In the realm of automotive engineering, suspension systems play a pivotal role in shaping a vehicle’s handling dynamics, ride comfort, and overall stability. Among the various configurations, the double wishbone suspension has garnered sustained attention for its ability to optimize tire contact, improve steering precision, and enhance ride quality. As vehicles increasingly demand superior handling to meet performance, safety, and driver experience expectations, understanding the intrinsic advantages of the double wishbone suspension becomes vital. This comprehensive analysis delves into the technical intricacies, historical development, and practical benefits of this suspension concept, drawing on recent industry studies and expert insights from leading automotive engineers.
Key Points
- Enhanced handling precision: Double wishbone designs allow for optimal camber control during cornering, leading to improved grip and stability.
- Superior tire contact patch maintenance: The configuration preserves consistent tire contact across various road conditions, contributing to safer and more predictable vehicle behavior.
- Reduced unwanted dynamic effects: By isolating influences of suspension kinematics, the system minimizes body roll and steering kickback.
- Design flexibility: The geometry permits tailored tuning for different vehicle applications, balancing comfort with performance objectives.
- Historical significance: Evolving from early independent suspension systems, double wishbone setups have become a benchmark in high-performance vehicles, rally cars, and luxury sedans.
Foundation of Double Wishbone Suspension in Automotive Design
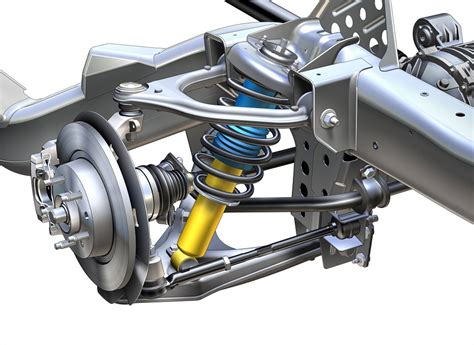
The double wishbone suspension—also known as double A-arm suspension—originated in early 20th-century racing and high-performance vehicle development. Its fundamental principle involves two ‘wishbone’-shaped arms per wheel—one upper and one lower—each pivotally attached to the vehicle chassis and wheel hub assembly. This layout affords precise control over wheel motion, especially camber angle, during various driving maneuvers.
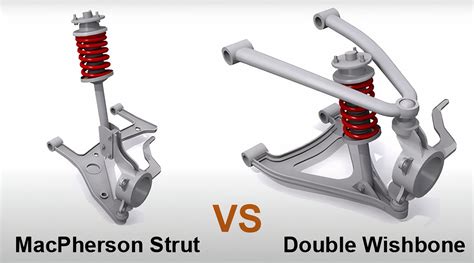
Contrasting with simpler setups like MacPherson struts, the double wishbone configuration provides a more complex but advantageous relationship between wheel alignment and vehicle dynamics. Over decades, industry experts and engineers have favorably observed its capacity to adapt to high-demand scenarios, from endurance racing to luxury touring. As automotive technology advanced, active suspension systems integrated with double wishbones further amplified these benefits, allowing real-time geometry adjustments for varying road conditions.
Technical Advantages of Double Wishbone Suspensions

Precise Camber and Caster Control
The primary technical merit of the double wishbone suspension lies in its ability to maintain optimal camber angles throughout the wheel’s range of movement. Camber— the tilt of the tire relative to vertical—crucially influences grip during cornering. The dual A-arms’ geometry ensures minimal camber change during straight-line driving, but effectively alters camber to optimize tire contact while turning. This dynamic adjustment enhances lateral grip, leading to more responsive steering and increased confidence during aggressive maneuvers.
Additionally, caster angles—titled axes affecting steering feedback—can be fine-tuned precisely. By adjusting the inclination of the wishbones and their mounting points, engineers can influence steering wheel feel and straight-line stability.
Minimized Body Roll and Improved Horizontal Stability
Because the double wishbone architecture allows for controlled toe and camber variations, it significantly reduces body roll during cornering. This stability results from the suspension’s ability to distribute lateral forces evenly and maintain tire contact, translating into reduced understeer or oversteer tendencies. Consequently, vehicles equipped with double wishbones often demonstrate superior lateral acceleration capabilities, particularly in high-performance contexts.
Enhanced Tuning Flexibility and Ride Quality
Factory and aftermarket tuners benefit from the geometric adaptability of this suspension type. With adjustable shock absorber mountings and custom wishbone geometries, the system can be calibrated to prioritize either comfort or performance, depending on the target application. That level of tuning fidelity makes it a perennial choice in racing disciplines, where minute geometry modifications can make substantial differences in lap times.
