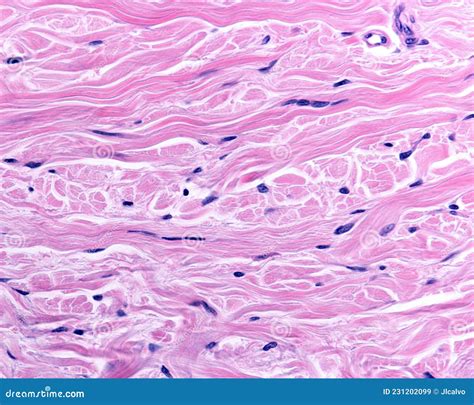
Dense irregular tissue, a type of connective tissue, plays a crucial role in the human body, providing support, strength, and elasticity to various organs and structures. This complex tissue is composed of a dense network of collagen and elastin fibers, embedded in a matrix of ground substance, which gives it a unique set of properties. In this article, we will delve into the world of dense irregular tissue, exploring its structure, functions, and significance in maintaining the integrity of the body.
Structure and Composition of Dense Irregular Tissue

The structure of dense irregular tissue is characterized by a dense arrangement of collagen and elastin fibers, which are randomly oriented in different directions. This random orientation of fibers provides the tissue with a high degree of strength and resistance to stress, allowing it to withstand significant mechanical forces. The ground substance, a gel-like matrix, surrounds the fibers, providing a medium for the exchange of nutrients and waste products. The combination of collagen, elastin, and ground substance gives dense irregular tissue its unique properties, including high tensile strength, elasticity, and resistance to compression.
Types of Cells and Fibers in Dense Irregular Tissue
Dense irregular tissue is composed of various cell types, including fibroblasts, macrophages, and mast cells, each playing a distinct role in the maintenance and function of the tissue. Fibroblasts are the primary cell type responsible for the production of collagen and elastin fibers, while macrophages and mast cells are involved in the immune response and the regulation of inflammation. The tissue also contains a variety of fiber types, including collagen fibers, which provide strength and stiffness, and elastin fibers, which impart elasticity and flexibility.
| Cell Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Fibroblasts | Production of collagen and elastin fibers |
| Macrophages | Immune response and regulation of inflammation |
| Mast cells | Regulation of inflammation and immune response |
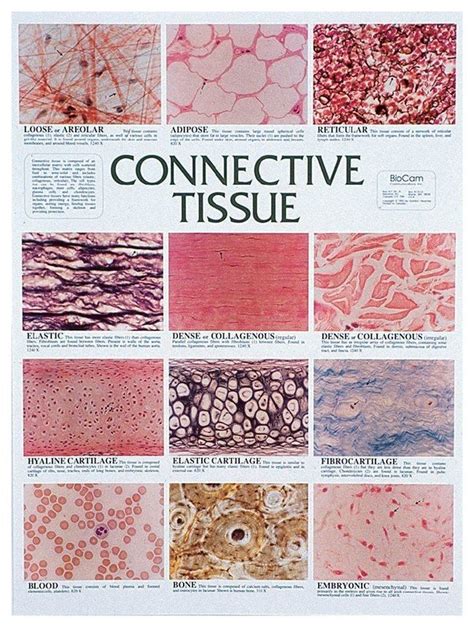
Functions and Significance of Dense Irregular Tissue

Dense irregular tissue plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the body, providing support, strength, and elasticity to various organs and structures. Its functions include:
- Providing mechanical support and stability to organs and structures
- Resisting external forces and stresses, such as tension and compression
- Regulating the exchange of nutrients and waste products
- Participating in the immune response and regulation of inflammation
The significance of dense irregular tissue is evident in its widespread distribution throughout the body, including the skin, tendons, ligaments, and organs such as the liver and kidneys. Its unique properties make it an essential component of various physiological processes, including movement, growth, and development.
Key Points
- Dense irregular tissue is a type of connective tissue characterized by a dense network of collagen and elastin fibers
- The tissue provides support, strength, and elasticity to various organs and structures
- Its unique composition and structure make it an essential component of various physiological processes
- Understanding the properties and functions of dense irregular tissue is crucial for the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases and injuries
- The tissue plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the body, resisting external forces and stresses, and regulating the exchange of nutrients and waste products
Pathological Conditions Associated with Dense Irregular Tissue
Dense irregular tissue is involved in various pathological conditions, including fibrosis, scar formation, and tissue injury. Fibrosis, a condition characterized by the excessive deposition of collagen fibers, can lead to the formation of scar tissue, which can impair the function of affected organs and structures. Tissue injury, such as that caused by trauma or surgery, can also affect the integrity of dense irregular tissue, leading to inflammation, scarring, and functional impairment.
In conclusion, dense irregular tissue is a complex and fascinating tissue that plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the body. Its unique composition and structure make it an essential component of various physiological processes, and its significance is evident in its widespread distribution throughout the body. Understanding the properties and functions of dense irregular tissue is crucial for the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases and injuries, and its study continues to be an active area of research in the field of anatomy and physiology.
What is the primary function of dense irregular tissue?
+The primary function of dense irregular tissue is to provide support, strength, and elasticity to various organs and structures, resisting external forces and stresses, and regulating the exchange of nutrients and waste products.
What are the types of cells and fibers found in dense irregular tissue?
+Dense irregular tissue is composed of various cell types, including fibroblasts, macrophages, and mast cells, and fiber types, including collagen and elastin fibers.
What are some pathological conditions associated with dense irregular tissue?
+Dense irregular tissue is involved in various pathological conditions, including fibrosis, scar formation, and tissue injury, which can impair the function of affected organs and structures.