Understanding elasticity is crucial in various fields, including economics, physics, and engineering. Elasticity refers to the measure of how much the quantity of a product or service changes in response to changes in price, income, or other factors. In physics and engineering, elasticity describes the ability of a material to return to its original shape after being stretched or compressed. Finding elasticity is essential for businesses, policymakers, and engineers to make informed decisions. Here are five ways to find elasticity, focusing on economic and physical perspectives.
Key Points
- Using the elasticity formula to calculate price elasticity of demand
- Conducting surveys and collecting data to estimate income elasticity
- Applying the concept of cross-price elasticity to understand substitute and complementary goods
- Measuring the elasticity of a material through stress-strain tests in physics and engineering
- Utilizing econometric models and statistical analysis to find elasticity in complex systems
Understanding Elasticity in Economics
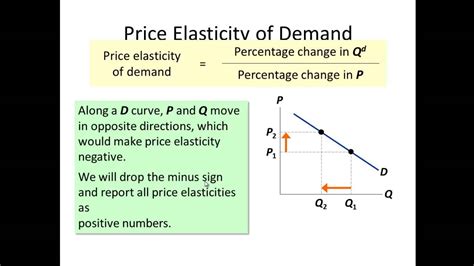
In economics, elasticity is a fundamental concept that helps understand how changes in one variable affect another. The most common type of elasticity in economics is the price elasticity of demand, which measures how responsive the quantity demanded of a product is to changes in its price. The formula for calculating price elasticity of demand is: Ed = (ΔQd / Qd) / (ΔP / P), where Ed is the price elasticity of demand, ΔQd is the change in quantity demanded, Qd is the original quantity demanded, ΔP is the change in price, and P is the original price.
Calculating Price Elasticity of Demand
A company like Apple, for instance, might want to know how a price increase in their iPhones would affect sales. By applying the elasticity formula and using historical sales data, Apple can estimate the price elasticity of demand for their iPhones. For example, if a 10% increase in price leads to a 15% decrease in sales, the price elasticity of demand would be 1.5, indicating that the demand is elastic. This means that a small price increase would lead to a proportionally larger decrease in quantity demanded, making the product highly sensitive to price changes.
Physical Elasticity: Material Science Perspective

In the context of material science, elasticity refers to the ability of a material to deform under stress and return to its original shape once the stress is removed. The elasticity of a material is typically measured through stress-strain tests, which involve applying a controlled amount of stress to the material and measuring the resulting strain. The elasticity of a material can be expressed in terms of its Young’s modulus, which is a measure of the material’s stiffness and resistance to deformation.
Measuring Elasticity through Stress-Strain Tests
Engineers and material scientists use stress-strain tests to determine the elasticity of various materials, such as metals, polymers, and composites. By analyzing the stress-strain curve, they can identify the material’s elastic limit, beyond which the material begins to deform plastically. For instance, the elasticity of steel is much higher than that of rubber, which means that steel can withstand much greater stresses without deforming permanently. Understanding the elasticity of materials is crucial for designing and building structures, machines, and devices that can withstand various types of loading and stress.
Econometric Models for Elasticity
In addition to the elasticity formula and stress-strain tests, econometric models can be used to estimate elasticity in complex systems. These models involve statistical analysis of historical data and can account for multiple variables and interactions. For example, a researcher might use a regression model to estimate the income elasticity of demand for a particular product, controlling for other factors such as price, advertising, and seasonality. By using econometric models, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the relationships between variables and make more accurate predictions about how changes in one variable will affect others.
Utilizing Statistical Analysis for Elasticity Estimation
Statistical analysis is a powerful tool for estimating elasticity in economics and other fields. By using techniques such as regression analysis, time series analysis, and panel data analysis, researchers can identify patterns and relationships in the data that might not be apparent through other methods. For instance, a study on the elasticity of demand for electricity might use a regression model to estimate the relationship between electricity consumption and factors such as income, price, and temperature. By controlling for other variables and accounting for potential biases, the researcher can obtain a more accurate estimate of the elasticity of demand and make informed recommendations for policymakers and industry stakeholders.
| Type of Elasticity | Formula or Method |
|---|---|
| Price Elasticity of Demand | Ed = (ΔQd / Qd) / (ΔP / P) |
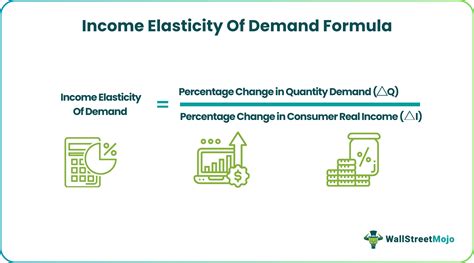
| Income Elasticity | Ey = (ΔQd / Qd) / (ΔI / I) |
| Cross-Price Elasticity | Exy = (ΔQx / Qx) / (ΔPy / Py) |
| Physical Elasticity (Young's Modulus) | E = σ / ε |

What is the difference between elastic and inelastic demand?
+Elastic demand refers to a situation where a small change in price leads to a proportionally larger change in quantity demanded. Inelastic demand, on the other hand, refers to a situation where a small change in price leads to a proportionally smaller change in quantity demanded.
How do engineers measure the elasticity of a material?
+Engineers measure the elasticity of a material through stress-strain tests, which involve applying a controlled amount of stress to the material and measuring the resulting strain. The elasticity of the material can be expressed in terms of its Young's modulus, which is a measure of the material's stiffness and resistance to deformation.
What is the significance of elasticity in economics?
+Elasticity is significant in economics because it helps businesses and policymakers understand how changes in price, income, and other factors affect the quantity demanded of a product or service. By estimating elasticity, firms can make informed decisions about pricing, production, and investment, while policymakers can design effective policies to promote economic growth and stability.
In conclusion, finding elasticity is a critical task in various fields, including economics, physics, and engineering. By using the right methods and tools, professionals can estimate elasticity and make informed decisions about how changes in one variable will affect others. Whether it’s understanding the price elasticity of demand, measuring the elasticity of a material, or estimating the income elasticity of demand, elasticity is a fundamental concept that has significant implications for businesses, policymakers, and engineers.