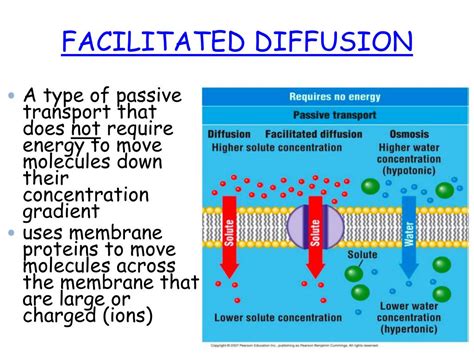
Diffusion, the process by which particles move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, is a fundamental concept in physics and chemistry. This process is essential for various biological and chemical reactions, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. One of the critical aspects of diffusion is its relationship with energy. In this article, we will explore five ways diffusion uses energy, highlighting the intricacies of this process and its implications for various systems.
Key Points
- Diffusion utilizes thermal energy to facilitate particle movement
- Energy is required to overcome the activation energy barrier in diffusion
- Diffusion can be enhanced or hindered by the presence of energy sources or sinks
- Biological systems exploit diffusion to optimize energy utilization
- Understanding the energy aspects of diffusion is crucial for designing efficient systems
Thermal Energy and Particle Movement
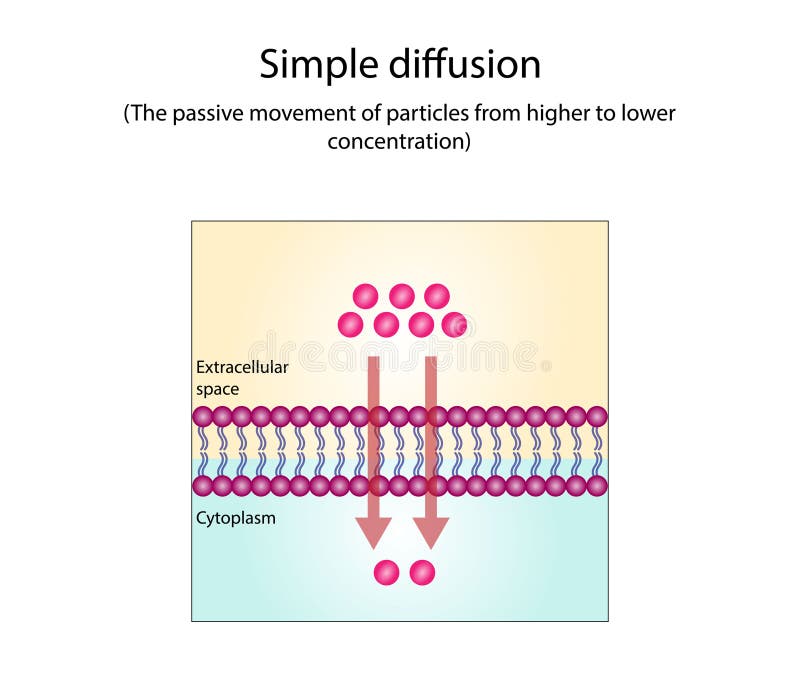
Diffusion is driven by thermal energy, which is the kinetic energy associated with the random motion of particles. As particles gain thermal energy, they move more rapidly and randomly, increasing the likelihood of crossing concentration gradients. This process is evident in gases, where molecules are in constant random motion due to thermal energy. The kinetic theory of gases describes how thermal energy influences the diffusion of gas molecules, providing a fundamental understanding of this phenomenon. For instance, the diffusion coefficient of a gas is directly proportional to the square root of the temperature, illustrating the significant impact of thermal energy on diffusion rates.
Activation Energy and Diffusion Barriers
For diffusion to occur, particles must overcome an energy barrier known as the activation energy. This barrier represents the minimum energy required for a particle to move from one location to another. In some systems, the activation energy can be substantial, hindering the diffusion process. Energy sources, such as heat or light, can provide the necessary energy to overcome this barrier, facilitating diffusion. For example, in chemical reactions, the activation energy can be lowered by the presence of catalysts, which enable particles to diffuse more readily and react with other particles. The relationship between activation energy and diffusion is critical in understanding the kinetics of chemical reactions and the optimization of reaction conditions.
| System | Activation Energy | Diffusion Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| Gases | Low | High |
| Liquids | Medium | Medium |
| Solids | High | Low |
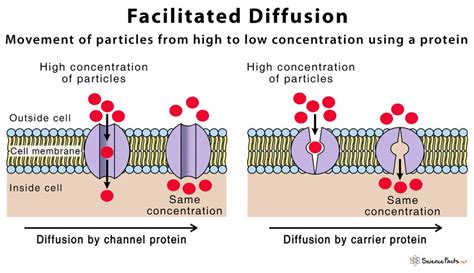
Energy Sources and Sinks in Diffusion
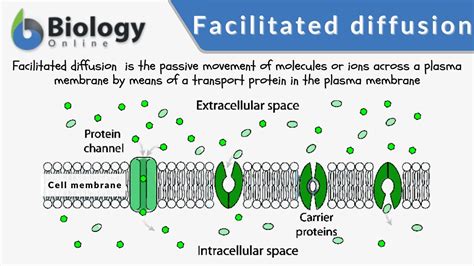
Energy sources and sinks can substantially influence diffusion processes. In some cases, energy sources can enhance diffusion by providing the necessary energy for particles to overcome activation energy barriers. Conversely, energy sinks can hinder diffusion by reducing the available energy for particle movement. For instance, in biological systems, energy sources like ATP can facilitate the diffusion of particles across cell membranes, while energy sinks like heat dissipation can slow down diffusion rates. The interplay between energy sources, sinks, and diffusion is complex and depends on the specific system and conditions.
Biological Systems and Energy Optimization
Biological systems have evolved to optimize energy utilization, often exploiting diffusion to achieve efficient energy transfer. For example, in photosynthesis, light energy is used to drive the diffusion of particles across thylakoid membranes, resulting in the production of ATP and NADPH. Similarly, in cellular respiration, the diffusion of oxygen and nutrients across cell membranes is critical for energy production. Understanding how biological systems optimize energy utilization through diffusion is essential for developing more efficient energy production and storage systems.
Designing Efficient Systems with Diffusion
Recognizing the critical role of energy in diffusion is essential for designing efficient systems. By understanding the energy requirements and barriers associated with diffusion, engineers and scientists can develop optimized systems that minimize energy consumption while maximizing performance. For instance, in the design of chemical reactors, understanding the diffusion of reactants and products can help optimize reaction conditions, leading to improved yields and reduced energy consumption. Similarly, in the development of energy storage systems, such as batteries, understanding the diffusion of ions and electrons can inform the design of more efficient and sustainable systems.
What is the primary energy source driving diffusion in gases?
+The primary energy source driving diffusion in gases is thermal energy, which is the kinetic energy associated with the random motion of particles.
How does activation energy influence diffusion rates?
+Activation energy represents the minimum energy required for a particle to move from one location to another. Higher activation energies can hinder diffusion, while lower activation energies can facilitate it.
What role does diffusion play in biological energy production?
+Diffusion plays a critical role in biological energy production, such as in photosynthesis and cellular respiration, where the diffusion of particles across membranes is essential for energy production.
In conclusion, diffusion is an intricate process that relies heavily on energy to facilitate particle movement. Understanding the relationship between energy and diffusion is crucial for optimizing system performance, designing efficient processes, and developing sustainable energy solutions. By recognizing the various ways diffusion uses energy, we can better appreciate the complexities of this phenomenon and its significance in biological, chemical, and physical systems.