The Medicaid program, a cornerstone of the United States' healthcare system, has undergone significant transformations under various administrations. The presidency of Donald Trump, from 2017 to 2021, was marked by several key changes to Medicaid, reflecting the administration's broader healthcare policy priorities. This article will delve into five critical ways in which the Trump administration altered the Medicaid landscape, exploring both the policy shifts and their implications for beneficiaries and healthcare providers.
Key Points
- The Trump administration implemented work requirements for Medicaid recipients in several states, aiming to promote employment and self-sufficiency.
- Changes to the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the expansion of short-term, limited-duration insurance plans affected Medicaid enrollment and coverage options.
- The administration's approach to Medicaid block grants and the introduction of Section 1115 demonstrations allowed for state-level innovation but also raised concerns about beneficiary access to care.
- Policy shifts on family planning and reproductive health services within Medicaid led to significant debates and changes in service accessibility.
- The administration's budget proposals and legislative actions impacted Medicaid funding and the overall structure of the program, influencing both federal and state-level healthcare policy.
Introduction of Work Requirements

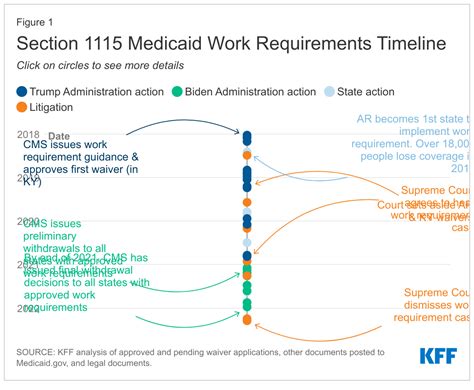
The Trump administration’s most notable change to Medicaid was the introduction of work requirements for recipients. This policy, enabled through Section 1115 demonstrations, allowed states to mandate that able-bodied adults work, volunteer, or participate in job training for a certain number of hours per week to maintain their Medicaid eligibility. By January 2020, ten states had received approval for such waivers, although legal challenges and the COVID-19 pandemic subsequently impacted the implementation and continuation of these requirements. Proponents argued that work requirements would promote self-sufficiency and employment, while critics warned that they could lead to a loss of health coverage for vulnerable populations.
Impact of Work Requirements on Medicaid Recipients
The introduction of work requirements was met with both support and criticism. On one hand, proponents believed that linking Medicaid eligibility to work or other community engagement activities could encourage personal responsibility and help recipients transition into the workforce. On the other hand, critics pointed out that many Medicaid recipients already work or face significant barriers to employment, such as lack of job opportunities, transportation issues, or health conditions that limit their ability to work. The impact of these requirements was further complicated by the need for states to track and enforce compliance, which added administrative burdens and potential costs.
| State | Work Requirement Details |
|---|---|
| Arkansas | 80 hours of work, volunteering, or job training per month |
| Kentucky | 80 hours of work, volunteering, or job training per month, with exemptions for certain populations |
| Indiana | 80 hours of work, volunteering, or job training per month, with a focus on helping recipients find and maintain employment |
Changes to the Affordable Care Act and Medicaid Expansion

The Trump administration’s efforts to repeal and replace the Affordable Care Act (ACA), also known as Obamacare, had direct implications for Medicaid. Although the ACA repeal efforts were unsuccessful, the administration took other steps to alter the healthcare landscape. This included expanding short-term, limited-duration insurance plans, which are not required to cover the same essential health benefits as ACA-compliant plans. These changes affected Medicaid in several ways, including altering the dynamics of health insurance markets and influencing decisions about Medicaid expansion in the states.
State-Level Responses to Federal Policy Changes
In response to federal policy shifts, several states took innovative approaches to Medicaid expansion and reform. Some states, like Utah and Idaho, passed ballot initiatives to expand Medicaid, reflecting a desire among voters to increase healthcare access. Other states, such as Wisconsin, explored alternatives to traditional expansion, such as seeking waivers to implement work requirements or other modifications to their Medicaid programs. These state-level actions demonstrate the complex interplay between federal policy, state priorities, and local healthcare needs.
