Gravitational energy is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the potential energy associated with the gravitational force. It is a measure of the energy an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field. The concept of gravitational energy is crucial in understanding various phenomena in the universe, from the motion of planets to the behavior of black holes. In this article, we will explore five ways to define gravitational energy, highlighting its significance and applications in different areas of physics.
Key Points
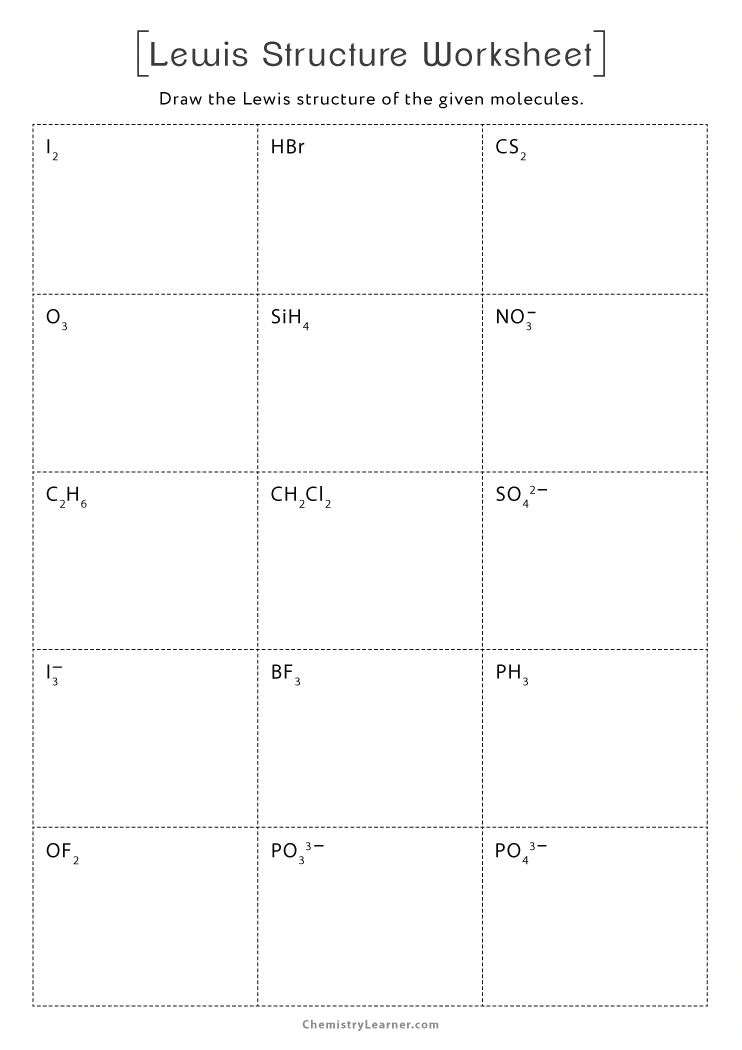
- Gravitational energy is a measure of the potential energy associated with the gravitational force.
- It is defined as the energy an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field.
- Gravitational energy is crucial in understanding various phenomena in the universe, from planetary motion to black hole behavior.
- There are different ways to define gravitational energy, including the gravitational potential energy, gravitational binding energy, gravitational kinetic energy, gravitational wave energy, and gravitational field energy.
- Understanding gravitational energy is essential for advances in fields such as astrophysics, cosmology, and gravitational physics.
Gravitational Potential Energy
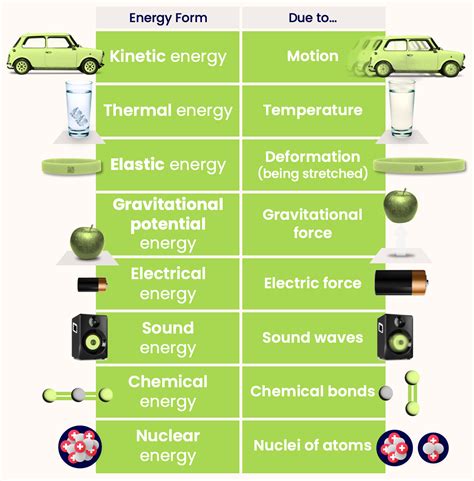
One way to define gravitational energy is through the concept of gravitational potential energy. This is the energy an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field. The gravitational potential energy of an object is given by the equation U = mgh, where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the object above a reference point. This definition is useful for understanding the behavior of objects on Earth, such as the motion of projectiles and the energy of falling objects.
