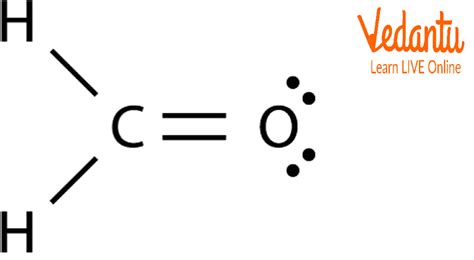The CH2O Lewis structure, also known as formaldehyde, is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry. To understand the structure of this molecule, it's essential to have a basic knowledge of Lewis structures and how they are constructed. In this article, we will delve into the world of Lewis structures, focusing specifically on the CH2O molecule, and explore its significance in the context of organic chemistry.
Key Points
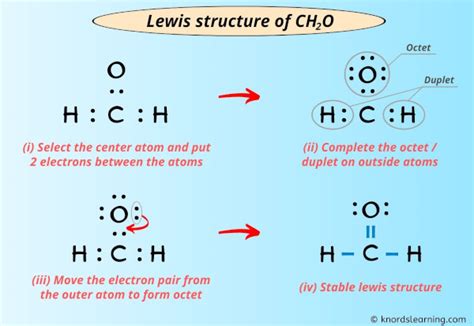
- The CH2O Lewis structure consists of a central carbon atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
- The carbon atom in CH2O has a trigonal planar geometry, with bond angles of approximately 120 degrees.
- The oxygen atom in CH2O is double-bonded to the carbon atom, resulting in a planar, unsaturated molecule.
- Understanding the CH2O Lewis structure is crucial for predicting the physical and chemical properties of formaldehyde.
- The Lewis structure of CH2O can be used to identify potential reactive sites and predict the outcomes of various chemical reactions.
Introduction to Lewis Structures
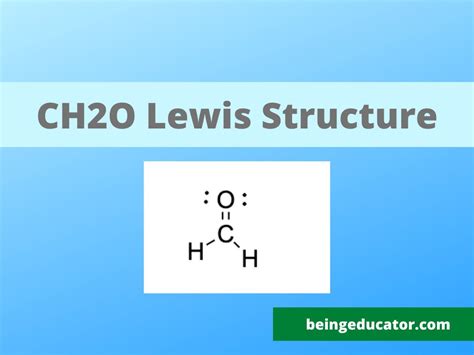
Lewis structures, also known as electron dot structures, are a way of representing the valence electrons in a molecule. They are constructed by following a set of rules, which involve determining the total number of valence electrons in the molecule, drawing the skeleton of the molecule, and then distributing the electrons to satisfy the octet rule. The octet rule states that each atom in a molecule should have eight electrons in its valence shell, which is typically achieved by forming covalent bonds with other atoms.
Constructing the CH2O Lewis Structure
To construct the CH2O Lewis structure, we start by determining the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. Carbon has four valence electrons, hydrogen has one, and oxygen has six. Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in CH2O is 4 © + 2(1) (H) + 6 (O) = 12. Next, we draw the skeleton of the molecule, which consists of a central carbon atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. We then distribute the electrons to satisfy the octet rule, resulting in a double bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms.
| Atom | Valence Electrons | Bonding Electrons | Lone Pair Electrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | 4 | 8 | 0 |
| Hydrogen | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| Oxygen | 6 | 4 | 2 |
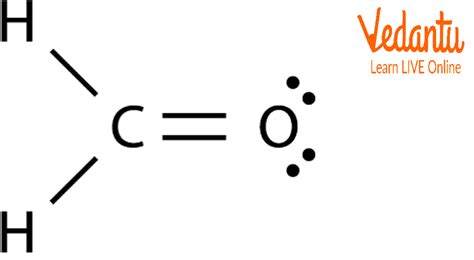
Significance of the CH2O Lewis Structure
The CH2O Lewis structure is significant because it allows us to predict the physical and chemical properties of formaldehyde. For example, the presence of a double bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms makes the molecule highly reactive, which is essential for many industrial applications. Additionally, the Lewis structure of CH2O can be used to identify potential reactive sites and predict the outcomes of various chemical reactions.
Applications of the CH2O Lewis Structure
The CH2O Lewis structure has numerous applications in organic chemistry, including the synthesis of various compounds, such as methanol, formic acid, and acetic acid. It is also used in the production of resins, adhesives, and other polymers. Furthermore, the Lewis structure of CH2O is essential for understanding the mechanism of various chemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, and addition reactions.
What is the molecular geometry of the CH2O molecule?
+The molecular geometry of the CH2O molecule is trigonal planar, with bond angles of approximately 120 degrees.
What is the hybridization of the carbon atom in the CH2O molecule?
+The carbon atom in the CH2O molecule is sp2 hybridized, which results in a planar, trigonal geometry.
What is the significance of the double bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms in the CH2O molecule?
+The double bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms in the CH2O molecule is responsible for the molecule's reactivity and plays a crucial role in many chemical reactions.
In conclusion, the CH2O Lewis structure is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry, and its significance extends beyond the molecule itself. Understanding the Lewis structure of CH2O is essential for predicting the physical and chemical properties of formaldehyde and for identifying potential reactive sites and predicting the outcomes of various chemical reactions. The applications of the CH2O Lewis structure are numerous, and it continues to play a vital role in the development of new compounds and materials.