Medicaid Block Grants and Section 1115 Demonstrations
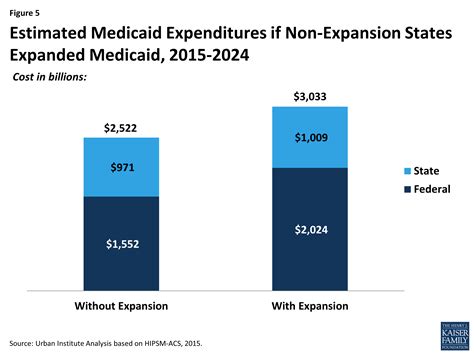
The Trump administration also explored the concept of Medicaid block grants, which would provide states with a fixed amount of funding for their Medicaid programs, rather than the traditional matching funds model. This approach, though not fully implemented, was part of a broader effort to give states more flexibility in managing their Medicaid programs. The use of Section 1115 demonstrations, which allow states to test innovative approaches to Medicaid, was another key strategy. These demonstrations enabled states to implement a range of reforms, from work requirements to expanded substance abuse treatment services.
Implications for State-Level Innovation and Flexibility
The emphasis on state-level innovation and flexibility reflects a philosophical shift towards decentralizing healthcare policy decisions. By giving states more autonomy to design and implement their Medicaid programs, the Trump administration aimed to foster creativity and efficiency. However, critics argued that such an approach could lead to uneven access to care across states and undermine the national standards and protections that Medicaid is intended to provide. The balance between state innovation and federal oversight remains a critical issue in Medicaid policy debates.
Family Planning and Reproductive Health Services
The Trump administration’s policies on family planning and reproductive health services within Medicaid were highly controversial. Changes to the Title X program, which provides funding for family planning services, and efforts to restrict access to abortion services, reflected the administration’s stance on these issues. These policy shifts had significant implications for Medicaid beneficiaries, particularly women, and sparked legal challenges and public debate.
Access to Care and the Role of Medicaid
Medicaid plays a crucial role in providing access to family planning and reproductive health services for low-income women. The administration’s policies in this area were seen as restrictive by critics, who argued that they could limit access to essential healthcare services. The interplay between federal policy, state-level decisions, and individual access to care is complex, highlighting the need for nuanced and multifaceted approaches to healthcare policy.
Budget Proposals and Legislative Actions
The Trump administration’s budget proposals and legislative actions had significant implications for Medicaid funding and the program’s overall structure. The administration’s support for converting Medicaid to a block grant program, as well as its efforts to reduce Medicaid spending through various means, reflected its broader goals of reducing federal healthcare expenditures and giving states more control over their Medicaid programs. These proposals were met with resistance from Democrats and advocacy groups, who argued that they could lead to cuts in benefits and eligibility for vulnerable populations.
Funding and the Future of Medicaid
The funding of Medicaid is a critical issue that reflects broader debates about healthcare policy and the role of government in ensuring access to care. The Trump administration’s proposals to reduce Medicaid funding and alter the program’s structure were part of a long-standing discussion about how to balance the program’s costs with the need to provide comprehensive healthcare services to eligible populations. As policymakers consider the future of Medicaid, they must navigate these complex issues, weighing the competing demands of fiscal responsibility, healthcare access, and social welfare.
What were the primary goals of the Trump administration's Medicaid work requirements?
+The primary goals were to promote employment and self-sufficiency among able-bodied Medicaid recipients, although the policy's implementation and impact were subject to legal and practical challenges.
How did the Trump administration's changes to the Affordable Care Act affect Medicaid?
+The changes, including the expansion of short-term insurance plans, affected Medicaid enrollment dynamics and state-level decisions about Medicaid expansion, reflecting the complex interplay between federal policy and state healthcare markets.
What is the significance of Medicaid block grants and Section 1115 demonstrations in the context of the Trump administration's healthcare policy?
+These policies represent a shift towards state-level flexibility and innovation in Medicaid, allowing states to experiment with new approaches to healthcare delivery and financing, although they also raise concerns about access to care and national standards.
How did the Trump administration's policies on family planning and reproductive health services impact Medicaid beneficiaries?
+The policies, including changes to Title X and restrictions on abortion services, had significant implications for access to care, particularly for women, and were the subject of legal challenges and public debate.
What were the implications of the Trump administration's budget proposals and legislative actions for Medicaid funding and structure?
+The proposals, including the conversion of Medicaid to a block grant program, aimed to reduce federal healthcare expenditures and give states more control, but were met with resistance due to concerns about potential cuts in benefits and eligibility for vulnerable populations.
The Trump administration’s changes to Medicaid reflect a complex interplay of policy goals, political priorities, and the evolving landscape of healthcare in the United States. As the healthcare system continues to evolve, understanding these changes and their implications is crucial for navigating the future of Medicaid and ensuring that it meets the needs of its beneficiaries.