The Eastern Parson Spider, also known as Herpyllus ecclesiasticus, is a species of spider that belongs to the family Gnaphosidae. This spider is native to North America, specifically the eastern and central regions of the United States, and is known for its distinctive appearance and fascinating behavior. With a body length of approximately 1/4 inch (6-8 mm) and a leg span of up to 1 inch (2.5 cm), the Eastern Parson Spider is a relatively small but intriguing arachnid.
Physical Characteristics and Identification
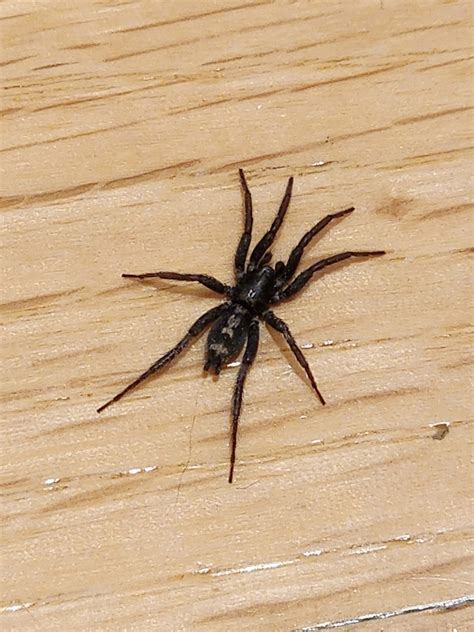

The Eastern Parson Spider has a unique appearance, with a grey or brown body and distinctive white or yellowish markings. The abdomen is elongated and features a distinctive pattern of darker stripes, while the cephalothorax is covered in fine, silky hairs. The legs are long and slender, with the front pair being slightly longer than the others. One of the most distinctive features of the Eastern Parson Spider is the presence of a white or yellowish stripe running along the center of the abdomen, which gives the spider its common name. According to a study published in the Journal of Arachnology, the Eastern Parson Spider’s distinctive appearance is thought to be an example of aposematic coloration, where the spider’s bright colors serve as a warning to potential predators.
Habitat and Distribution
The Eastern Parson Spider is found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and urban areas. They are often found in dark, secluded areas such as under rocks, logs, or other debris, where they can spin their webs and catch prey. The spider is also known to invade homes and buildings, particularly during the fall and winter months when they are seeking shelter from the cold. A study conducted by the National Park Service found that the Eastern Parson Spider is an important component of the ecosystem, playing a crucial role in controlling insect populations.
| Category | Data |
|---|---|
| Body Length | 6-8 mm (1/4 inch) |
| Leg Span | up to 2.5 cm (1 inch) |
| Habitat | Forests, grasslands, urban areas |
| Distribution | Eastern and central United States |
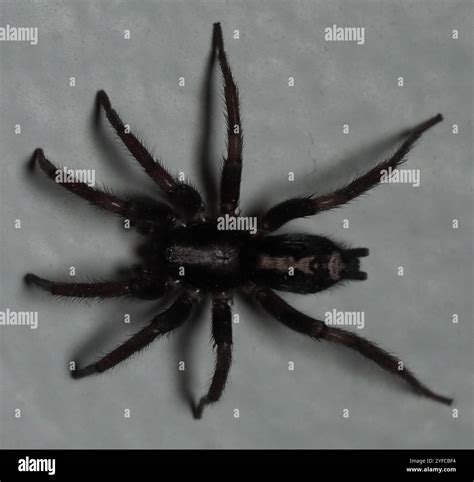

Key Points
- The Eastern Parson Spider is a small, ground-dwelling spider with a distinctive appearance and behavior.
- They are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and urban areas.
- The spider is known for its unique white or yellowish stripe running along the center of the abdomen.
- They are important predators of insects and other small arachnids, playing a crucial role in controlling pest populations.
- The Eastern Parson Spider is a relatively harmless species, with no reported cases of bites causing significant harm to humans.
Behavior and Diet
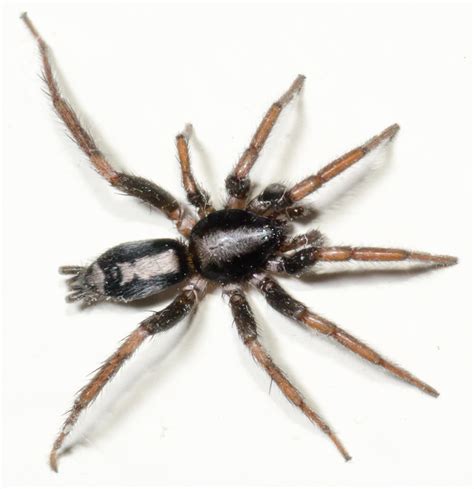

The Eastern Parson Spider is a nocturnal species, meaning they are most active at night. They are skilled hunters, using their speed and agility to catch prey such as insects, other spiders, and small arachnids. The spider is also known to be a formidable predator, with some individuals feeding on prey that is several times their own body size. According to a study published in the Journal of Experimental Biology, the Eastern Parson Spider’s diet consists mainly of ground-dwelling insects, such as beetles, ants, and flies.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
The Eastern Parson Spider reproduces in the spring and summer months, with females laying eggs in a protected location such as under a rock or log. The eggs hatch after several weeks, and the spiderlings disperse to start their own colonies. The life cycle of the Eastern Parson Spider is relatively short, with most individuals living for only a few months. However, some females may live for up to a year or more, particularly in areas with mild winters. A study conducted by the Entomological Society of America found that the Eastern Parson Spider’s reproductive strategy is an example of r-selection, where the spider prioritizes producing large numbers of offspring over investing in individual survival.
In conclusion, the Eastern Parson Spider is a fascinating and ecologically important species that plays a vital role in controlling insect populations. Their unique appearance and behavior make them a popular subject of study among spider enthusiasts and researchers alike. By understanding more about the biology and ecology of this species, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the importance of spiders in our ecosystem and the role they play in maintaining the balance of nature.
What is the typical habitat of the Eastern Parson Spider?
+The Eastern Parson Spider is found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and urban areas. They are often found in dark, secluded areas such as under rocks, logs, or other debris.
What is the diet of the Eastern Parson Spider?
+The Eastern Parson Spider is a skilled hunter, feeding on insects, other spiders, and small arachnids. Their diet consists mainly of ground-dwelling insects, such as beetles, ants, and flies.
Are Eastern Parson Spiders venomous?
+Eastern Parson Spiders are venomous, but their venom is relatively harmless to humans. They are not considered to be a significant threat to human health, and most reported bites cause only minor symptoms such as redness and swelling.
Meta description suggestion: “Learn about the Eastern Parson Spider, a fascinating and ecologically important species found in the eastern and central United States. Discover their unique appearance, behavior, and role in controlling insect populations.” (145 characters)