To find the cumulative frequency of a dataset, it's essential to understand the concept of frequency distribution and how it relates to data analysis. The cumulative frequency, also known as the cumulative relative frequency, is a statistical measure that represents the running total of frequencies for a dataset. This concept is crucial in various fields, including economics, sociology, and engineering, as it helps researchers and analysts understand the distribution of data and make informed decisions.
Understanding Frequency Distribution
Frequency distribution refers to the way data is spread out or dispersed. It can be represented in various forms, including tables, graphs, and charts. The frequency distribution is a fundamental concept in statistics, and it provides a clear understanding of the data’s characteristics, such as central tendency, variability, and skewness. By analyzing the frequency distribution, researchers can identify patterns, trends, and correlations within the data.
Types of Frequency Distribution
There are several types of frequency distributions, including:
- Univariate frequency distribution: This type of distribution involves a single variable, and it provides information about the frequency of each value or category.
- Bivariate frequency distribution: This type of distribution involves two variables, and it provides information about the relationship between the variables.
- Multivariate frequency distribution: This type of distribution involves multiple variables, and it provides information about the relationships between the variables.
| Type of Distribution | Description |
|---|---|
| Univariate | Single variable distribution |
| Bivariate | Two-variable distribution |
| Multivariate | Multiple-variable distribution |
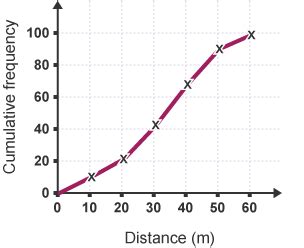
Calculating Cumulative Frequency
To calculate the cumulative frequency, follow these steps:
- Arrange the data in ascending or descending order, depending on the type of distribution.
- Count the frequency of each value or category.
- Calculate the cumulative frequency by adding the frequency of each value or category to the previous cumulative frequency.
| Value | Frequency | Cumulative Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 5 | 5 |
| 20 | 8 | 13 |
| 30 | 12 | 25 |
Interpreting Cumulative Frequency
The cumulative frequency provides valuable information about the data distribution. By analyzing the cumulative frequency, researchers can:
- Identify the proportion of data that falls below a certain value or category.
- Determine the median, quartiles, and percentiles of the data.
- Visualize the data distribution using cumulative frequency plots or ogives.
Key Points
- Cumulative frequency represents the running total of frequencies for a dataset.
- Frequency distribution provides information about the characteristics of the data, such as central tendency and variability.
- Cumulative frequency can be used to identify patterns, trends, and correlations within the data.
- The level of measurement is crucial when analyzing frequency distributions.
- Cumulative frequency plots or ogives can be used to visualize the data distribution.
Applications of Cumulative Frequency
Cumulative frequency has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Economics: Cumulative frequency is used to analyze income distribution, poverty rates, and economic inequality.
- Sociology: Cumulative frequency is used to study social mobility, education, and healthcare outcomes.
- Engineering: Cumulative frequency is used to analyze failure rates, reliability, and quality control.
Cumulative frequency is a powerful tool for data analysis, providing insights into the distribution of data and helping researchers make informed decisions. By understanding the concept of cumulative frequency and its applications, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of their data and make more accurate predictions and recommendations.
What is the difference between frequency and cumulative frequency?
+Frequency refers to the number of times a value or category occurs in a dataset, while cumulative frequency represents the running total of frequencies.
How do I calculate cumulative frequency?
+To calculate cumulative frequency, arrange the data in ascending or descending order, count the frequency of each value or category, and then add the frequency of each value or category to the previous cumulative frequency.
What are the applications of cumulative frequency?
+Cumulative frequency has numerous applications in various fields, including economics, sociology, and engineering, where it is used to analyze data distribution, identify patterns, and make informed decisions.
Meta Description: Learn how to find cumulative frequency easily and understand its importance in data analysis, including its applications in various fields and how to calculate it. (149 characters)