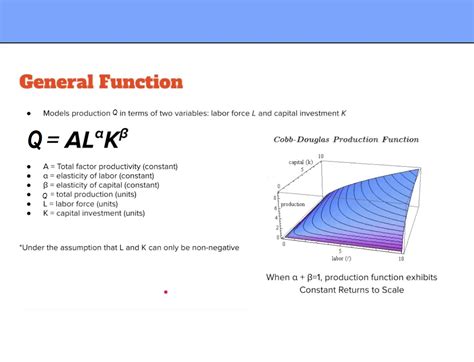
The Cobb-Douglas production function is a fundamental concept in economics, particularly in the field of microeconomics. It is used to describe the relationship between the inputs and outputs of a production process. The function is typically represented as Y = AL^αK^β, where Y is the total output, A is the total factor productivity, L is the labor input, K is the capital input, and α and β are the output elasticities of labor and capital, respectively. Understanding the Cobb-Douglas production function is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and economists to analyze the productivity of firms and the overall economy.
Understanding the Cobb-Douglas Production Function
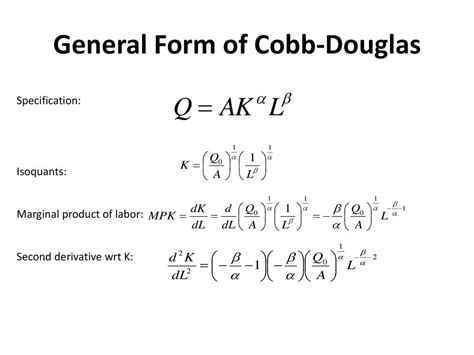
The Cobb-Douglas production function is a mathematical representation of the relationship between the inputs of labor and capital and the output of a production process. It assumes that the production process exhibits constant returns to scale, meaning that if all inputs are increased by a certain percentage, the output will increase by the same percentage. The function also assumes that the inputs of labor and capital are substitutable, but at a diminishing rate. This means that as more of one input is used, the marginal product of that input will decrease.
Key Components of the Cobb-Douglas Production Function
The Cobb-Douglas production function has several key components that are essential to understanding its application and interpretation. The total factor productivity (A) represents the overall efficiency of the production process, and it is often seen as a measure of technological progress. The output elasticities of labor (α) and capital (β) represent the percentage change in output resulting from a 1% change in labor and capital, respectively. These elasticities are critical in determining the marginal products of labor and capital and the optimal input combination.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Total Factor Productivity (A) | Represents the overall efficiency of the production process |
| Output Elasticity of Labor (α) | Represents the percentage change in output resulting from a 1% change in labor |
| Output Elasticity of Capital (β) | Represents the percentage change in output resulting from a 1% change in capital |

Key Points
- The Cobb-Douglas production function is a mathematical representation of the relationship between labor, capital, and output.
- The function assumes constant returns to scale and the substitutability of labor and capital at a diminishing rate.
- The total factor productivity (A) represents the overall efficiency of the production process.
- The output elasticities of labor (α) and capital (β) are critical in determining the marginal products of labor and capital.
- The Cobb-Douglas production function provides a useful framework for analyzing productivity, but it has limitations, such as the assumption of constant returns to scale.
Applying the Cobb-Douglas Production Function
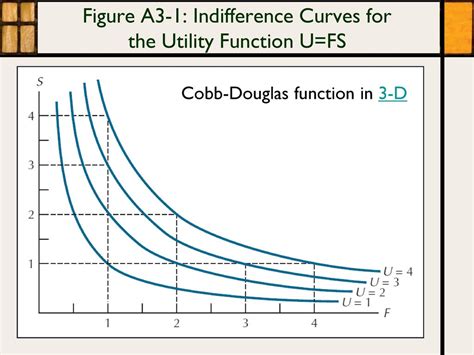
The Cobb-Douglas production function has numerous applications in economics, including the analysis of firm productivity, the determination of optimal input combinations, and the evaluation of technological progress. By estimating the parameters of the Cobb-Douglas production function, policymakers and businesses can gain insights into the productivity of firms and the overall economy. This information can be used to inform policy decisions, such as investments in education and training, and to develop strategies for improving productivity and competitiveness.
Estimating the Parameters of the Cobb-Douglas Production Function
Estimating the parameters of the Cobb-Douglas production function typically involves the use of econometric techniques, such as ordinary least squares (OLS) regression. The estimation process requires data on output, labor, and capital, as well as other variables that may affect the production process, such as technology and institutional factors. The estimated parameters of the Cobb-Douglas production function can be used to analyze the productivity of firms and the overall economy, as well as to evaluate the impact of policy interventions and technological progress.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Output (Y) | The total output of the production process |
| Labor (L) | The input of labor in the production process |
| Capital (K) | The input of capital in the production process |
| Technology (A) | The overall efficiency of the production process |
What is the Cobb-Douglas production function?
+The Cobb-Douglas production function is a mathematical representation of the relationship between labor, capital, and output. It is used to analyze the productivity of firms and the overall economy.
What are the key components of the Cobb-Douglas production function?
+The key components of the Cobb-Douglas production function are the total factor productivity (A), the output elasticity of labor (α), and the output elasticity of capital (β).
How is the Cobb-Douglas production function estimated?
+The Cobb-Douglas production function is typically estimated using econometric techniques, such as ordinary least squares (OLS) regression. The estimation process requires data on output, labor, and capital, as well as other variables that may affect the production process.
Meta Description: The Cobb-Douglas production function is a mathematical representation of the relationship between labor, capital, and output. Learn about its key components, estimation, and applications in economics. (145 characters)
Related Terms:
- Cobb douglas function formula
- Cobb Douglas utility function
- Cobb Douglas production function PDF
- Cobb douglas function example
- Cobb-Douglas demand function
- Importance of Cobb-Douglas production function