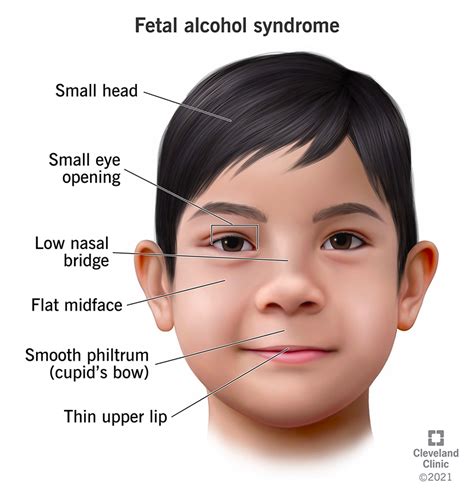
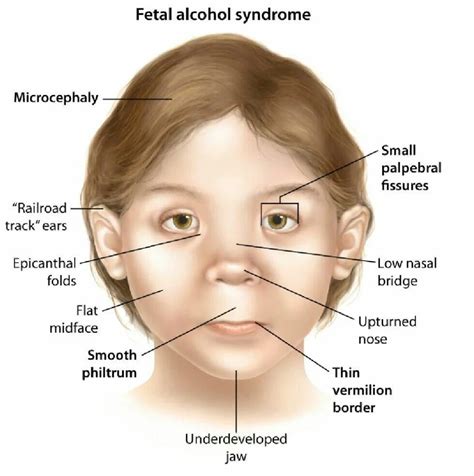
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) is a condition that affects individuals whose mothers consumed alcohol during pregnancy, leading to a range of physical, cognitive, and behavioral abnormalities. One of the key diagnostic features of FAS is the presence of distinct facial characteristics. These facial features are critical in identifying individuals with FAS, as they can be indicative of the condition's severity and impact on the individual's overall development.
Research has shown that the facial features associated with FAS are caused by the disruptive effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on fetal development, particularly during the critical periods of facial formation. The exact mechanisms underlying these effects are complex and involve the alteration of gene expression, disruption of cellular signaling pathways, and changes in the migration and differentiation of cells that contribute to facial development. Studies have identified that alcohol exposure during pregnancy can lead to changes in the expression of genes involved in craniofacial development, such as those in the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway, which plays a crucial role in the formation of facial structures.
Key Points
- The facial features of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome include short palpebral fissures, a thin upper lip, and a smooth philtrum.
- These features are caused by prenatal alcohol exposure, which disrupts fetal development and alters gene expression.
- The severity of FAS facial features can vary, and they may be more pronounced in individuals with a higher level of prenatal alcohol exposure.
- A comprehensive diagnosis of FAS involves a combination of physical examinations, cognitive and behavioral assessments, and medical history reviews.
- Early identification and intervention are critical for individuals with FAS, as they can help mitigate the condition's effects and improve long-term outcomes.
FAS Facial Features: A Diagnostic Criterion
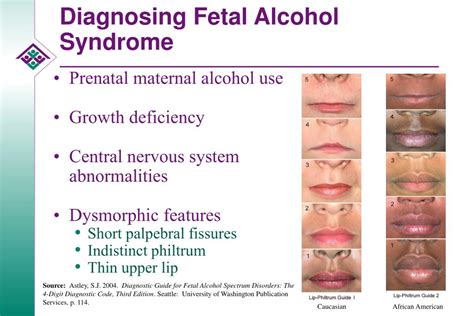
The facial features of FAS are a critical component of the diagnostic criteria for the condition. The key facial characteristics include short palpebral fissures (the distance between the inner and outer corners of the eye), a thin upper lip, and a smooth philtrum (the groove between the nose and upper lip). These features are often referred to as the “FAS face” and can be used to identify individuals with the condition. For example, a study published in the Journal of Pediatrics found that the presence of short palpebral fissures, a thin upper lip, and a smooth philtrum was associated with a higher risk of FAS in children.
Short Palpebral Fissures: A Key Diagnostic Feature
Short palpebral fissures are one of the most distinctive facial features of FAS. This characteristic is defined as a palpebral fissure length that is less than or equal to the 10th percentile for the individual’s age and sex. In other words, individuals with FAS tend to have eyes that appear smaller than average. This feature is thought to result from the disruptive effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on the development of the eye and surrounding facial structures. For instance, a case study published in the American Journal of Medical Genetics found that a child with FAS had short palpebral fissures, which were associated with a reduction in the size of the orbit and a change in the shape of the eye.
| Facial Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Short Palpebral Fissures | Eyes appear smaller than average, with a palpebral fissure length less than or equal to the 10th percentile |
| Thin Upper Lip | The upper lip appears thin and lacks the usual Cupid's bow shape |
| Smooth Philtrum | The groove between the nose and upper lip is smooth and lacks the usual indentation |

Diagnosis and Intervention
A comprehensive diagnosis of FAS involves a multidisciplinary approach, including physical examinations, cognitive and behavioral assessments, and medical history reviews. Healthcare professionals use standardized diagnostic criteria, such as the Diagnostic Guide for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders, to evaluate individuals for FAS. Early identification and intervention are critical for individuals with FAS, as they can help mitigate the condition’s effects and improve long-term outcomes. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Pediatrics found that early intervention services, such as speech and language therapy, occupational therapy, and special education, can improve cognitive and behavioral functioning in children with FAS.
Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention is essential for individuals with FAS, as it can help address the condition’s cognitive, behavioral, and physical effects. Research has shown that early intervention services, such as speech and language therapy, occupational therapy, and special education, can improve cognitive and behavioral functioning in children with FAS. Additionally, early intervention can help individuals with FAS develop essential life skills, such as social skills, emotional regulation, and adaptive behaviors. For example, a case study published in the Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics found that a child with FAS who received early intervention services showed significant improvements in social skills and emotional regulation.
What are the key facial features of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
+The key facial features of FAS include short palpebral fissures, a thin upper lip, and a smooth philtrum.
How is Fetal Alcohol Syndrome diagnosed?
+A comprehensive diagnosis of FAS involves a combination of physical examinations, cognitive and behavioral assessments, and medical history reviews.
What is the importance of early intervention for individuals with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
+Early intervention is essential for individuals with FAS, as it can help address the condition's cognitive, behavioral, and physical effects, and improve long-term outcomes.
In conclusion, the facial features of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome are a critical component of the diagnostic criteria for the condition. The presence of short palpebral fissures, a thin upper lip, and a smooth philtrum can be indicative of FAS, and early identification and intervention are essential for mitigating the condition's effects and improving long-term outcomes. By understanding the causes and effects of FAS facial features, healthcare professionals can provide more effective diagnosis, treatment, and support for individuals with this condition.
Meta description suggestion: “Learn about the facial features of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome, including short palpebral fissures, thin upper lip, and smooth philtrum, and understand the importance of early intervention for individuals with FAS.” (147 characters)