Calculating the average rate is a fundamental concept in mathematics and statistics, widely used in various fields such as finance, economics, and science. The average rate, often confused with the average speed, is a measure that can provide insights into the overall performance or change of a quantity over a specified period. In this article, we will explore five distinct methods to find the average rate, each with its unique application and importance.
Key Points
- Understanding the difference between average rate and average speed
- Calculating average rate using the formula: Average Rate = Total Change / Total Time
- Applying the concept of average rate in real-world scenarios
- Using graphical methods to determine average rates
- Considering the harmonic mean for rates
Method 1: Using the Formula for Average Rate

The most straightforward method to find the average rate involves using the formula: Average Rate = Total Change / Total Time. This formula applies to various scenarios, including calculating the average rate of return on an investment, the average rate of change of a function in calculus, or the average rate of a chemical reaction in chemistry. For instance, if an investment grows from 100 to 120 over a period of 2 years, the average rate of return can be calculated as (120 - 100) / 2 = $10 per year.
Example Calculation
Consider a car traveling from City A to City B. The total distance covered is 200 miles, and the total time taken is 4 hours. Using the formula, the average rate (or speed, in this context) can be calculated as 200 miles / 4 hours = 50 miles per hour.
| Distance | Time | Average Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 200 miles | 4 hours | 50 miles/hour |

Method 2: Graphical Method
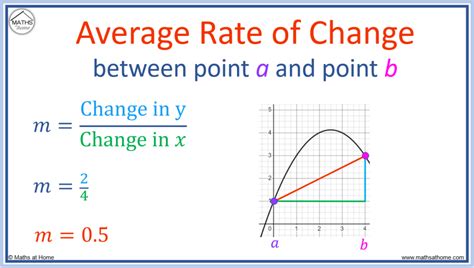
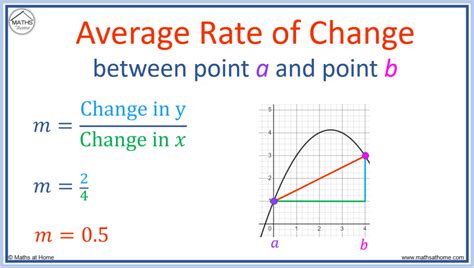
A graphical method can be employed to find the average rate, particularly when dealing with functions or data that vary over time. By plotting the function or data points on a graph, the average rate over a specified interval can be visually estimated or calculated using the slope of a line that best fits the data points within that interval. This method is especially useful in physics and engineering to determine the average rate of change of quantities like velocity or acceleration.
Graphical Representation
Imagine a position-time graph of an object’s motion. The slope of the line connecting the initial and final points on the graph represents the average velocity (or rate of change of position) of the object over the given time interval. This method provides a visual and intuitive way to understand and calculate average rates.
Method 3: Using the Harmonic Mean
For rates that vary significantly over time, such as speeds at different parts of a journey, the harmonic mean provides a more accurate representation of the average rate than the arithmetic mean. The harmonic mean is calculated as the reciprocal of the arithmetic mean of the reciprocals of the rates. This method is particularly relevant in scenarios where the average speed or rate needs to account for varying conditions, such as in transportation or when analyzing the performance of systems.
Harmonic Mean Calculation
Suppose a car travels at 60 mph for 2 hours and then at 30 mph for 1 hour. The average speed using the arithmetic mean would be (60 + 30) / 2 = 45 mph, which does not account for the time spent at each speed. The harmonic mean, however, provides a more realistic average speed: 2 / ((1⁄60) + (1⁄30)) = 40 mph.
| Speed | Time |
|---|---|
| 60 mph | 2 hours |
| 30 mph | 1 hour |
Method 4: Average Rate of Change in Calculus
In calculus, the average rate of change of a function over a given interval [a, b] can be found using the formula: Average Rate of Change = [f(b) - f(a)] / (b - a), where f(x) is the function in question. This concept is crucial in understanding how functions behave over specific intervals and has applications in optimization problems, economics, and physics.
Calculus Example
Given a function f(x) = x^2, to find the average rate of change from x = 1 to x = 3, we calculate [f(3) - f(1)] / (3 - 1) = (9 - 1) / 2 = 4. This means the function’s output increases at an average rate of 4 units per unit increase in x over the interval from 1 to 3.
Method 5: Real-World Applications and Adjustments
In real-world scenarios, calculating the average rate often requires adjustments for the specific context. For instance, in finance, the average rate of return on an investment might need to account for compounding interest or inflation. In science, the average rate of a chemical reaction might depend on factors like temperature, concentration of reactants, and catalysts. Understanding these factors and how they influence the average rate is crucial for accurate calculations and meaningful interpretations.
What is the difference between average rate and average speed?
+Average rate and average speed are often used interchangeably but can have different meanings. Average speed typically refers to the total distance traveled divided by the total time, while average rate can refer to the rate of change of any quantity over time.
How do I calculate the average rate of return on an investment?
+The average rate of return on an investment can be calculated using the formula: Average Rate = (Final Value - Initial Value) / Time. This formula provides a simple way to understand the investment's performance over time.
What is the harmonic mean, and when is it used?
+The harmonic mean is a type of average that is calculated as the reciprocal of the arithmetic mean of the reciprocals of the values. It is particularly useful when dealing with rates or speeds that vary significantly over time, providing a more accurate representation of the average rate than the arithmetic mean.
In conclusion, finding the average rate involves a variety of methods, each suited to different contexts and types of data. Whether using the basic formula, graphical methods, the harmonic mean, calculus, or considering real-world applications, understanding the average rate is fundamental to analyzing and interpreting changes over time in numerous fields. By selecting the appropriate method and considering the nuances of the data, individuals can gain valuable insights into the performance, efficiency, or behavior of systems, processes, or investments.