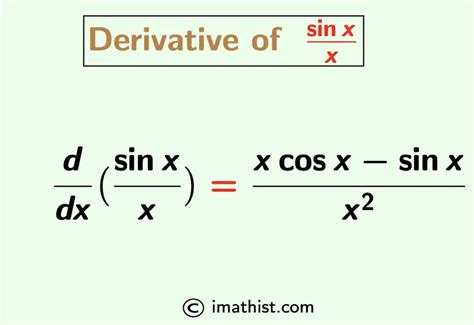The derivative of sin x is a fundamental concept in calculus, and it's crucial for understanding various mathematical and real-world phenomena. The derivative of a function represents the rate of change of the function with respect to its input. In this case, we're interested in finding the derivative of the sine function, which is a periodic function that oscillates between -1 and 1. The sine function is commonly used to model periodic behavior in physics, engineering, and other fields.
To derive the derivative of sin x, we can use the definition of a derivative as a limit. The definition states that the derivative of a function f(x) is given by the limit as h approaches 0 of the difference quotient [f(x + h) - f(x)]/h. Applying this definition to the sine function, we get the derivative of sin x as the limit as h approaches 0 of [sin(x + h) - sin(x)]/h. Using the angle addition formula for sine, we can simplify this expression and arrive at the derivative of sin x as cos x.
Key Points
- The derivative of sin x represents the rate of change of the sine function with respect to its input.
- The derivative of sin x can be found using the definition of a derivative as a limit.
- The angle addition formula for sine is used to simplify the expression and arrive at the derivative of sin x as cos x.
- The derivative of sin x has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and other fields where periodic behavior is modeled.
- Understanding the derivative of sin x is essential for solving problems involving optimization, physics, and engineering.
Derivation of the Derivative of Sin X
The derivation of the derivative of sin x involves using the definition of a derivative as a limit. We start by applying the definition to the sine function: the derivative of sin x is given by the limit as h approaches 0 of [sin(x + h) - sin(x)]/h. Using the angle addition formula for sine, which states that sin(a + b) = sin(a)cos(b) + cos(a)sin(b), we can simplify the expression sin(x + h) as sin(x)cos(h) + cos(x)sin(h). Substituting this into the definition of the derivative, we get the limit as h approaches 0 of [sin(x)cos(h) + cos(x)sin(h) - sin(x)]/h.
Simplifying further, we can use the fact that cos(h) approaches 1 as h approaches 0, and sin(h)/h approaches 1 as h approaches 0. This allows us to simplify the expression to the limit as h approaches 0 of [sin(x)(1) + cos(x)h - sin(x)]/h, which reduces to the limit as h approaches 0 of cos(x)h/h. Canceling out the h terms, we're left with the limit as h approaches 0 of cos(x), which is simply cos(x). Therefore, the derivative of sin x is cos x.
Geometric Interpretation of the Derivative of Sin X
The derivative of sin x can also be interpreted geometrically. The sine function can be represented as the y-coordinate of a point on the unit circle. As we move around the unit circle, the y-coordinate changes, and the rate of change of the y-coordinate with respect to the angle is given by the derivative of sin x. Using the geometric definition of the derivative, we can see that the derivative of sin x represents the slope of the tangent line to the unit circle at a given point. This slope is given by the cosine of the angle, which is consistent with our earlier result that the derivative of sin x is cos x.
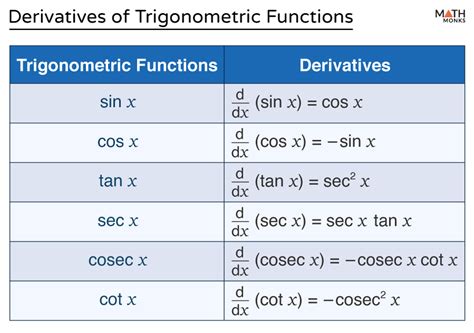
| Function | Derivative |
|---|---|
| sin(x) | cos(x) |
| cos(x) | -sin(x) |
| tan(x) | sec^2(x) |
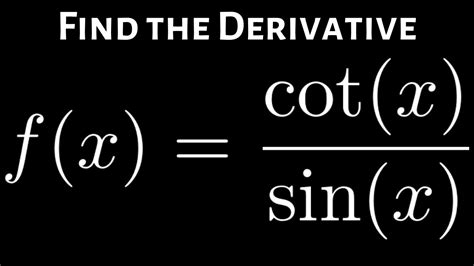
Applications of the Derivative of Sin X
The derivative of sin x has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and other fields. In mechanics, the derivative of sin x can be used to model the motion of a pendulum or a spring-mass system. The equation of motion for a simple pendulum can be written as θ”(t) + (g/L)sin(θ(t)) = 0, where θ(t) is the angle of the pendulum from the vertical, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and L is the length of the pendulum. Using the derivative of sin x, we can linearize this equation and solve for the motion of the pendulum.
In electrical engineering, the derivative of sin x is used to analyze AC circuits and filters. The voltage and current in an AC circuit can be represented as sinusoidal functions, and the derivative of sin x can be used to find the impedance of the circuit. The impedance of a circuit is a measure of the total opposition to the flow of current, and it's an essential concept in AC circuit analysis.
Optimization Problems Involving the Derivative of Sin X
The derivative of sin x can also be used to solve optimization problems. For example, consider a problem where we want to maximize the area of a rectangle with a fixed perimeter. The area of the rectangle can be represented as A(x) = x sin(x), where x is the width of the rectangle. To find the maximum area, we can take the derivative of A(x) with respect to x and set it equal to 0. Using the product rule and the derivative of sin x, we get A’(x) = sin(x) + x cos(x) = 0. Solving for x, we can find the width of the rectangle that maximizes the area.
What is the derivative of sin x?
+The derivative of sin x is cos x.
How is the derivative of sin x used in physics?
+The derivative of sin x is used to model the motion of a pendulum or a spring-mass system.
What is the geometric interpretation of the derivative of sin x?
+The derivative of sin x represents the slope of the tangent line to the unit circle at a given point.
Meta description: Learn about the derivative of sin x, its geometric interpretation, and its applications in physics and engineering. Discover how to use the derivative of sin x to solve optimization problems and model real-world phenomena. (145 characters)