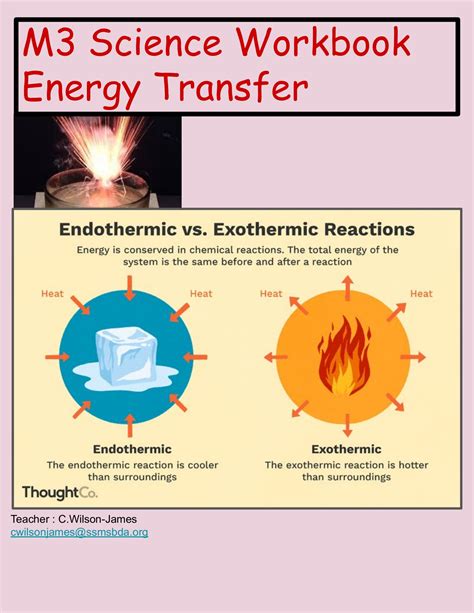
Exothermic reactions are a fundamental concept in chemistry, characterized by the release of heat energy into the surroundings. These reactions are not only fascinating to observe but also play a crucial role in various industrial and natural processes. Understanding the principles and applications of exothermic reactions is essential for chemists, researchers, and students alike. In this article, we will delve into the world of exothermic reactions, exploring their characteristics, examples, and safety considerations, while providing valuable tips for working with these energetic reactions.
Key Points
- Exothermic reactions release heat energy into the surroundings, often resulting in an increase in temperature.
- Examples of exothermic reactions include combustion, neutralization, and oxidation reactions.
- Safety considerations are crucial when working with exothermic reactions, including the use of protective gear and ventilation.
- Controlled conditions, such as temperature and concentration, are essential for optimizing exothermic reactions.
- Understanding the thermodynamics of exothermic reactions is vital for predicting and manipulating their outcomes.
Understanding Exothermic Reactions
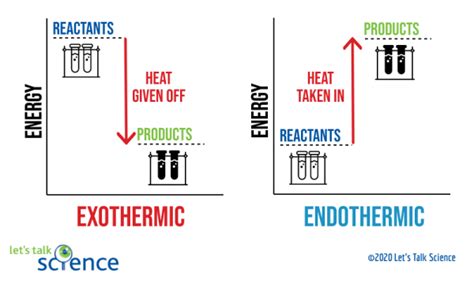
Exothermic reactions are characterized by a negative change in enthalpy (ΔH), indicating that heat energy is released into the surroundings. This release of energy can result in an increase in temperature, which can be measured using thermometers or calorimeters. The equation for an exothermic reaction typically includes the release of heat energy, denoted by the symbol “q” or “ΔH.” For example, the combustion of methane (CH4) is an exothermic reaction that releases heat energy: CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + heat.
Examples of Exothermic Reactions
Exothermic reactions are ubiquitous in nature and industry. Some common examples include:
- Combustion reactions, such as the burning of fossil fuels or wood.
- Neutralization reactions, such as the reaction between acids and bases.
- Oxidation reactions, such as the rusting of iron or the combustion of fuels.
These reactions are not only interesting to study but also have significant practical applications. For instance, exothermic reactions are used in the production of energy, the manufacture of chemicals, and the development of new materials.
Safety Considerations and Tips
When working with exothermic reactions, it is essential to prioritize safety. Here are some valuable tips to keep in mind:
- Use protective gear: Wear gloves, goggles, and a lab coat to protect yourself from potential splashes or spills.
- Ensure proper ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area to prevent the accumulation of toxic fumes or gases.
- Control reaction conditions: Monitor and control temperature, concentration, and other reaction conditions to prevent uncontrolled reactions.
- Use suitable containers: Choose containers that can withstand the heat and pressure generated by the reaction.
- Follow established protocols: Adhere to established procedures and guidelines for working with exothermic reactions.
By following these safety tips and guidelines, you can minimize the risks associated with exothermic reactions and ensure a safe and successful experiment.
Optimizing Exothermic Reactions
To optimize exothermic reactions, it is crucial to understand the thermodynamics involved. The Gibbs free energy equation (ΔG = ΔH - TΔS) provides a useful framework for predicting the spontaneity of a reaction. By controlling the temperature, concentration, and other reaction conditions, you can influence the reaction rate and outcome. Additionally, understanding the kinetics of the reaction can help you identify the rate-determining step and optimize the reaction conditions accordingly.
| Reaction Condition | Optimization Strategy |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Control temperature to maximize reaction rate and yield |
| Concentration | Optimize reactant concentrations to achieve the desired reaction rate and outcome |
| Catalyst | Use catalysts to enhance reaction rates and selectivity |
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, exothermic reactions are a fascinating and important area of study in chemistry. By understanding the principles and applications of these reactions, you can unlock new opportunities for energy production, chemical synthesis, and materials development. As research continues to advance our understanding of exothermic reactions, we can expect to see new breakthroughs and innovations in the field. Whether you are a student, researcher, or industry professional, mastering the concepts and techniques of exothermic reactions can help you achieve your goals and contribute to the advancement of science and technology.
What is the difference between an exothermic and endothermic reaction?
+An exothermic reaction releases heat energy into the surroundings, while an endothermic reaction absorbs heat energy from the surroundings.
How can I control the temperature of an exothermic reaction?
+You can control the temperature of an exothermic reaction by using a thermometer, a cooling system, or by adjusting the reaction conditions, such as the concentration of reactants or the presence of a catalyst.
What are some common examples of exothermic reactions in everyday life?
+Common examples of exothermic reactions in everyday life include the combustion of fossil fuels, the burning of wood, and the reaction between acids and bases.