Comparative Analysis with Other Suspension Types
While the double wishbone is lauded for its handling finesse, it’s crucial to recognize its relative complexity and cost:
| Category | Double Wishbone |
|---|---|
| Handling | Exceptional, especially in cornering and steering accuracy |
| Design Complexity | Higher, requires precise geometry and robust mounting structures |
| Cost | More expensive due to manufacturing and maintenance requirements |
| Space Requirements | Generally larger footprint; less suitable for tight packaging constraints |
| Durability | High, but sensitive to misalignment if not properly maintained |

Compared to MacPherson strut suspensions—more compact, simpler, and cost-effective—the double wishbone excels in performance-oriented applications. Conversely, in mass-market vehicles prioritizing economy and space efficiency, simpler designs often prevail. The choice hinges on balancing desired handling benefits against practical constraints.
Historical Context and Evolution
The origins of the double wishbone suspension trace back to the early race cars of the 1910s and 1920s, where automotive engineers sought superior steering response and tire control. Notably, innovations during the 1950s and 1960s, driven by racing pioneers such as Lotus and Ferrari, refined the geometry—particularly the incorporation of ‘double wishbone’ arrangements that optimized aero dynamics and tire contact patches.
Over subsequent decades, advancements in materials—lightweight alloys and composites—and the advent of computer-aided design (CAD) enabled more precise and complex wishbone geometries. These innovations translated into commercial vehicles that deliver high-speed stability, safety, and comfort. Today, the integration of electronic suspension control systems continues to evolve, combining the mechanical advantages of double wishbones with real-time adaptive tuning based on sensor feedback.
Practical Implications for Modern Automotive Engineering
In the context of current automotive trends toward electrification, autonomous driving, and high-performance sports cars, the advantages of double wishbone suspension become ever more pertinent. Electric vehicles (EVs), with their heavy batteries, demand optimal handling to ensure safety and comfort. The ability of double wishbones to fine-tune wheel alignment dynamically supports these needs.
High-performance brands, such as Lamborghini, Ferrari, and specialized racing divisions, continue to rely on double wishbone geometries to attain peaks in lateral grip, steering sharpness, and predictable behavior at the limit. Meanwhile, for luxury sedans aiming for ride comfort without sacrificing handling precision, the design's adaptability makes it a preferred choice—often paired with active damping and suspension management systems.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite its numerous benefits, the double wishbone suspension isn’t devoid of drawbacks. The complexity leads to higher manufacturing costs and maintenance efforts, particularly in maintaining precise alignment over time. Additionally, space constraints can limit its application in smaller vehicles. For manufacturers and engineers, these factors necessitate weighing the performance gains against production and operational practicality.
Furthermore, the geometric sensitivity means that improper setup or component wear can significantly degrade performance, underscoring the importance of regular suspension diagnostics and adjustments.
Future Perspectives and Technological Innovations
The future of double wishbone suspension systems points toward integrating smart technologies—such as active geometry control, predictive damping, and sensor feedback loops—aimed at dynamically optimizing handling in real-time. Such innovations could even compensate for vehicle load changes, tire wear, and road surface variations, fostering an era of ‘adaptive chassis’ systems.
Moreover, research into lightweight, high-strength materials like carbon fiber composites is poised to reduce the weight penalty traditionally associated with complex suspension setups, making double wishbones more feasible in a broader range of vehicles.
Conclusion
The advantages of the double wishbone suspension for better vehicle handling are rooted in its ability to deliver refined control over wheel alignment and motion. Its historical pedigree and ongoing technological evolutions affirm its stature as a critical component in high-performance and luxury automotive design. While its complexity and cost mean it isn’t universally applicable, for those vehicles and applications where handling precision, stability, and tunability are paramount, the double wishbone remains an exemplary choice. Continued innovation in materials and active control systems promises to extend its relevance even further, maintaining its position at the forefront of automotive suspension technology.
What are the main differences between double wishbone and MacPherson strut suspensions?
+The double wishbone suspension offers superior handling and precise camber control by using two control arms per wheel, enabling better tire contact and stability during cornering. In contrast, MacPherson struts are simpler, more compact, and cost-effective, making them suitable for mass-market vehicles but with reduced handling finesse. The double wishbone’s complexity allows for more sophisticated tuning but at a higher manufacturing and maintenance cost.
How does the geometry of a double wishbone suspension influence tire grip?
+The geometry, including the angles and lengths of the wishbones, affects camber change and wheel contact during steering and suspension travel. Properly tuned geometries maintain an optimal contact patch—maximizing tire grip—especially during high lateral forces. This precise control enhances handling responsiveness and safety in performance driving scenarios.
Can dual wishbone suspensions be adapted for electric vehicles?
+Yes, their adaptability makes them suitable for EVs, especially given the need for precise handling to compensate for added weight from batteries. Active geometry adjustment and integration with electronic suspension systems enable EV manufacturers to harness the full potential of double wishbones, ensuring ride stability, safety, and driving comfort in electric platforms.