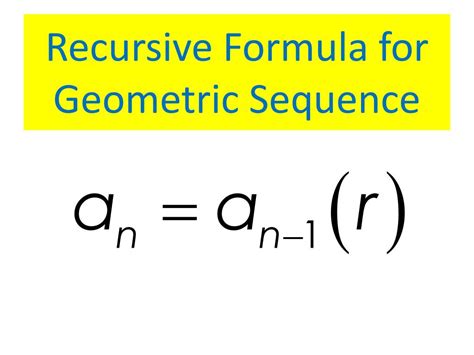
The geometric sequence formula is a fundamental concept in mathematics, used to describe a sequence of numbers where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous term by a fixed, non-zero number called the common ratio. This formula has numerous applications in various fields, including finance, physics, and computer science. The geometric sequence formula is given by: $a_n = a_1 \cdot r^{(n-1)}$, where $a_n$ is the nth term of the sequence, $a_1$ is the first term, $r$ is the common ratio, and $n$ is the term number.
The geometric sequence formula can be used to model population growth, compound interest, and other real-world phenomena where a quantity changes at a constant rate. For example, if a population of bacteria doubles every hour, the number of bacteria after $n$ hours can be modeled using the geometric sequence formula, where the first term $a_1$ is the initial population, the common ratio $r$ is 2, and the term number $n$ represents the number of hours. By understanding and applying the geometric sequence formula, individuals can better analyze and predict the behavior of complex systems and make informed decisions in various fields.
Key Points
- The geometric sequence formula is $a_n = a_1 \cdot r^{(n-1)}$, where $a_n$ is the nth term, $a_1$ is the first term, $r$ is the common ratio, and $n$ is the term number.
- The formula has numerous applications in finance, physics, and computer science, among other fields.
- It can be used to model population growth, compound interest, and other real-world phenomena where a quantity changes at a constant rate.
- Understanding the geometric sequence formula enables individuals to analyze and predict the behavior of complex systems and make informed decisions.
- The formula is a fundamental concept in mathematics, and its applications continue to expand into various disciplines.
Derivation of the Geometric Sequence Formula
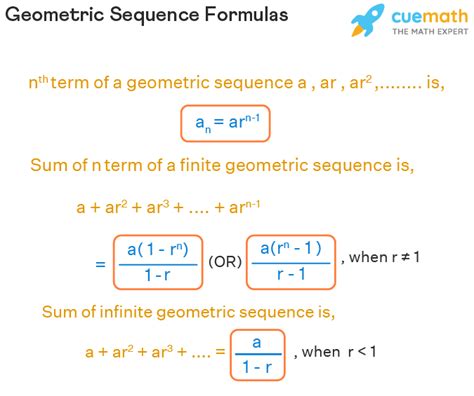
The geometric sequence formula can be derived by analyzing the pattern of a geometric sequence. A geometric sequence is a sequence of numbers where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous term by a fixed, non-zero number called the common ratio. For example, if the first term is a_1 and the common ratio is r, the sequence can be written as: a_1, a_1 \cdot r, a_1 \cdot r^2, a_1 \cdot r^3,....
By examining the pattern, we can see that each term is obtained by multiplying the previous term by the common ratio $r$. Therefore, the nth term $a_n$ can be expressed as: $a_n = a_1 \cdot r^{(n-1)}$. This formula provides a concise way to calculate any term in a geometric sequence, given the first term and the common ratio.
Example Applications of the Geometric Sequence Formula
The geometric sequence formula has numerous applications in various fields. For instance, in finance, it can be used to calculate the future value of an investment, given the initial principal, interest rate, and time period. In physics, it can be used to model the motion of objects under constant acceleration, such as the trajectory of a projectile.
In computer science, the geometric sequence formula can be used to analyze the time complexity of algorithms, which is essential for optimizing software performance. Additionally, the formula has applications in biology, where it can be used to model population growth and the spread of diseases.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Finance | Calculating future value of investments, compound interest |
| Physics | Modeling motion under constant acceleration, projectile trajectories |
| Computer Science | Analyzing time complexity of algorithms, optimizing software performance |
| Biology | Modeling population growth, spread of diseases |
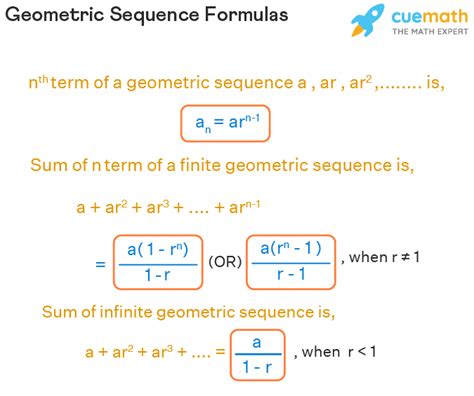
Common Ratio and Its Impact on Geometric Sequences

The common ratio r plays a crucial role in determining the behavior of a geometric sequence. If |r| > 1, the sequence diverges, meaning that the terms increase without bound. On the other hand, if |r| < 1, the sequence converges, meaning that the terms approach a limiting value. If r = 1, the sequence is constant, and if r = -1, the sequence alternates between two values.
The common ratio can be used to analyze the growth or decay of a geometric sequence. For example, if a population of bacteria triples every hour, the common ratio is 3, and the sequence will diverge. However, if a radioactive substance decays at a rate of 10% per hour, the common ratio is 0.9, and the sequence will converge.
Calculating the Common Ratio
The common ratio r can be calculated by dividing any term by its preceding term. For example, if the first term is a_1 and the second term is a_2, the common ratio is: r = \frac{a_2}{a_1}. This formula provides a simple way to determine the common ratio, given any two consecutive terms of a geometric sequence.
In conclusion, the geometric sequence formula is a fundamental concept in mathematics, with numerous applications in various fields. By understanding and applying this formula, individuals can analyze and predict the behavior of complex systems, make informed decisions, and develop a deeper appreciation for the underlying patterns and structures that govern our world.
What is the geometric sequence formula?
+The geometric sequence formula is a_n = a_1 \cdot r^{(n-1)}, where a_n is the nth term, a_1 is the first term, r is the common ratio, and n is the term number.
What is the common ratio in a geometric sequence?
+The common ratio r is a fixed, non-zero number that is multiplied by each term to obtain the next term in the sequence.
What are some applications of the geometric sequence formula?
+The geometric sequence formula has numerous applications in finance, physics, computer science, biology, and other fields, including modeling population growth, compound interest, and the spread of diseases.
How do you calculate the common ratio in a geometric sequence?
+The common ratio r can be calculated by dividing any term by its preceding term: r = \frac{a_2}{a_1}.
What is the difference between a convergent and divergent geometric sequence?
+A convergent geometric sequence has a common ratio |r| < 1, meaning that the terms approach a limiting value, while a divergent geometric sequence has a common ratio |r| > 1, meaning that the terms increase without bound.