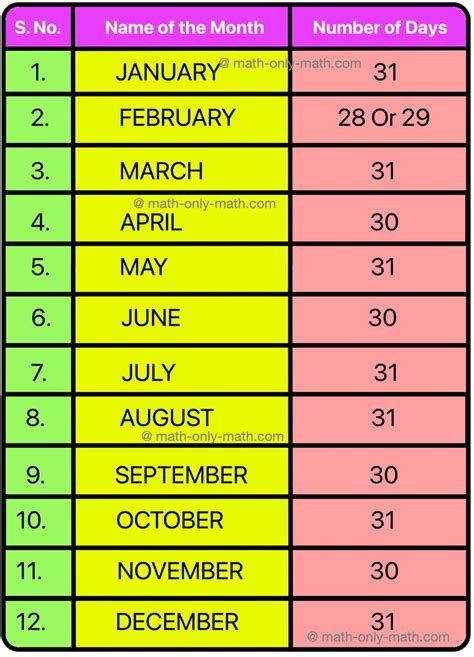
The assertion that 10 months have 305 days is a statement that requires examination and clarification. To address this, we must consider the standard Gregorian calendar, which is the most widely used civil calendar in the world. This calendar organizes the year into 12 months, with each month having either 28, 29, 30, or 31 days. The months with 31 days are January, March, May, July, August, October, and December. The months with 30 days are April, June, September, and November. February has 28 days in non-leap years and 29 days in leap years.
Calculating the total number of days in 10 months involves adding the days of each month. For simplicity, let's consider a non-leap year and calculate the total days from January to October, as these months include a mix of 31, 30, and the possibility of a 28 or 29-day February. January (31 days) + February (28 days, for a non-leap year) + March (31 days) + April (30 days) + May (31 days) + June (30 days) + July (31 days) + August (31 days) + September (30 days) + October (31 days) gives us a total of 31 + 28 + 31 + 30 + 31 + 30 + 31 + 31 + 30 + 31 = 304 days.
Understanding the Calendar System
The calendar system is designed to keep our months and years in sync with the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. A standard year has 365 days, and to account for the extra fraction of a day, an extra day is added to February every four years, making it a 29-day month in leap years. This adjustment ensures that our calendar stays aligned with the seasons and the astronomical year.
Leap Years and Their Impact
In a leap year, the total number of days in 10 months would be slightly different due to February having 29 days instead of 28. Thus, for a leap year, the calculation from January to October would be: January (31 days) + February (29 days) + March (31 days) + April (30 days) + May (31 days) + June (30 days) + July (31 days) + August (31 days) + September (30 days) + October (31 days), totaling 31 + 29 + 31 + 30 + 31 + 30 + 31 + 31 + 30 + 31 = 305 days.
| Month | Number of Days (Non-Leap Year) | Number of Days (Leap Year) |
|---|---|---|
| January | 31 | 31 |
| February | 28 | 29 |
| March | 31 | 31 |
| April | 30 | 30 |
| May | 31 | 31 |
| June | 30 | 30 |
| July | 31 | 31 |
| August | 31 | 31 |
| September | 30 | 30 |
| October | 31 | 31 |
| Total for 10 Months | 304 | 305 |
Key Points
- The total number of days in 10 months can vary between 304 and 305 days, depending on whether the period includes a leap year February.
- Understanding the difference between leap and non-leap years is essential for accurate date and time calculations.
- The Gregorian calendar's structure, with its mix of 28, 29, 30, and 31-day months, is designed to keep our civil calendar in sync with the Earth's orbit around the Sun.
- Leap years occur every four years and add an extra day to February, ensuring the calendar stays aligned with astronomical observations.
- Accurate calculation of days in any period requires consideration of the calendar's nuances, including the variable length of February.
In conclusion, the assertion that 10 months have 305 days can be true, specifically in a leap year when the extra day in February is included. This highlights the importance of considering the specific years and months involved in any calculation to ensure accuracy. Whether for personal, professional, or academic purposes, understanding the intricacies of our calendar system can help avoid mistakes and ensure better planning and organization.
How do leap years affect the total number of days in a 10-month period?
+Leap years add an extra day to February, changing it from a 28-day month to a 29-day month. This extra day increases the total number of days in a 10-month period from 304 days in non-leap years to 305 days in leap years.
Why is it important to consider the type of year when calculating days in a month period?
+Considering whether a year is a leap year or not is crucial for accuracy in date and time calculations. The difference of one day can significantly impact planning, scheduling, and organization, especially over longer periods.
How does the Gregorian calendar ensure it stays aligned with the Earth’s orbit?
+The Gregorian calendar achieves this through the inclusion of leap years. By adding an extra day to February every four years, the calendar accounts for the Earth taking approximately 365.24 days to orbit the Sun, thereby keeping the calendar in sync with the astronomical year.