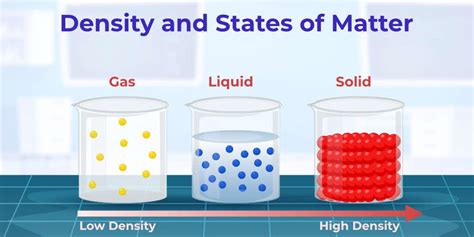
Understanding density, whether in the context of physics, engineering, or even data storage, is crucial for a variety of applications and studies. Density, defined as mass per unit volume of a substance, is a fundamental property that can significantly affect the behavior and characteristics of materials. In this article, we will delve into five distinct methods or approaches to achieving or understanding density, spanning from theoretical calculations to experimental measurements and practical applications.
Naturally Worded Primary Topic Section with Semantic Relevance
The pursuit of understanding and manipulating density is a multifaceted endeavor that involves both theoretical foundations and practical experimentation. In physics and engineering, density is a critical parameter that influences the design and functionality of structures, devices, and systems. For instance, in aerospace engineering, achieving high strength-to-weight ratios (which often involves managing density) is essential for the efficiency and safety of aircraft and spacecraft. Similarly, in materials science, the density of a material can affect its electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties, making it a key consideration in the development of new materials for various applications.
Specific Subtopic with Natural Language Phrasing
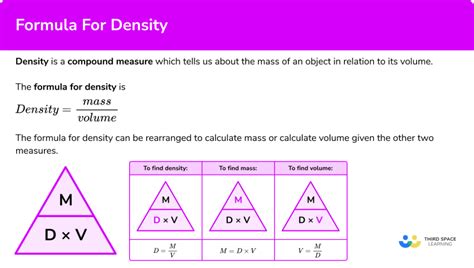
One of the primary ways to get density is through theoretical calculations. These calculations involve using the known mass and volume of a substance to determine its density. The formula for density, ρ = m/V, where ρ is density, m is mass, and V is volume, provides a straightforward method for calculating density when the mass and volume are known. This approach is particularly useful in educational settings and in initial stages of material design, where understanding the theoretical density of a material can guide further experimental work and application development.
| Method | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Theoretical Calculation | Using the formula ρ = m/V | Material design, educational purposes |
| Experimental Measurement | Measuring mass and volume directly | Lab settings, quality control |
| Density Gradient Column | Comparing densities of substances | Lab demonstrations, material comparison |
| Hydrometer | Measuring density of liquids | Industrial quality control, research |
| Archimedes' Principle | Determining density by displacement | Research, educational experiments |
Practical Applications of Density
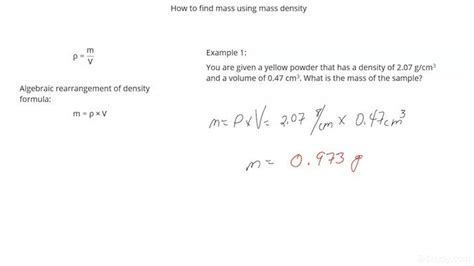
Beyond theoretical calculations, there are several practical methods for determining or achieving specific densities. Experimental measurement involves directly measuring the mass and volume of a sample to calculate its density. This approach is widely used in laboratory settings and in quality control processes in industries where the density of materials is a critical parameter. Another method is using a density gradient column, which allows for the comparison of densities of different substances by observing how they settle in a column of varying density. This method is particularly useful for demonstrations and comparative studies.
Specific Tools for Measuring Density
For liquids, a hydrometer is a common tool used to measure density. By floating a hydrometer in the liquid, one can read the density directly from the scale on the hydrometer. This method is rapid and accurate, making it suitable for industrial quality control and research applications. Another classic method for determining density is Archimedes’ Principle, which states that the buoyancy force on an object immersed in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. By measuring the weight of an object in air and then in a fluid of known density, one can calculate the density of the object.
Key Points
- Theoretical calculations provide a foundational understanding of density through the formula ρ = m/V.
- Experimental measurements offer a direct method for determining density in lab and industrial settings.
- Density gradient columns, hydrometers, and Archimedes' Principle are specific tools and methods for comparing and measuring densities.
- Understanding density is crucial for material design, quality control, and optimizing performance in various applications.
- Interpreting density in the context of a material's application involves considering its impact on other material properties.
In conclusion, achieving or understanding density involves a range of approaches, from theoretical calculations to experimental measurements and the use of specific tools like hydrometers and density gradient columns. Each method has its applications and advantages, and the choice of method depends on the specific context and requirements of the study or application. By mastering these methods and understanding the significance of density, researchers and engineers can develop materials and systems with optimized properties for a wide range of industries and applications.
What is the formula for calculating density?
+The formula for density is ρ = m/V, where ρ is density, m is mass, and V is volume.
How is density measured in liquids?
+Density in liquids is commonly measured using a hydrometer, which floats in the liquid and provides a direct reading of density.
What is Archimedes’ Principle used for?
+Archimedes’ Principle is used to determine the density of an object by measuring the weight of the fluid displaced when the object is immersed in it.