Calculating density is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, and it is essential to understand the different methods of calculating density to solve various problems. Density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance, and it is typically denoted by the symbol ρ (rho). In this article, we will explore five ways to calculate density, including the use of formulas, equations, and real-world examples.
Key Points
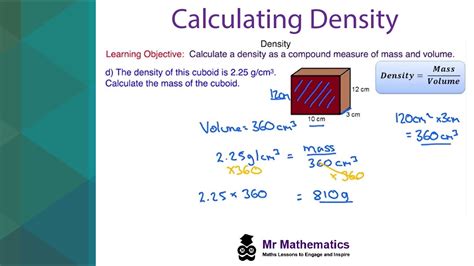
- The formula for calculating density is ρ = m/V, where ρ is the density, m is the mass, and V is the volume.
- Density can be calculated using the equation ρ = ρ0 \* (1 + β \* ΔT), where ρ0 is the initial density, β is the coefficient of thermal expansion, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
- The density of a mixture can be calculated using the formula ρ = (m1 \* ρ1 + m2 \* ρ2) / (m1 + m2), where m1 and m2 are the masses of the two components, and ρ1 and ρ2 are their respective densities.
- Density can be measured using various experimental methods, including the use of a hydrometer, a pycnometer, or a densitometer.
- Understanding density is crucial in various fields, including engineering, physics, and materials science, as it affects the behavior and properties of materials.
Method 1: Using the Formula ρ = m/V

The most common method of calculating density is by using the formula ρ = m/V, where ρ is the density, m is the mass, and V is the volume. This formula is straightforward and can be applied to any substance, as long as the mass and volume are known. For example, if we have a block of aluminum with a mass of 10 kg and a volume of 3.7 liters, we can calculate its density as follows:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Mass (m) | 10 kg |
| Volume (V) | 3.7 liters |
| Density (ρ) | 2.7 g/cm³ |
In this example, the density of the aluminum block is calculated to be 2.7 g/cm³, which is a typical value for aluminum.
Method 2: Using the Equation ρ = ρ0 * (1 + β * ΔT)
Another method of calculating density is by using the equation ρ = ρ0 * (1 + β * ΔT), where ρ0 is the initial density, β is the coefficient of thermal expansion, and ΔT is the change in temperature. This equation takes into account the effect of temperature on the density of a substance. For example, if we have a sample of water with an initial density of 1 g/cm³ and a coefficient of thermal expansion of 0.0002 K⁻¹, and we heat it up by 10°C, we can calculate its new density as follows:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Initial Density (ρ0) | 1 g/cm³ |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (β) | 0.0002 K⁻¹ |
| Change in Temperature (ΔT) | 10°C |
| New Density (ρ) | 0.998 g/cm³ |
In this example, the new density of the water is calculated to be 0.998 g/cm³, which is slightly lower than the initial density due to the expansion of the water with temperature.
Method 3: Using the Formula ρ = (m1 * ρ1 + m2 * ρ2) / (m1 + m2)

A third method of calculating density is by using the formula ρ = (m1 * ρ1 + m2 * ρ2) / (m1 + m2), where m1 and m2 are the masses of the two components, and ρ1 and ρ2 are their respective densities. This formula is used to calculate the density of a mixture of two substances. For example, if we have a mixture of 20% ethanol and 80% water, with densities of 0.789 g/cm³ and 1 g/cm³ respectively, we can calculate the density of the mixture as follows:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Mass of Ethanol (m1) | 200 g |
| Mass of Water (m2) | 800 g |
| Density of Ethanol (ρ1) | 0.789 g/cm³ |
| Density of Water (ρ2) | 1 g/cm³ |
| Density of Mixture (ρ) | 0.942 g/cm³ |
In this example, the density of the mixture is calculated to be 0.942 g/cm³, which is between the densities of the two components.
Method 4: Using Experimental Methods
A fourth method of calculating density is by using experimental methods, such as measuring the mass and volume of a substance directly. This method is often used in laboratory settings, where the density of a substance needs to be measured accurately. For example, a hydrometer can be used to measure the density of a liquid, while a pycnometer can be used to measure the density of a solid.
Method 5: Using a Densitometer
A fifth method of calculating density is by using a densitometer, which is a device that measures the density of a substance directly. Densitometers use various methods, such as ultrasound or radiation, to measure the density of a substance. For example, a densitometer can be used to measure the density of a liquid or a solid, and it can provide accurate results with minimal sample preparation.
In conclusion, calculating density is a crucial concept in physics and engineering, and there are various methods to calculate density, including using formulas, equations, and experimental methods. Understanding these methods and their applications is essential for solving problems and making accurate calculations in various fields.
What is the formula for calculating density?
+The formula for calculating density is ρ = m/V, where ρ is the density, m is the mass, and V is the volume.
How does temperature affect the density of a substance?
+Temperature can affect the density of a substance by causing it to expand or contract. The equation ρ = ρ0 * (1 + β * ΔT) can be used to calculate the new density of a substance after a change in temperature.
What is the difference between a hydrometer and a pycnometer?
+A hydrometer is used to measure the density of a liquid, while a pycnometer is used to measure the density of a solid.