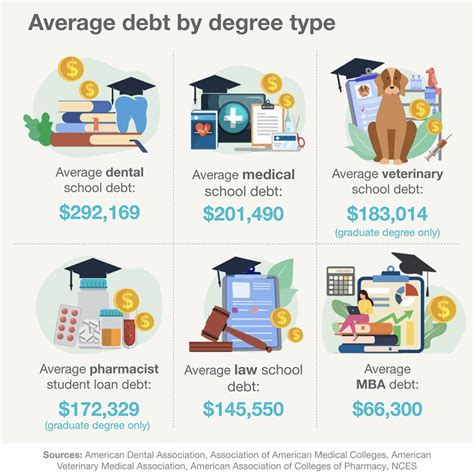
As the cost of higher education continues to rise, graduate school loans have become an essential part of financing advanced degrees for many students. With the increasing demand for specialized skills and knowledge, pursuing a graduate degree can be a significant investment in one's career. However, navigating the complex world of grad school loans can be overwhelming, especially for those who are new to the process. In this article, we will break down the key aspects of graduate school loans, providing you with a comprehensive guide to make informed decisions about your financial aid options.
Key Points
- Understanding the different types of graduate school loans, including federal and private options
- Learning about the various repayment plans and forgiveness programs available
- Developing a strategy for managing debt and creating a personalized repayment plan
- Exploring alternative funding options, such as scholarships and assistantships
- Considering the long-term implications of graduate school loans on your financial future
Types of Graduate School Loans

There are two primary categories of graduate school loans: federal loans and private loans. Federal loans are provided by the US Department of Education and offer more flexible repayment terms and lower interest rates compared to private loans. The most common types of federal graduate school loans include Direct Unsubsidized Loans and Grad PLUS Loans. Direct Unsubsidized Loans have a fixed interest rate of 6.54% for the 2022-2023 academic year, while Grad PLUS Loans have a fixed interest rate of 7.54% for the same period.
Federal Graduate School Loans
Federal graduate school loans are a popular choice among students due to their favorable terms and conditions. To be eligible for federal loans, students must complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) and demonstrate financial need. The FAFSA is a critical step in determining eligibility for federal, state, and institutional financial aid. By submitting the FAFSA, students can access a range of financial resources, including grants, loans, and work-study programs.
| Loan Type | Interest Rate | Repayment Terms |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Unsubsidized Loans | 6.54% | 10-25 years |
| Grad PLUS Loans | 7.54% | 10-25 years |

Private Graduate School Loans

Private graduate school loans are offered by banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions. These loans often have higher interest rates and less flexible repayment terms compared to federal loans. However, private loans can provide additional funding options for students who have exhausted their federal loan eligibility or require more specialized loan products. When considering private loans, it’s essential to compare interest rates, fees, and repayment terms among different lenders to find the most suitable option for your needs.
Repayment Plans and Forgiveness Programs
Graduate school loans offer various repayment plans and forgiveness programs to help borrowers manage their debt. The most common repayment plans include the Standard Repayment Plan, Graduated Repayment Plan, and Income-Driven Repayment Plan. Forgiveness programs, such as Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) and Teacher Loan Forgiveness, can provide significant debt relief for borrowers who work in specific fields or meet certain eligibility criteria.
Managing Debt and Creating a Repayment Plan
Developing a strategy for managing debt and creating a personalized repayment plan is crucial for graduate school loan borrowers. This involves tracking expenses, creating a budget, and prioritizing debt repayment. By understanding your financial situation and making informed decisions about your loan repayment, you can minimize your debt burden and achieve long-term financial stability.
Alternative Funding Options
In addition to loans, there are alternative funding options available to graduate students, such as scholarships, assistantships, and fellowships. These options can provide significant financial support and help reduce reliance on loans. By exploring these alternatives and creating a comprehensive funding plan, students can minimize their debt and achieve their academic and professional goals.
What is the difference between federal and private graduate school loans?
+Federal graduate school loans are provided by the US Department of Education and offer more flexible repayment terms and lower interest rates compared to private loans. Private loans, on the other hand, are offered by banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions, and often have higher interest rates and less flexible repayment terms.
How do I apply for federal graduate school loans?
+To apply for federal graduate school loans, you must complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) and demonstrate financial need. The FAFSA is a critical step in determining eligibility for federal, state, and institutional financial aid.
What are the repayment options for graduate school loans?
+Graduate school loans offer various repayment plans, including the Standard Repayment Plan, Graduated Repayment Plan, and Income-Driven Repayment Plan. Forgiveness programs, such as Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) and Teacher Loan Forgiveness, can also provide significant debt relief for borrowers who work in specific fields or meet certain eligibility criteria.
In conclusion, navigating the complex world of graduate school loans requires careful consideration and planning. By understanding the different types of loans, repayment plans, and forgiveness programs available, students can make informed decisions about their financial aid options and create a personalized repayment plan. Remember to prioritize federal loans, explore alternative funding options, and develop a strategy for managing debt to achieve long-term financial stability.