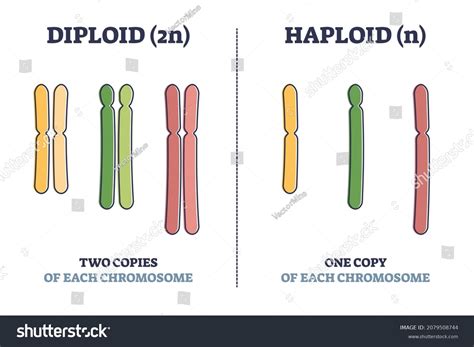
The human body is composed of approximately 30 trillion cells, each containing a unique set of genetic material that defines who we are. However, not all cells in the body are the same; they can be broadly classified into two categories based on the number of chromosomes they contain: diploid and haploid cells. Understanding the differences between these two types of cells is essential for grasping various biological processes, including reproduction, growth, and development.
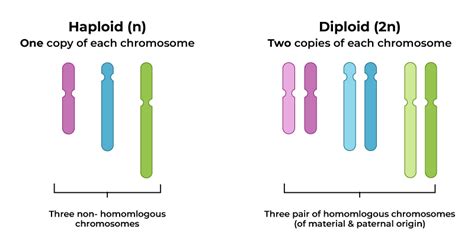
Diploid cells, also known as somatic cells, contain two complete sets of chromosomes, one inherited from each parent. In humans, this means that diploid cells have a total of 46 chromosomes, consisting of 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes (either XX in females or XY in males). Diploid cells are the building blocks of the body and make up the majority of cells in tissues and organs, including skin, muscle, and blood cells.
Characteristics of Diploid Cells

Diploid cells have several distinct characteristics that set them apart from haploid cells. For one, they contain a complete set of genetic material, which allows them to perform various functions necessary for maintaining the body’s overall health. Diploid cells can divide through a process called mitosis, resulting in two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. This process is essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues.
Furthermore, diploid cells can undergo meiosis, a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in haploid cells. Meiosis is a critical process that occurs in reproductive cells, such as sperm and egg cells, and is necessary for sexual reproduction. The ability of diploid cells to undergo meiosis ensures genetic diversity and increases the chances of producing healthy offspring.
Haploid Cells: Definition and Characteristics
Haploid cells, on the other hand, contain only one complete set of chromosomes, with a total of 23 chromosomes in humans. These cells are typically found in the reproductive system and are responsible for transmitting genetic material from one generation to the next. Haploid cells are produced through meiosis and are characterized by their unique genetic makeup, which is distinct from that of diploid cells.
Haploid cells have several key characteristics that distinguish them from diploid cells. For one, they contain half the number of chromosomes, which reduces the amount of genetic material and increases the chances of genetic recombination. Haploid cells are also highly specialized and are designed to fuse with other haploid cells during fertilization, resulting in the formation of a diploid zygote. This process is essential for the development of a new individual and ensures the continuation of the species.
| Cell Type | Number of Chromosomes | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Diploid Cells | 46 | Growth, repair, maintenance, meiosis |
| Haploid Cells | 23 | Reproduction, genetic transmission, fertilization |
Key Points
- Diploid cells contain two complete sets of chromosomes and are the building blocks of the body.
- Haploid cells contain one complete set of chromosomes and are responsible for transmitting genetic material.
- Diploid cells can divide through mitosis and undergo meiosis, resulting in haploid cells.
- Haploid cells are highly specialized and are designed to fuse with other haploid cells during fertilization.
- The distinction between diploid and haploid cells is essential for understanding various biological processes, including reproduction, growth, and development.
In conclusion, the difference between diploid and haploid cells is a fundamental concept in biology that has significant implications for our understanding of life. By recognizing the unique characteristics and functions of each cell type, we can gain valuable insights into the intricacies of life and develop new treatments for diseases. As research continues to uncover the complexities of cellular biology, it is essential to appreciate the distinction between diploid and haploid cells and their critical roles in maintaining the balance of life.
What is the main difference between diploid and haploid cells?
+The main difference between diploid and haploid cells is the number of chromosomes they contain. Diploid cells have two complete sets of chromosomes, while haploid cells have only one complete set.
What is the function of diploid cells in the body?
+Diploid cells are the building blocks of the body and perform various functions necessary for maintaining the body’s overall health, including growth, repair, and maintenance.
What is the role of haploid cells in reproduction?
+Haploid cells are responsible for transmitting genetic material from one generation to the next and are designed to fuse with other haploid cells during fertilization, resulting in the formation of a diploid zygote.