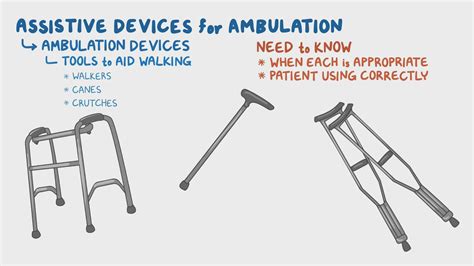
Ambulation refers to the act of walking or moving from one place to another on foot. It is a complex process that involves the coordinated effort of multiple physiological systems, including the musculoskeletal, nervous, and cardiovascular systems. Ambulation is an essential aspect of human mobility and is critical for maintaining independence, performing daily activities, and overall quality of life. The ability to ambulate is often taken for granted, but it requires a range of physical and cognitive skills, including balance, strength, flexibility, and coordination.
In the context of healthcare, ambulation is often used as a measure of a person's functional ability and mobility. Healthcare professionals use various assessments and tools to evaluate a person's ambulation, including the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test, the 6-Minute Walk Test, and the Berg Balance Scale. These assessments help to identify individuals who may be at risk of falls or mobility impairments, and inform the development of targeted interventions to improve ambulation and overall mobility.
Key Points
- Ambulation is the act of walking or moving from one place to another on foot
- Ambulation requires the coordinated effort of multiple physiological systems, including the musculoskeletal, nervous, and cardiovascular systems
- Ambulation is an essential aspect of human mobility and is critical for maintaining independence, performing daily activities, and overall quality of life
- Healthcare professionals use various assessments and tools to evaluate a person's ambulation, including the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test, the 6-Minute Walk Test, and the Berg Balance Scale
- Assessments of ambulation help to identify individuals who may be at risk of falls or mobility impairments, and inform the development of targeted interventions to improve ambulation and overall mobility
Physiological Components of Ambulation

Ambulation is a complex process that involves the coordinated effort of multiple physiological systems. The musculoskeletal system provides the structural framework and movement capabilities necessary for ambulation, including the bones, joints, muscles, and tendons. The nervous system plays a critical role in controlling and coordinating the movements involved in ambulation, including the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. The cardiovascular system also plays an essential role in ambulation, providing the necessary oxygen and nutrients to the muscles and other tissues involved in movement.
Musculoskeletal System
The musculoskeletal system is composed of the bones, joints, muscles, and tendons that provide the structural framework and movement capabilities necessary for ambulation. The bones provide the skeletal structure, while the joints allow for movement and flexibility. The muscles, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and gluteals, work together to control and coordinate the movements involved in ambulation. The tendons and ligaments provide additional support and stability to the joints and muscles.
Nervous System
The nervous system plays a critical role in controlling and coordinating the movements involved in ambulation. The brain processes sensory information and sends signals to the muscles and other tissues involved in movement, while the spinal cord and peripheral nerves transmit and receive signals. The nervous system also regulates balance, posture, and reflexes, which are essential for maintaining stability and preventing falls during ambulation.
Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system provides the necessary oxygen and nutrients to the muscles and other tissues involved in ambulation. The heart pumps blood throughout the body, while the blood vessels transport oxygen and nutrients to the muscles and other tissues. The cardiovascular system also helps to regulate body temperature, which is essential for maintaining optimal muscle function during ambulation.
| Physiological System | Role in Ambulation |
|---|---|
| Musculoskeletal System | Provides structural framework and movement capabilities |
| Nervous System | Controls and coordinates movements, regulates balance and posture |
| Cardiovascular System | Provides oxygen and nutrients to muscles and other tissues |

Assessments and Interventions for Ambulation
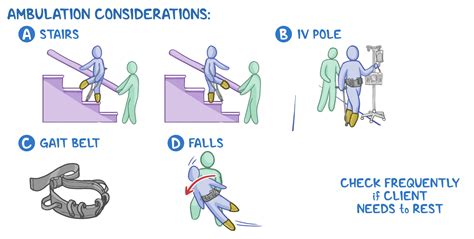
Healthcare professionals use various assessments and tools to evaluate a person’s ambulation, including the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test, the 6-Minute Walk Test, and the Berg Balance Scale. These assessments help to identify individuals who may be at risk of falls or mobility impairments, and inform the development of targeted interventions to improve ambulation and overall mobility. Interventions may include exercise programs, balance training, and assistive devices, such as canes or walkers.
Timed Up and Go (TUG) Test
The TUG test is a widely used assessment of ambulation that measures the time it takes for an individual to rise from a chair, walk 10 feet, and return to the chair. The test is a reliable indicator of mobility and balance, and can be used to identify individuals who may be at risk of falls or mobility impairments.
6-Minute Walk Test
The 6-Minute Walk Test is a standardized assessment of ambulation that measures the distance an individual can walk in 6 minutes. The test is a reliable indicator of cardiovascular endurance and mobility, and can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions aimed at improving ambulation.
Berg Balance Scale
The Berg Balance Scale is a widely used assessment of balance and mobility that measures an individual’s ability to perform a series of balance-related tasks. The test is a reliable indicator of balance and mobility, and can be used to identify individuals who may be at risk of falls or mobility impairments.
What is ambulation and why is it important?
+Ambulation refers to the act of walking or moving from one place to another on foot. It is an essential aspect of human mobility and is critical for maintaining independence, performing daily activities, and overall quality of life.
What are the physiological components of ambulation?
+The physiological components of ambulation include the musculoskeletal, nervous, and cardiovascular systems. The musculoskeletal system provides the structural framework and movement capabilities necessary for ambulation, while the nervous system controls and coordinates the movements involved in ambulation. The cardiovascular system provides the necessary oxygen and nutrients to the muscles and other tissues involved in ambulation.
What assessments and interventions are used to evaluate and improve ambulation?
+Healthcare professionals use various assessments and tools to evaluate a person's ambulation, including the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test, the 6-Minute Walk Test, and the Berg Balance Scale. Interventions may include exercise programs, balance training, and assistive devices, such as canes or walkers.
Meta Description: Learn about the definition, physiological components, and assessments of ambulation, and discover how healthcare professionals can improve mobility and prevent falls. (149 characters)