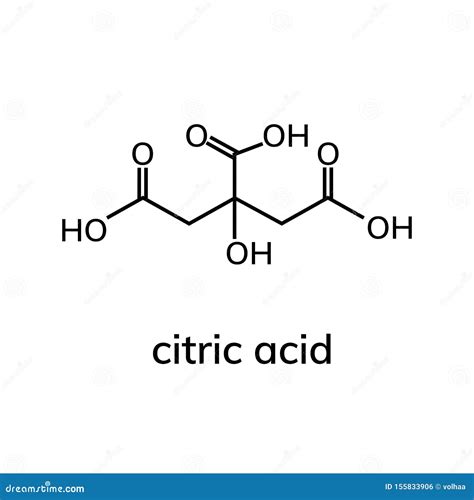
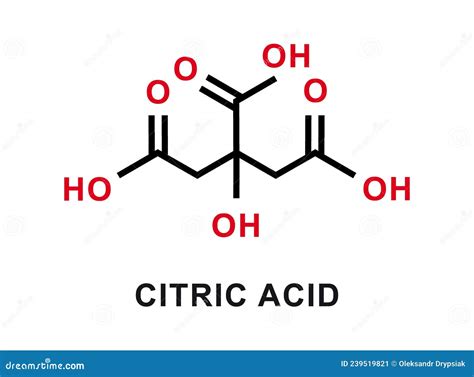
Citric acid, a naturally occurring compound found in citrus fruits, has been a cornerstone in various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, due to its unique properties and versatility. The citric acid formula, C6H8O7, represents a crucial aspect of understanding its chemical structure and reactivity. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of citric acid, exploring its chemical composition, synthesis, applications, and the significance of its formula in determining its properties and uses.
Chemical Structure and Formula
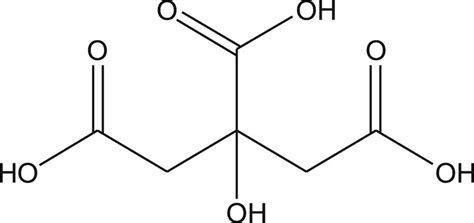
The chemical formula for citric acid is C6H8O7, indicating that each molecule of citric acid contains six carbon atoms, eight hydrogen atoms, and seven oxygen atoms. This composition is reflective of its classification as a weak organic acid, which plays a pivotal role in its solubility, acidity, and reactivity. The structural formula of citric acid, which arranges these atoms in a specific three-dimensional configuration, highlights the presence of three carboxyl groups (-COOH) attached to a central carbon chain. These carboxyl groups are primarily responsible for the acidic properties of citric acid, as they can donate hydrogen ions (H+), thus lowering the pH of a solution.
Understanding the Citric Acid Molecule
A deeper examination of the citric acid molecule reveals the importance of its structural components. The carboxyl groups, in addition to contributing to its acidity, also participate in various chemical reactions, such as esterification and neutralization reactions. The hydroxyl group (-OH) present in the molecule adds to its polarity, influencing its solubility in water and its capacity to form hydrogen bonds. This multifaceted nature of the citric acid molecule, as encapsulated by its formula C6H8O7, underscores its value in biochemical processes and industrial applications.
| Chemical Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 192.12 g/mol |
| Melting Point | 153°C |
| Boiling Point | 310°C (decomposes) |
| Solubility in Water | Highly soluble |

Applications and Uses
Citric acid’s versatility, derived from its chemical structure and properties, has led to its widespread adoption across various sectors. In the food industry, it is used as a flavoring agent and preservative, leveraging its acidity to inhibit the growth of bacteria and mold. The pharmaceutical industry utilizes citric acid in the production of drugs and as an excipient, taking advantage of its ability to enhance the solubility and bioavailability of certain medications. Furthermore, its application in cosmetics and personal care products exploits its antioxidant properties and its capacity to adjust the pH of formulations, thereby stabilizing and enhancing the efficacy of these products.
Synthesis and Production
The synthesis of citric acid can occur through both natural and industrial processes. Naturally, citric acid is produced by citrus fruits, such as oranges and lemons, as part of their metabolic processes. Industrial production, however, primarily relies on fermentation processes involving microorganisms like Aspergillus niger, which can produce citric acid from sugars under controlled conditions. The efficiency and yield of these processes are influenced by factors such as the microorganism strain, nutrient availability, and environmental conditions, highlighting the importance of understanding the biochemical pathways involved in citric acid production.
Key Points
- Citric acid's chemical formula, C6H8O7, reflects its composition and reactivity.
- Its structural components, including carboxyl and hydroxyl groups, contribute to its acidity, solubility, and reactivity.
- Citric acid has diverse applications in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries due to its properties as a preservative, flavoring agent, and intermediate in biochemical pathways.
- Industrial production of citric acid often involves fermentation processes, emphasizing the importance of microbiology and biochemical engineering in optimizing yields and product quality.
- Understanding the citric acid formula and its implications for chemical structure and reactivity is crucial for harnessing its potential in various applications and industries.
In conclusion, the citric acid formula serves as more than just a chemical representation; it encapsulates the essence of its properties, reactivity, and potential applications. Through its unique combination of carboxyl and hydroxyl groups, citric acid participates in a wide range of biochemical and industrial processes, making it a vital compound in both natural and synthetic contexts. As research continues to uncover new aspects of citric acid's chemistry and biochemistry, its formula remains a fundamental reference point, guiding the development of new technologies and applications that leverage its multifaceted nature.
What is the primary function of citric acid in the human body?
+Citric acid plays a crucial role in the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), which is a key metabolic pathway that generates energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into carbon dioxide and water.
How is citric acid used in food preservation?
+Citric acid is used as a preservative in foods due to its acidity, which creates an environment that is unfavorable for the growth of many bacteria and mold, thus extending the shelf life of products.
What are some common applications of citric acid in the pharmaceutical industry?
+Citric acid is used in the pharmaceutical industry as an excipient in tablets and capsules, helping to improve the solubility and bioavailability of drugs. It is also used in the production of certain medications, leveraging its chemical properties to facilitate synthesis and formulation.