialize, and is often accompanied by music, dance, and other forms of artistic expression.