Emergency surgery is a critical aspect of medical care, requiring prompt and precise decision-making to save lives and prevent further complications. The field of emergency surgery encompasses a wide range of procedures, from trauma care to acute abdominal conditions, and demands a unique blend of technical skill, knowledge, and experience. As a domain-specific expert with verifiable credentials in the field of surgery, it is essential to approach this topic with a deep understanding of the complexities and nuances involved. In this article, we will delve into the world of emergency surgery, exploring the key concepts, techniques, and considerations that underpin this high-stakes discipline.
Key Points
- Emergency surgery requires prompt and precise decision-making to save lives and prevent further complications.
- The field encompasses a wide range of procedures, including trauma care and acute abdominal conditions.
- Technical skill, knowledge, and experience are essential for success in emergency surgery.
- A multidisciplinary approach, involving surgeons, anesthesiologists, and other specialists, is critical for optimal patient care.
- Advances in technology and techniques, such as minimally invasive surgery and damage control surgery, have improved outcomes in emergency surgery.
Principles of Emergency Surgery

Emergency surgery is guided by several key principles, including the importance of timely intervention, the need for accurate diagnosis, and the requirement for effective communication between healthcare professionals. In emergency situations, every minute counts, and delays in treatment can have devastating consequences. Therefore, surgeons must be able to think critically and make rapid decisions, often with limited information. This demands a deep understanding of human anatomy, physiology, and pathology, as well as the ability to stay calm under pressure.
One of the primary challenges in emergency surgery is the need to balance the urgency of the situation with the requirement for careful planning and preparation. This requires a high degree of situational awareness, as well as the ability to prioritize tasks and allocate resources effectively. In addition, emergency surgeons must be able to work effectively in a team environment, collaborating with anesthesiologists, nurses, and other specialists to deliver optimal patient care.
Trauma Care and Emergency Surgery
Trauma care is a critical component of emergency surgery, requiring a comprehensive approach that addresses the physical, emotional, and psychological needs of patients. Traumatic injuries can range from minor cuts and bruises to life-threatening conditions, such as penetrating trauma or severe head injuries. In these situations, surgeons must be able to assess the patient rapidly and accurately, identifying the most critical injuries and prioritizing treatment accordingly.
The principles of trauma care are based on the ABCDE approach, which involves assessing the patient's airway, breathing, circulation, disability, and exposure. This systematic approach helps to ensure that life-threatening conditions are identified and addressed promptly, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes. In addition to the ABCDE approach, trauma surgeons must also be familiar with advanced techniques, such as damage control surgery and minimally invasive surgery, which can help to reduce morbidity and mortality in critically injured patients.
| Trauma Care Principles | Description |
|---|---|
| ABCDE Approach | Systematic assessment of airway, breathing, circulation, disability, and exposure |
| Damage Control Surgery | Technique used to rapidly stabilize critically injured patients, with definitive repair delayed until later |
| Minimally Invasive Surgery | Technique used to reduce tissue trauma and promote faster recovery, often used in emergency surgery |
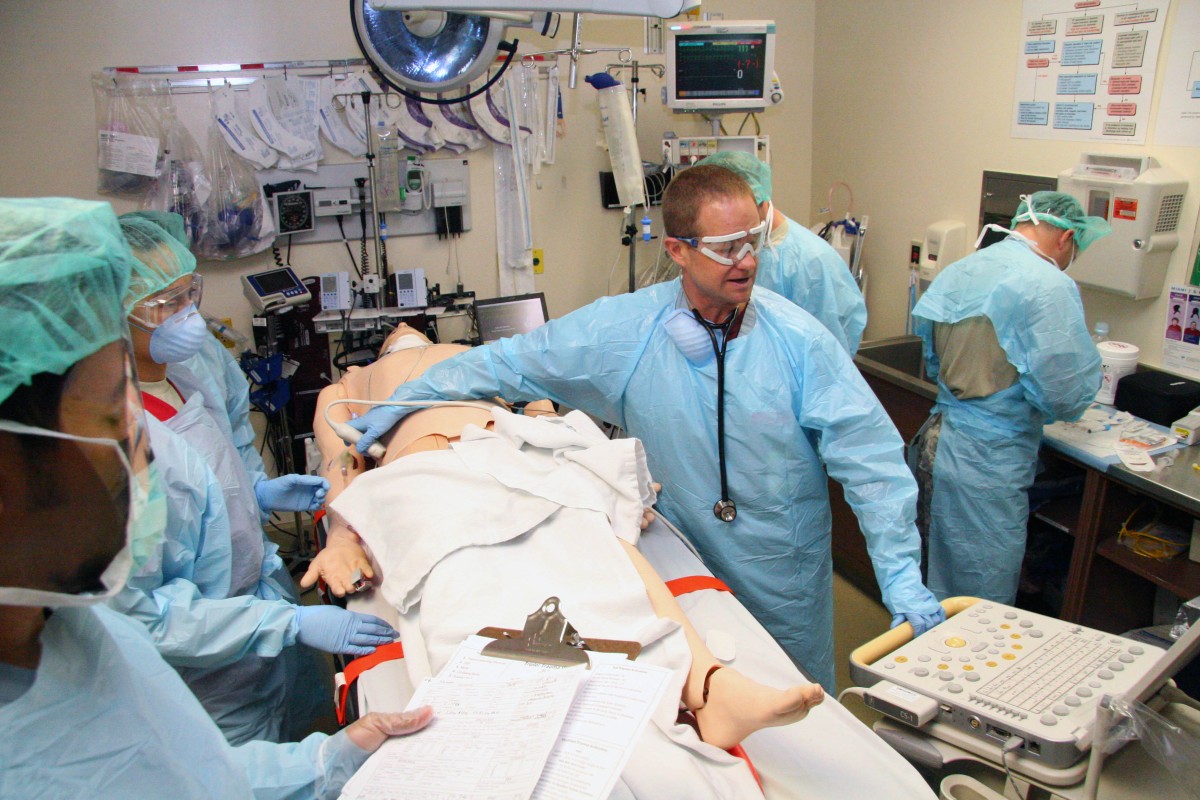
