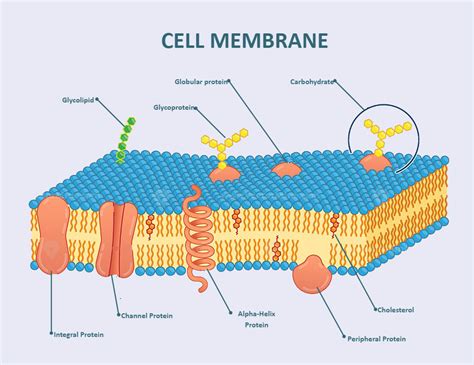
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin layer of lipid and protein molecules that surrounds the cell and regulates the movement of materials in and out. A labeled diagram of the cell membrane is essential for understanding its structure and function. The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, with the hydrophilic (water-loving) heads facing outwards and the hydrophobic (water-fearing) tails facing inwards.
Components of the Cell Membrane
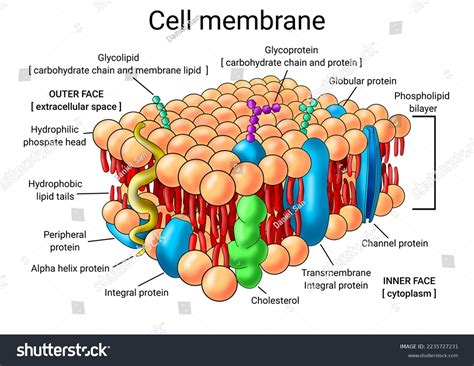
The cell membrane is composed of several key components, including phospholipids, proteins, and cholesterol. Phospholipids are the main structural component of the cell membrane, making up about 50-60% of its total weight. Proteins, on the other hand, make up about 20-30% of the cell membrane and play a crucial role in its function. Cholesterol is also present in the cell membrane, helping to maintain its fluidity and structure.
Phospholipid Bilayer
The phospholipid bilayer is the main structural component of the cell membrane. It is composed of two layers of phospholipid molecules, with the hydrophilic heads facing outwards and the hydrophobic tails facing inwards. This arrangement allows the cell membrane to be semi-permeable, regulating the movement of materials in and out of the cell. The phospholipid bilayer is also responsible for maintaining the cell’s shape and structure.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Phospholipids | Provide structure and semi-permeability to the cell membrane |
| Proteins | Regulate the movement of materials in and out of the cell, provide receptors for signaling molecules, and maintain cell shape |
| Cholesterol | Maintains fluidity and structure of the cell membrane |

Key Points
- The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, with the hydrophilic heads facing outwards and the hydrophobic tails facing inwards.
- Phospholipids, proteins, and cholesterol are the main components of the cell membrane.
- The cell membrane is semi-permeable, regulating the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
- Proteins play a crucial role in regulating the movement of materials in and out of the cell, providing receptors for signaling molecules, and maintaining cell shape.
- Cholesterol helps to maintain the fluidity and structure of the cell membrane.
Function of the Cell Membrane
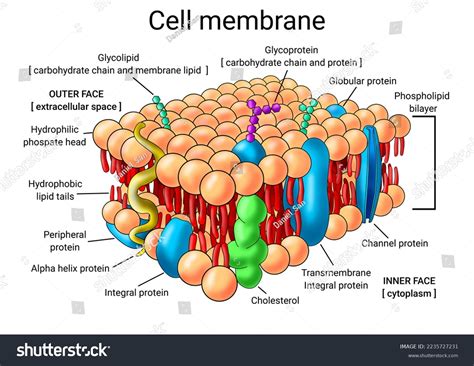
The cell membrane plays a crucial role in maintaining the cell’s homeostasis and regulating its interactions with the environment. It regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell, providing a barrier against harmful substances and allowing essential nutrients and oxygen to enter the cell. The cell membrane also provides receptors for signaling molecules, allowing the cell to respond to its environment and communicate with other cells.
Transport Across the Cell Membrane
There are several types of transport that occur across the cell membrane, including passive transport, active transport, and bulk transport. Passive transport involves the movement of materials from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, without the use of energy. Active transport, on the other hand, involves the movement of materials against their concentration gradient, requiring the use of energy. Bulk transport involves the movement of large molecules, such as proteins and carbohydrates, across the cell membrane.
What is the main function of the cell membrane?
+The main function of the cell membrane is to regulate the movement of materials in and out of the cell, providing a barrier against harmful substances and allowing essential nutrients and oxygen to enter the cell.
What are the main components of the cell membrane?
+The main components of the cell membrane are phospholipids, proteins, and cholesterol.
What is the role of proteins in the cell membrane?
+Proteins play a crucial role in regulating the movement of materials in and out of the cell, providing receptors for signaling molecules, and maintaining cell shape.
In conclusion, the cell membrane is a complex and dynamic structure that plays a crucial role in maintaining the cell’s homeostasis and regulating its interactions with the environment. Understanding the structure and function of the cell membrane is essential for understanding how cells work and how they respond to their environment. By recognizing the importance of the cell membrane, we can appreciate the intricate mechanisms that govern cellular life and the complex interactions that occur between cells and their environment.