The metric system is a widely used method of measurement, and understanding the relationships between its units is essential for everyday applications and scientific calculations. One of the fundamental relationships in the metric system is between meters and kilometers. A kilometer is a unit of length in the metric system, equivalent to one thousand meters. This relationship is crucial for converting between different units of length and for calculating distances, speeds, and other physical quantities.
In the context of geography and transportation, kilometers are often used to express long distances, such as the distance between cities or countries. For instance, the distance from Paris to Berlin is approximately 877 kilometers. On the other hand, meters are typically used for shorter distances, such as the length of a room or the distance between two objects. To give a better understanding, a standard football field is about 100 meters long, which is one-tenth of a kilometer.
Key Points
- 1 kilometer is equal to 1,000 meters, providing a basis for converting between these units of length.
- Kilometers are used for long distances, such as geographical distances between cities or countries.
- Meters are used for shorter distances, such as the length of a room or the distance between two objects.
- Understanding the relationship between meters and kilometers is essential for various applications, including geography, transportation, and physics.
- Conversions between meters and kilometers are straightforward, with 1 kilometer being equal to 1,000 meters and 1 meter being equal to 0.001 kilometers.
Understanding the Metric System
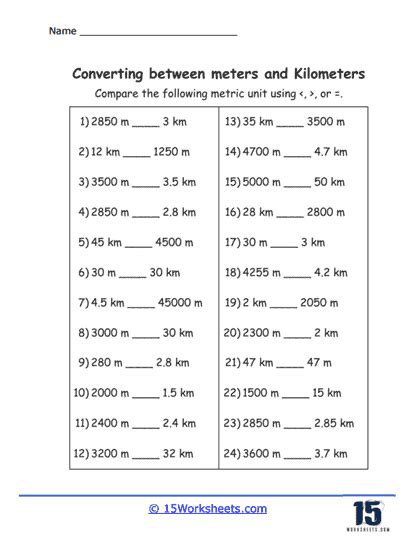
The metric system is based on the International System of Units (SI), which provides a coherent and logical framework for measurement. The system includes units for length, mass, time, temperature, and other physical quantities. The meter is the base unit of length in the metric system, and all other units of length are derived from it. The kilometer, being equal to 1,000 meters, is a larger unit of length that is commonly used for expressing long distances.
Conversions and Applications
Converting between meters and kilometers is straightforward. To convert kilometers to meters, multiply the number of kilometers by 1,000. For example, 5 kilometers is equal to 5,000 meters. To convert meters to kilometers, divide the number of meters by 1,000. For instance, 2,500 meters is equal to 2.5 kilometers. These conversions are essential in various fields, including geography, physics, engineering, and everyday applications like measuring the distance of a marathon or the height of a mountain.
| Unit of Length | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|
| 1 kilometer | 1,000 meters |
| 1 meter | 0.001 kilometers |

Practical Applications and Implications
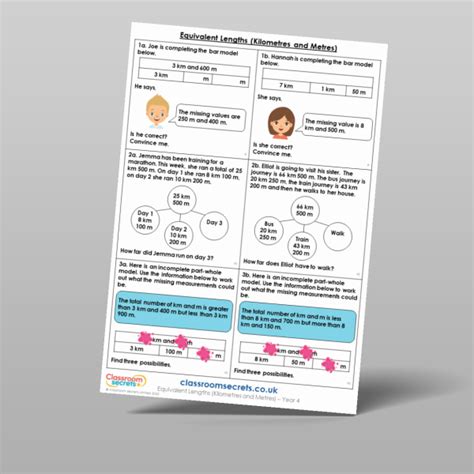
The distinction between meters and kilometers has significant implications in practical applications. In sports, for example, athletes may compete in events that are measured in meters (like the 100-meter dash) or kilometers (like the 5-kilometer run). In construction, architects and engineers must accurately measure and convert between these units to design and build structures that meet specific dimensions and spatial requirements.
In conclusion, the relationship between meters and kilometers is a fundamental aspect of the metric system, with 1 kilometer being equal to 1,000 meters. This relationship is crucial for a wide range of applications, from geography and transportation to physics and engineering. Understanding and being able to convert between these units is essential for accurately measuring distances, calculating speeds, and solving problems in various fields.
How many meters are in a kilometer?
+There are 1,000 meters in a kilometer.
What is the metric system based on?
+The metric system is based on the International System of Units (SI), which provides a coherent and logical framework for measurement.
Why is understanding the relationship between meters and kilometers important?
+Understanding the relationship between meters and kilometers is important for converting between units of length, calculating distances and speeds, and solving problems in various fields such as geography, physics, and engineering.