Python, a versatile and widely used programming language, provides several ways to express the concept of "does not equal" in its syntax. The most common way to denote "does not equal" in Python is by using the `!=` operator. This operator is used to compare two values and returns `True` if they are not equal, and `False` otherwise.
Basic Usage of the “Does Not Equal” Operator
The != operator can be used with various data types in Python, including numbers, strings, lists, and more. Here are a few examples demonstrating its usage:
# Comparing integers
print(5!= 3) # Expected output: True
print(5!= 5) # Expected output: False
# Comparing strings
print("hello"!= "world") # Expected output: True
print("hello"!= "hello") # Expected output: False
# Comparing lists
print([1, 2, 3]!= [4, 5, 6]) # Expected output: True
print([1, 2, 3]!= [1, 2, 3]) # Expected output: False
Using “Does Not Equal” in Conditional Statements
The != operator is often used within conditional statements (if, elif, else) to make decisions based on whether two values are not equal. Here’s how you can use it:
x = 5
y = 3
if x!= y:
print("x and y are not equal")
else:
print("x and y are equal")
# Expected output: x and y are not equal
Key Points
- The `!=` operator in Python is used to check if two values are not equal.
- This operator can be used with various data types, including integers, floats, strings, lists, and more.
- It returns `True` if the values are not equal and `False` if they are equal.
- The `!=` operator is commonly used in conditional statements to control the flow of a program based on whether two values are not equal.
- Understanding how to use the `!=` operator is fundamental for writing conditional logic in Python.
Advanced Usage and Considerations

While the != operator is straightforward to use, there are some advanced considerations and edge cases to be aware of, especially when dealing with custom objects or complex data structures.
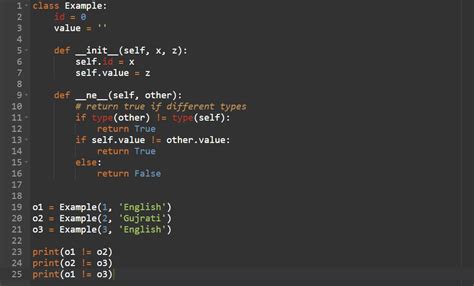
Custom Objects and the __ne__ Method
For custom objects, the behavior of the != operator can be defined by implementing the __ne__ method. This method should return True if the objects are not equal and False otherwise.
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def __ne__(self, other):
return not (self.name == other.name and self.age == other.age)
person1 = Person("John", 30)
person2 = Person("Jane", 30)
print(person1!= person2) # Expected output: True
Nan (Not a Number) in Float Comparisons
In floating-point comparisons, NaN (Not a Number) values behave uniquely. According to the IEEE 754 floating-point standard, NaN is not equal to anything, including itself. Thus, NaN!= NaN evaluates to True.
import math
nan_value = float('nan')
print(nan_value!= nan_value) # Expected output: True
Best Practices and Conclusion
Using the != operator in Python is a straightforward way to compare values and determine if they are not equal. Remember that the behavior of this operator can vary with custom objects and certain data types like floating-point numbers. By understanding these nuances and using the != operator judiciously, you can write more robust and effective conditional logic in your Python programs.
What does the != operator do in Python?
+
The != operator in Python checks if two values are not equal and returns True if they are not, and False otherwise.
Can the != operator be used with custom objects?
+
Yes, the != operator can be used with custom objects by defining the __ne__ method within the class definition.
How does NaN behave with the != operator?
+
NaN (Not a Number) values are not equal to anything, including themselves, according to the IEEE 754 floating-point standard.