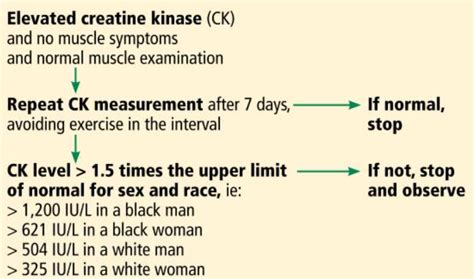
Creatine kinase (CK) is an enzyme found in the body, primarily in muscle tissue. It plays a crucial role in the energy production process, converting creatine into phosphocreatine, which is then used to replenish ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell. A high level of creatine kinase in the blood can indicate muscle damage or disease, as it leaks out of damaged muscle cells into the bloodstream. This condition is known as elevated creatine kinase or high CK levels.
Causes of Elevated Creatine Kinase

Several factors can contribute to high creatine kinase levels, including muscle injury, intense physical activity, and certain medical conditions. Muscle injury, such as that caused by a blow to the muscle, can lead to an increase in CK levels. Similarly, engaging in strenuous exercise, especially if one is new to such activities, can cause muscle damage and subsequently elevate CK levels. Certain medical conditions, including muscular dystrophy, inflammatory myopathies, and myopathies caused by drug or toxin exposure, can also result in high CK levels.
Muscle Injury and Intense Physical Activity
Muscle injury, whether due to acute trauma or overuse, is a common cause of elevated CK levels. When muscle fibers are damaged, they release CK into the bloodstream, leading to increased levels. This is particularly evident in athletes who engage in high-intensity, high-impact sports. The intensity and duration of physical activity can significantly influence CK levels, with more intense and prolonged activities tend to cause greater muscle damage and, consequently, higher CK levels.
| Cause | CK Level Increase |
|---|---|
| Mild Muscle Injury | 2-5 times the normal range |
| Moderate Muscle Injury | 5-10 times the normal range |
| Severe Muscle Injury | 10-20 times the normal range or more |
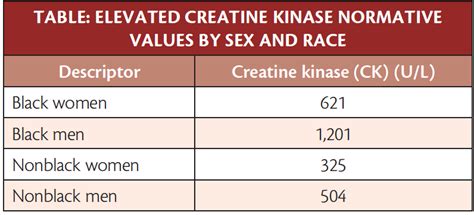
Medical Conditions Associated with High Creatine Kinase
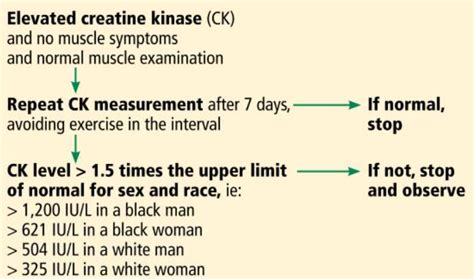
Certain medical conditions can lead to elevated CK levels due to ongoing muscle damage or disease. Muscular dystrophy, a group of inherited disorders characterized by progressive muscle weakness and degeneration, is associated with high CK levels. Inflammatory myopathies, such as polymyositis and dermatomyositis, can also cause elevated CK levels due to muscle inflammation and damage. Additionally, exposure to certain drugs or toxins can lead to muscle damage and increased CK levels.
Diagnosis and Monitoring
The diagnosis of conditions associated with high CK levels often involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and sometimes imaging studies. The CK test is typically used to assess muscle damage and to monitor the progression of muscle diseases. It’s crucial to interpret CK levels in the context of the patient’s clinical presentation and other diagnostic findings. Regular monitoring of CK levels can help in assessing the response to treatment and in adjusting the therapeutic approach as needed.
Key Points
- High creatine kinase levels can indicate muscle damage or disease.
- Muscle injury, intense physical activity, and certain medical conditions are common causes of elevated CK levels.
- The degree of CK elevation can provide clues about the underlying cause and severity of muscle damage.
- Clinical context is crucial in interpreting CK levels, considering factors such as recent physical activity and underlying medical conditions.
- Monitoring CK levels over time can help in managing conditions associated with muscle damage and in assessing the effectiveness of treatment.
In conclusion, elevated creatine kinase levels are a significant indicator of muscle damage or disease, and understanding the causes and implications of high CK levels is essential for proper diagnosis and management. By considering the clinical context, interpreting CK levels accurately, and employing appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic strategies, healthcare providers can offer effective care for individuals with elevated CK levels.
What are normal creatine kinase levels?
+Normal creatine kinase levels typically range from 24 to 195 U/L for males and 24 to 170 U/L for females, though these ranges can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the specific assay used.
How long do elevated CK levels last after muscle injury?
+The duration of elevated CK levels after muscle injury can vary, but CK levels typically peak within 24 to 48 hours after injury and return to normal within 7 to 10 days. However, this timeframe can be influenced by the severity of the injury and individual factors.
Can high CK levels be treated?
+Treatment of high CK levels focuses on addressing the underlying cause, whether it be muscle injury, a medical condition, or another factor. This may involve rest, physical therapy, medication to reduce inflammation or manage symptoms, and in some cases, more specialized treatments depending on the specific diagnosis.