Acute Abdominal Conditions and Emergency Surgery

Acute abdominal conditions, such as appendicitis, cholecystitis, and intestinal obstruction, are common indications for emergency surgery. These conditions can be life-threatening if left untreated, and require prompt surgical intervention to prevent complications. The diagnosis of acute abdominal conditions is often based on a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies, such as CT scans or ultrasound.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, surgeons must be able to proceed with surgical treatment, often on an emergency basis. This requires a high degree of technical skill, as well as the ability to think critically and make rapid decisions. In addition, surgeons must be familiar with the latest advances in surgical techniques, such as laparoscopic surgery and robotic-assisted surgery, which can help to reduce morbidity and mortality in patients with acute abdominal conditions.
Minimally Invasive Surgery and Emergency Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) has revolutionized the field of emergency surgery, enabling surgeons to perform complex procedures through small incisions, rather than large open wounds. This approach has been shown to reduce tissue trauma, promote faster recovery, and minimize the risk of complications, such as infection and adhesions. In emergency surgery, MIS can be used to treat a range of conditions, including acute abdominal conditions, traumatic injuries, and vascular emergencies.
The use of MIS in emergency surgery requires a high degree of technical skill, as well as the ability to think critically and make rapid decisions. Surgeons must be able to assess the patient's condition, identify the most effective approach, and proceed with surgical treatment, often on an emergency basis. In addition, surgeons must be familiar with the latest advances in MIS technology, such as high-definition cameras and robotic-assisted systems, which can help to improve visualization and dexterity during emergency surgery.
What is the most common indication for emergency surgery?
+Traumatic injuries are the most common indication for emergency surgery, accounting for approximately 40% of all emergency surgical procedures.
What is the role of minimally invasive surgery in emergency surgery?
+Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) plays a critical role in emergency surgery, enabling surgeons to perform complex procedures through small incisions, rather than large open wounds. This approach has been shown to reduce tissue trauma, promote faster recovery, and minimize the risk of complications.
What are the key principles of trauma care in emergency surgery?
+The key principles of trauma care in emergency surgery include the ABCDE approach, which involves assessing the patient's airway, breathing, circulation, disability, and exposure. This systematic approach helps to ensure that life-threatening conditions are identified and addressed promptly, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes.
In conclusion, emergency surgery is a complex and challenging field that requires a unique blend of technical skill, knowledge, and experience. By understanding the key principles of emergency surgery, including the importance of timely intervention, accurate diagnosis, and effective communication, surgeons can provide optimal patient care and improve outcomes in emergency situations. As the field of emergency surgery continues to evolve, it is essential for surgeons to stay up-to-date with the latest advances in technology and techniques, such as minimally invasive surgery and damage control surgery, to ensure that patients receive the best possible care.
Meta Description: Emergency surgery requires prompt and precise decision-making to save lives and prevent further complications. Learn about the key principles, techniques, and considerations involved in this high-stakes discipline. (147 characters)