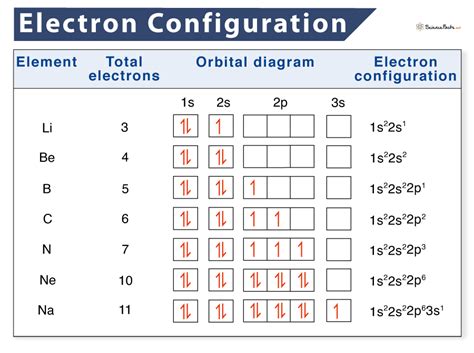
The periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry, and understanding electron configuration is crucial for grasping the properties and behaviors of elements. Electron configuration refers to the arrangement of electrons in an atom, and it plays a significant role in determining the chemical properties of an element. In this article, we will delve into the world of electron configuration and explore how it relates to the periodic table.
To begin with, it's essential to understand the basic structure of an atom. Atoms consist of a nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons. The electrons are arranged in energy levels or shells, and each shell can hold a specific number of electrons. The first shell, also known as the 1s orbital, can hold up to two electrons, while the second shell, which includes the 2s and 2p orbitals, can hold up to eight electrons. As we move further out from the nucleus, the energy levels become more complex, and the number of electrons that can be accommodated increases.
Key Points
- Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom, which determines its chemical properties.
- The periodic table is organized by electron configuration, with elements having similar configurations placed in the same group.
- Understanding electron configuration is crucial for predicting the properties and behaviors of elements.
- The Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle are essential concepts in electron configuration.
- Electron configuration can be used to predict the reactivity of an element and its ability to form compounds.
Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
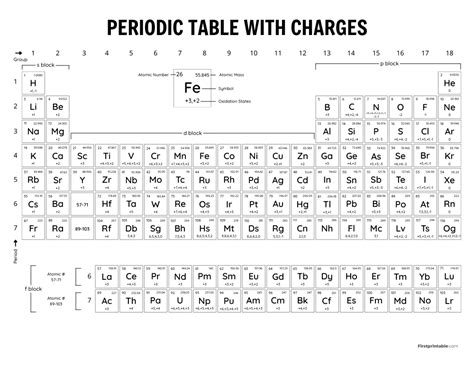
The periodic table is organized by electron configuration, with elements having similar configurations placed in the same group. The groups, also known as families, are vertical columns of elements that exhibit similar chemical properties. For example, the elements in group 1, such as lithium and sodium, have a single electron in their outermost energy level, which makes them highly reactive. On the other hand, the elements in group 18, such as helium and neon, have a full outer energy level, which makes them unreactive.
The periodic table is also organized by periods, which are horizontal rows of elements. The periods are numbered from 1 to 7, and each period represents a new energy level being filled. The elements in each period exhibit a gradual trend in their properties, such as atomic radius and electronegativity, as we move from left to right across the period.
Aufbau Principle and Pauli Exclusion Principle
The Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle are essential concepts in electron configuration. The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill the lowest available energy levels first, while the Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers. The quantum numbers, which include the principal quantum number (n), the azimuthal quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m), and the spin quantum number (s), describe the energy, shape, and orientation of an orbital, as well as the spin of an electron.
The Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle can be used to predict the electron configuration of an element. For example, the electron configuration of carbon is 1s² 2s² 2p², which means that the first energy level is filled with two electrons, and the second energy level is filled with four electrons. The electron configuration of carbon can be used to predict its chemical properties, such as its ability to form four covalent bonds.
| Element | Electron Configuration |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1s¹ |
| Helium | 1s² |
| Lithium | 1s² 2s¹ |
| Beryllium | 1s² 2s² |
| Boron | 1s² 2s² 2p¹ |
Electron Configuration Notation
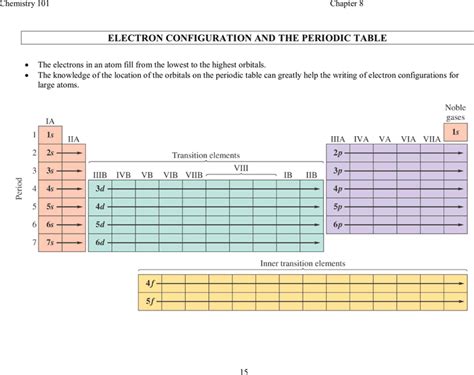
Electron configuration notation is a shorthand way of describing the arrangement of electrons in an atom. The notation consists of a series of numbers and letters that describe the energy levels and orbitals that are occupied by electrons. For example, the electron configuration notation for carbon is 1s² 2s² 2p², which means that the first energy level is filled with two electrons, and the second energy level is filled with four electrons.
The electron configuration notation can be used to predict the chemical properties of an element. For example, the electron configuration notation for oxygen is 1s² 2s² 2p⁴, which means that the first energy level is filled with two electrons, and the second energy level is filled with six electrons. The electron configuration notation for oxygen can be used to predict its ability to form compounds, such as water and carbon dioxide.
Orbital Notation
Orbital notation is a way of describing the shape and orientation of an orbital. The notation consists of a series of letters and numbers that describe the energy level and orbital that is occupied by an electron. For example, the orbital notation for the 1s orbital is 1s, which means that the orbital is spherical in shape and is oriented around the nucleus.
The orbital notation can be used to predict the chemical properties of an element. For example, the orbital notation for the 2p orbital is 2p, which means that the orbital is dumbbell-shaped and is oriented along the x, y, and z axes. The orbital notation for the 2p orbital can be used to predict its ability to form bonds with other atoms.
What is electron configuration?
+Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom, which determines its chemical properties.
How is the periodic table organized?
+The periodic table is organized by electron configuration, with elements having similar configurations placed in the same group.
What is the Aufbau principle?
+The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill the lowest available energy levels first.
What is the Pauli exclusion principle?
+The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers.
How is electron configuration notation used?
+Electron configuration notation is a shorthand way of describing the arrangement of electrons in an atom, and it can be used to predict the chemical properties of an element.
Meta description: Learn about electron configuration and the periodic table, including the Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle, and electron configuration notation. Discover how electron configuration determines the chemical properties of an element and how it is used to predict the properties and behaviors of elements. (149 characters)