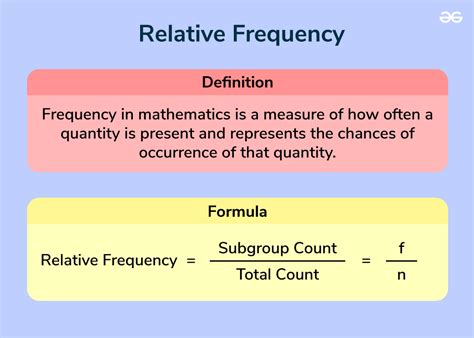
To calculate relative frequency easily, it's essential to understand the concept and its application in data analysis. Relative frequency is a statistical measure that describes the proportion of times a particular value or category occurs within a dataset. It's calculated by dividing the frequency of each value or category by the total number of observations in the dataset. This measure is crucial for understanding the distribution of data and making informed decisions based on it.
Understanding Relative Frequency
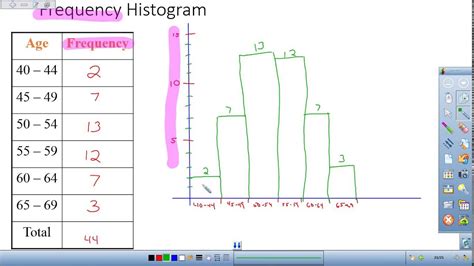
Relative frequency is often expressed as a percentage or a proportion. For instance, if a survey of 100 people shows that 20 of them prefer a certain brand of coffee, the relative frequency of this preference would be 20% or 0.20. This means that 20 out of every 100 people in the sample prefer that particular brand. The calculation is straightforward: (Frequency of the category / Total number of observations) * 100 for percentage, or simply the frequency divided by the total for proportion.
Steps to Calculate Relative Frequency
The steps to calculate relative frequency are simple and systematic:
- Identify the categories or values within your dataset for which you want to calculate the relative frequency.
- Count the frequency of each category or value. This means determining how many times each category or value appears in your dataset.
- Determine the total number of observations in your dataset. This is the total count of all data points.
- Calculate the relative frequency for each category by dividing its frequency by the total number of observations and then multiplying by 100 if you want the result as a percentage.
| Category | Frequency | Relative Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Category A | 20 | 20% |
| Category B | 30 | 30% |
| Category C | 50 | 50% |
| Total | 100 | 100% |
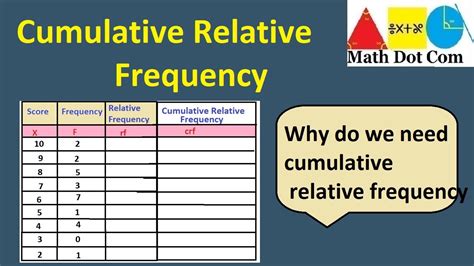
Practical Applications of Relative Frequency
Relative frequency has numerous practical applications across various fields, including business, healthcare, and social sciences. In business, for example, understanding the relative frequency of customer preferences can help companies tailor their products and marketing strategies to meet the needs of their target audience. Similarly, in healthcare, analyzing the relative frequency of different symptoms or diseases can aid in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Tools and Methods for Calculating Relative Frequency
There are several tools and methods available for calculating relative frequency, ranging from simple manual calculations to sophisticated statistical software. Spreadsheets like Microsoft Excel are particularly useful for calculating and visualizing relative frequencies due to their ability to handle large datasets and perform complex calculations quickly.
Key Points
- Relative frequency is a measure of the proportion of times a value or category occurs in a dataset.
- It's calculated by dividing the frequency of each category by the total number of observations and then multiplying by 100 for percentage.
- Understanding relative frequency is crucial for data analysis and decision-making in various fields.
- Tools like spreadsheets can simplify the calculation and visualization of relative frequencies.
- Relative frequency distributions can reveal trends and patterns within datasets.
By understanding and applying the concept of relative frequency, individuals can gain deeper insights into their data, make more informed decisions, and drive meaningful outcomes in their respective fields. Whether it's market research, medical studies, or social surveys, the ability to calculate and interpret relative frequencies is a fundamental skill in data analysis.
What is relative frequency, and why is it important in data analysis?
+Relative frequency refers to the proportion of times a particular value or category occurs within a dataset. It’s important because it helps in understanding the distribution of data, identifying trends, and making informed decisions based on data analysis.
How do you calculate relative frequency?
+To calculate relative frequency, divide the frequency of each category by the total number of observations and then multiply by 100 to express it as a percentage.
What tools can be used to calculate relative frequency?
+Spreadsheets like Microsoft Excel are commonly used for calculating relative frequencies due to their ability to handle large datasets and perform calculations efficiently.