The Omicron XBB variant, a recombinant of the Omicron BA.2.10.1 and BA.2.75 lineages, has been gaining attention globally due to its potential for increased transmissibility and immune evasion. As of the latest reports, this variant has spread across multiple continents, raising concerns about its impact on public health. Understanding the characteristics and implications of Omicron XBB is crucial for individuals, healthcare systems, and governments to prepare and respond effectively.
Key Points
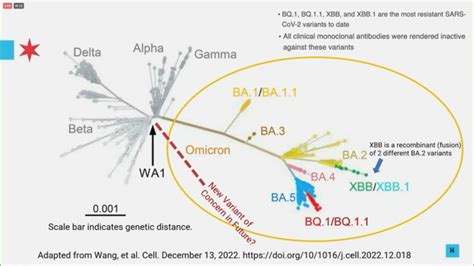
- The Omicron XBB variant is a result of recombination between BA.2.10.1 and BA.2.75, showing potential for higher transmissibility and immune evasion.
- Studies suggest that XBB may have a reduced susceptibility to neutralization by sera from vaccinated or previously infected individuals, indicating a possible need for updated vaccines.
- Despite concerns, the severity of disease caused by XBB does not appear to be significantly different from other Omicron variants, with most cases reported as mild.
- Public health strategies, including vaccination, mask-wearing, and social distancing, remain crucial in controlling the spread of XBB and other COVID-19 variants.
- Continuous monitoring and research are necessary to understand the evolution of SARS-CoV-2 and the emergence of new variants like XBB, informing evidence-based policy decisions.
Understanding the Omicron XBB Variant

The emergence of the Omicron XBB variant underscores the ongoing evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. With recombination being a key factor in its development, XBB exhibits a combination of mutations from its parent lineages, potentially altering its behavior in terms of transmission and immune response. Phylogenetic analysis has helped in tracing the lineage and spread of this variant, offering insights into its epidemiological characteristics.
Transmission and Immune Evasion
Research into the Omicron XBB variant suggests that it may possess enhanced transmissibility compared to other circulating variants. This is attributed to its unique combination of mutations, particularly in the spike protein, which is crucial for viral entry into host cells. Furthermore, immune evasion properties of XBB have raised concerns, as it may partially evade the neutralizing antibodies generated by current vaccines or previous infections, potentially leading to breakthrough infections.
| Variant Characteristics | Implications |
|---|---|
| Recombination Origin | Potential for increased transmissibility and immune evasion |
| Mutations in Spike Protein | Altered interaction with host cells and immune system components |
| Global Spread | Necessity for enhanced surveillance and public health measures |
Public Health Response and Future Directions
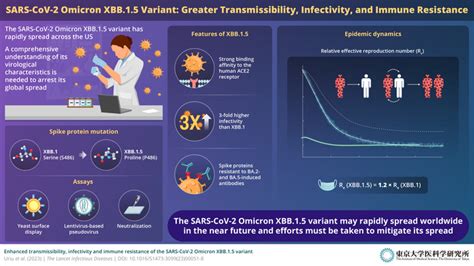
The response to the Omicron XBB variant involves a multifaceted approach, emphasizing vaccination, mask-wearing, and social distancing as primary measures to control its spread. Additionally, continuous monitoring of the variant’s spread and its impact on healthcare systems is crucial for informing policy decisions and guiding resource allocation. The development of updated vaccines or booster shots specifically targeting XBB and other emerging variants is under consideration, reflecting the dynamic nature of the pandemic response.
Global Cooperation and Research
Given the global nature of the COVID-19 pandemic, international cooperation in research, data sharing, and public health policy is vital. This cooperation enables the rapid dissemination of information on new variants, facilitates collaborative research efforts, and supports the development of globally effective strategies to combat the pandemic. The WHO and other global health authorities play a pivotal role in this effort, providing guidance and support to countries navigating the challenges posed by variants like Omicron XBB.
What is the Omicron XBB variant, and how did it emerge?
+The Omicron XBB variant is a recombinant of the BA.2.10.1 and BA.2.75 lineages of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. It emerged through a process of recombination, where genetic material from these two lineages combined to form a new variant with unique characteristics.
How transmissible is the Omicron XBB variant compared to other variants?
+Studies suggest that the Omicron XBB variant may have an enhanced ability to transmit compared to other circulating variants. However, the exact extent of its transmissibility is still under investigation and may vary depending on several factors, including the population's immunity level and public health measures in place.
Does the Omicron XBB variant cause more severe disease than other Omicron variants?
+As of the latest reports, there is no significant evidence to suggest that the Omicron XBB variant causes more severe disease than other Omicron variants. Most cases have been reported as mild, although the variant's ability to evade immune responses may lead to an increased number of infections, including among those who are vaccinated or have been previously infected.
In conclusion, the Omicron XBB variant represents another challenge in the evolving landscape of the COVID-19 pandemic. Through continued research, global cooperation, and adaptive public health strategies, it is possible to mitigate the impact of this and future variants, ultimately working towards a more resilient and responsive global health system.