Water is one of the most abundant substances on Earth, covering over 70% of the planet's surface. Its unique properties make it an essential component of various natural and industrial processes. One of the key characteristics of water is its ability to act as a heat conductor, facilitating the transfer of thermal energy. In this article, we will delve into the role of water as a heat conductor, exploring its thermal properties, applications, and implications for various fields.
The thermal conductivity of water is relatively high, with a value of approximately 0.6 W/m·K at 20°C. This means that water can efficiently transfer heat energy, making it an effective medium for cooling and heating applications. The thermal conductivity of water is influenced by its temperature, pressure, and purity. For instance, the thermal conductivity of seawater is lower than that of fresh water due to the presence of dissolved salts and other impurities. Understanding the thermal properties of water is crucial for designing and optimizing systems that utilize water as a heat conductor.
Key Points
- Water's thermal conductivity is approximately 0.6 W/m·K at 20°C, making it an effective heat conductor.
- The thermal conductivity of water is influenced by its temperature, pressure, and purity.
- Water is used as a heat conductor in various applications, including cooling systems, heat exchangers, and thermal energy storage systems.
- The specific heat capacity of water is high, allowing it to absorb and release large amounts of thermal energy without significant changes in temperature.
- Water's thermal properties make it an essential component of various industrial and natural processes, including power generation, climate regulation, and geological processes.
Thermal Properties of Water
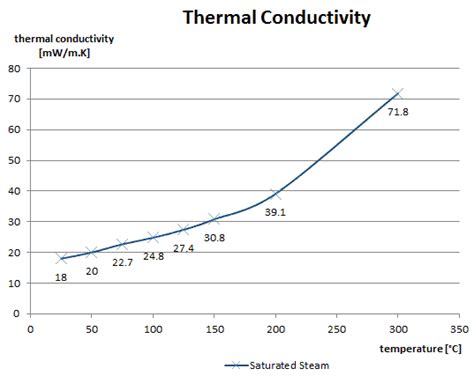
The thermal properties of water are characterized by its specific heat capacity, thermal conductivity, and latent heat of vaporization. The specific heat capacity of water is approximately 4.184 J/g·K, which is one of the highest among common substances. This means that water can absorb and release large amounts of thermal energy without significant changes in temperature. The high specific heat capacity of water makes it an effective medium for regulating temperature and maintaining thermal stability in various systems.
Applications of Water as a Heat Conductor
Water is used as a heat conductor in various applications, including cooling systems, heat exchangers, and thermal energy storage systems. In cooling systems, water is used to absorb heat from a source and transfer it to a sink, such as a radiator or a cooling tower. Heat exchangers, on the other hand, utilize water to transfer heat from one fluid to another, often in industrial processes such as power generation and chemical processing. Thermal energy storage systems use water to store thermal energy, which can be released as needed to provide heating or cooling.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Cooling Systems | Water is used to absorb heat from a source and transfer it to a sink. |
| Heat Exchangers | Water is used to transfer heat from one fluid to another in industrial processes. |
| Thermal Energy Storage Systems | Water is used to store thermal energy, which can be released as needed to provide heating or cooling. |

Implications of Water as a Heat Conductor
The implications of water as a heat conductor are far-reaching, influencing various fields such as energy, environment, and geology. In the context of energy, water plays a critical role in power generation, cooling, and heating. The use of water as a heat conductor can help reduce energy consumption and increase efficiency in various industrial processes. Additionally, water’s thermal properties make it an essential component of natural processes, such as climate regulation and geological processes.
Environmental Implications
The environmental implications of water as a heat conductor are significant, particularly in the context of climate change. Water’s high specific heat capacity and thermal conductivity make it an effective medium for regulating temperature and maintaining thermal stability in various ecosystems. However, human activities such as industrialization and urbanization can alter water’s thermal properties, leading to changes in local and global climate patterns. Understanding the environmental implications of water as a heat conductor is crucial for developing sustainable and environmentally friendly technologies.
What is the thermal conductivity of water?
+The thermal conductivity of water is approximately 0.6 W/m·K at 20°C.
What are the applications of water as a heat conductor?
+Water is used as a heat conductor in various applications, including cooling systems, heat exchangers, and thermal energy storage systems.
What are the environmental implications of water as a heat conductor?
+The environmental implications of water as a heat conductor are significant, particularly in the context of climate change. Water's high specific heat capacity and thermal conductivity make it an effective medium for regulating temperature and maintaining thermal stability in various ecosystems.
In conclusion, water’s role as a heat conductor is vital for various natural and industrial processes. Its unique thermal properties make it an effective medium for cooling, heating, and thermal energy storage. Understanding the implications of water as a heat conductor is crucial for developing sustainable and environmentally friendly technologies, as well as mitigating the effects of climate change. By recognizing the importance of water as a heat conductor, we can optimize its use in various applications and promote a more sustainable future.