Introduction to Calculating Variance
Calculating variance is a fundamental concept in statistics and data analysis, as it measures the dispersion or spread of a set of data points from their mean value. Understanding variance is crucial for assessing the risk or volatility of a dataset, whether in finance, social sciences, or any field involving data analysis. There are several methods to calculate variance, each suited to different types of data and analysis needs. In this article, we will explore five ways to calculate variance, providing a comprehensive understanding of the concept and its applications.
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of variance and its importance in data analysis
- Calculating variance for a population and a sample
- Using different formulas for variance calculation based on the data type and analysis requirements
- Applying variance in real-world scenarios, such as finance and quality control
- Interpreting variance results to make informed decisions
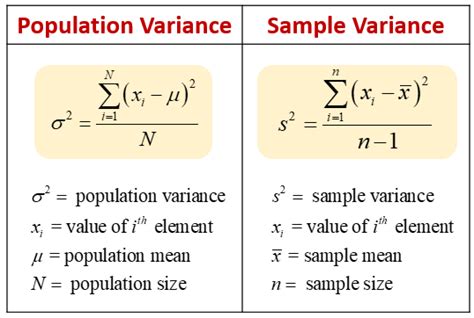
Population Variance Calculation
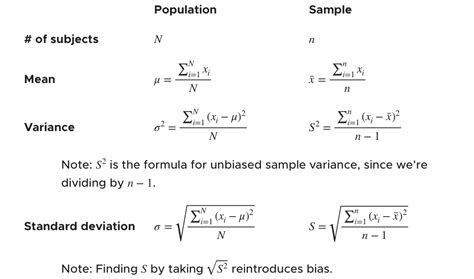
The population variance is calculated when the entire population’s data is available. It is denoted by the symbol σ² (sigma squared) and is calculated using the formula: [ \sigma^2 = \frac{\sum_{i=1}^{N} (x_i - \mu)^2}{N} ] where (x_i) represents each individual data point, (\mu) is the population mean, and (N) is the total number of data points in the population.
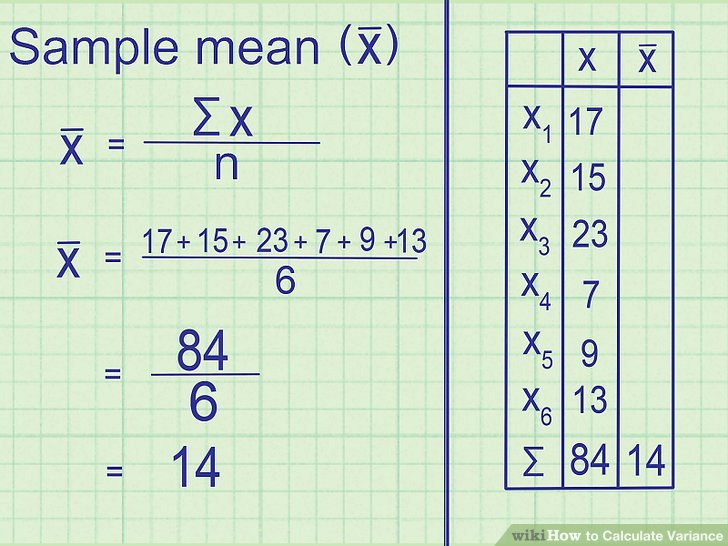
Sample Variance Calculation
When dealing with a sample of the population, the sample variance is used. It is denoted by (s^2) and is calculated using the formula: [ s^2 = \frac{\sum_{i=1}^{n} (x_i - \bar{x})^2}{n-1} ] where (x_i) represents each data point in the sample, (\bar{x}) is the sample mean, and (n) is the number of data points in the sample. The division by (n-1) instead of (n) is known as Bessel’s correction, which helps to make the sample variance a more unbiased estimator of the population variance.
Variance Calculation Using Standard Deviation
The standard deviation (σ or s) is the square root of the variance. If the standard deviation is known, the variance can be easily calculated by squaring the standard deviation: [ \sigma^2 = \sigma \times \sigma ] or [ s^2 = s \times s ] This method is straightforward and is often used when the standard deviation is already calculated or given.
Variance Calculation for Discrete Random Variables

For discrete random variables, the variance can be calculated using the formula: [ \sigma^2 = \sum_{i=1}^{n} p_i (x_i - \mu)^2 ] where (p_i) is the probability of each outcome (x_i), and (\mu) is the expected value (mean) of the random variable. This formula is particularly useful in probability theory and statistics when dealing with discrete distributions.
Variance Calculation Using Online Calculators or Software
In today’s digital age, calculating variance can be simplified using online calculators or statistical software like Excel, Python libraries (e.g., NumPy, pandas), or R. These tools can calculate variance with just a few clicks or lines of code, making data analysis more efficient. For instance, in Excel, the VAR.P function calculates the population variance, and the VAR.S function calculates the sample variance.
Practical Applications of Variance
Understanding and calculating variance has numerous practical applications. In finance, variance is used to measure the volatility of stocks or portfolios, helping investors assess risk. In quality control, variance is used to monitor the consistency of manufacturing processes. By analyzing variance, businesses can make informed decisions, manage risk, and improve processes.
Conclusion
Calculating variance is a fundamental skill in data analysis, offering insights into the spread of data. By mastering the different methods of variance calculation, individuals can better understand their data, assess risks, and make informed decisions. Whether using traditional formulas or leveraging modern statistical software, calculating variance is an essential tool in the toolkit of any data analyst or researcher.
What is the primary difference between population and sample variance?
+The primary difference lies in the divisor used in the formula: the population variance divides by N (the total number of data points), while the sample variance divides by n-1 (the number of data points in the sample minus one), applying Bessel’s correction for unbiased estimation.
How does variance relate to standard deviation?
+Variance is the square of the standard deviation. Thus, if the standard deviation is known, the variance can be found by squaring it, and vice versa.
What are some practical applications of variance in real-world scenarios?
+Variance is used in finance to measure the volatility of investments, in quality control to monitor manufacturing process consistency, and in various fields of research to understand data dispersion and make informed decisions.