Gravitational Binding Energy
Another way to define gravitational energy is through the concept of gravitational binding energy. This is the energy required to separate an object from a gravitational system, such as a planet or a star. The gravitational binding energy of an object is given by the equation U = -GMm/r, where G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the gravitational system, m is the mass of the object, and r is the distance between the object and the center of the gravitational system. This definition is useful for understanding the behavior of celestial bodies, such as the formation of stars and galaxies.
| Gravitational Energy Type | Equation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Gravitational Potential Energy | U = mgh | Energy an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field |
| Gravitational Binding Energy | U = -GMm/r | Energy required to separate an object from a gravitational system |
| Gravitational Kinetic Energy | K = (1/2)mv^2 | Energy an object possesses due to its motion in a gravitational field |
| Gravitational Wave Energy | E = (1/2)mc^2 | Energy carried by gravitational waves |
| Gravitational Field Energy | U = (1/8π)∫E^2 dV | Energy stored in a gravitational field |
Gravitational Kinetic Energy

A third way to define gravitational energy is through the concept of gravitational kinetic energy. This is the energy an object possesses due to its motion in a gravitational field. The gravitational kinetic energy of an object is given by the equation K = (1⁄2)mv^2, where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity. This definition is useful for understanding the behavior of objects in motion, such as the orbits of planets and the trajectories of projectiles.
Gravitational Wave Energy
A fourth way to define gravitational energy is through the concept of gravitational wave energy. This is the energy carried by gravitational waves, which are ripples in the fabric of spacetime produced by the acceleration of massive objects. The gravitational wave energy of an object is given by the equation E = (1⁄2)mc^2, where m is the mass of the object and c is the speed of light. This definition is useful for understanding the behavior of gravitational waves, which were first detected directly in 2015.
Gravitational Field Energy
A fifth way to define gravitational energy is through the concept of gravitational field energy. This is the energy stored in a gravitational field, which is a region of spacetime where the gravitational force is nonzero. The gravitational field energy of an object is given by the equation U = (1/8π)∫E^2 dV, where E is the gravitational field strength and dV is the volume element. This definition is useful for understanding the behavior of gravitational fields, which are essential for understanding the behavior of celestial bodies and the large-scale structure of the universe.
What is the difference between gravitational potential energy and gravitational binding energy?
+Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field, while gravitational binding energy is the energy required to separate an object from a gravitational system.
How is gravitational wave energy different from other forms of gravitational energy?
+Gravitational wave energy is the energy carried by gravitational waves, which are ripples in the fabric of spacetime produced by the acceleration of massive objects. This is distinct from other forms of gravitational energy, which are related to the position or motion of objects in a gravitational field.
What are some of the applications of gravitational energy in astrophysics and cosmology?
+Gravitational energy is essential for understanding various phenomena in astrophysics and cosmology, including the behavior of black holes, the formation of stars and galaxies, and the large-scale structure of the universe. It is also crucial for understanding the behavior of gravitational waves, which are a key area of research in modern astrophysics.
In conclusion, gravitational energy is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the potential energy associated with the gravitational force. There are different ways to define gravitational energy, including gravitational potential energy, gravitational binding energy, gravitational kinetic energy, gravitational wave energy, and gravitational field energy. Understanding these different definitions is essential for advances in fields such as astrophysics, cosmology, and gravitational physics. By exploring the various aspects of gravitational energy, we can gain a deeper understanding of the behavior of celestial bodies and the large-scale structure of the universe.
Meta Description: Discover the different definitions of gravitational energy and their applications in astrophysics and cosmology. Learn about gravitational potential energy, gravitational binding energy, and more. (149 characters)