The "I before E" spelling rule is a widely recognized guideline in the English language, aiming to help individuals determine the correct order of the letters "I" and "E" in words. This rule has been taught in schools and used by language learners for decades, but its application and exceptions can be complex. In this article, we will delve into the history, explanation, and usage of the "I before E" rule, as well as explore its limitations and exceptions.
Understanding the “I before E” Rule
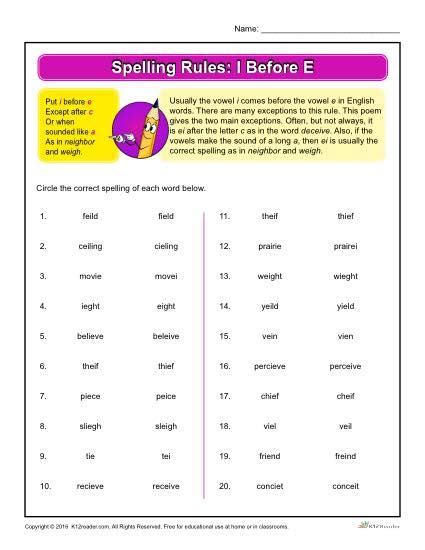
The traditional “I before E” rule states that when the letters “I” and “E” appear together in a word, “I” usually comes before “E” unless the letters are sounded as a single “e” sound, in which case “E” comes before “I”. However, this rule is not absolute and has numerous exceptions. To apply the rule effectively, it’s essential to understand the phonetic and linguistic context of the words in question.
Key Points
- The "I before E" rule is a general guideline rather than a strict rule.
- The rule applies to words where "I" and "E" are sounded separately.
- Exceptions to the rule often involve words with a single "e" sound or words with silent letters.
- Understanding the etymology and phonetics of words can help in applying the rule correctly.
- Practice and familiarity with English vocabulary are crucial for mastering the "I before E" rule.
Origins and Evolution of the Rule
The “I before E” rule has its roots in the Middle English period, where the letters “I” and “E” were often used interchangeably. Over time, as the English language evolved, the rule became more standardized. However, the rule’s limitations and exceptions were already apparent, even in its early formulations. Despite these challenges, the “I before E” rule has remained a fundamental part of English language instruction.
One of the primary reasons for the rule's persistence is its simplicity and apparent logic. By providing a straightforward guideline for the ordering of "I" and "E", the rule offers a sense of structure and predictability in the otherwise complex English spelling system. Nevertheless, this simplicity comes at the cost of oversimplification, as the rule fails to account for the numerous exceptions and complexities that arise in actual language use.
Exceptions and Limitations

Despite its widespread recognition, the “I before E” rule is plagued by exceptions and limitations. Words like “science”, “neither”, and “seize” defy the rule, with “E” appearing before “I” despite the letters being sounded separately. Furthermore, words with a single “e” sound, such as “vein” or “reign”, often have “E” before “I”, contradicting the rule.
| Word | Exception Type |
|---|---|
| Science | E before I with separate sounds |
| Neither | E before I with separate sounds |
| Vein | Single "e" sound with E before I |
| Reign | Single "e" sound with E before I |

Practical Applications and Tips
So, how can learners and language users navigate the complexities of the “I before E” rule? One approach is to focus on the phonetic and linguistic context of the words in question. By listening to the sounds and pronunciations of words, individuals can develop a more intuitive sense of the correct ordering of “I” and “E”. Additionally, familiarity with English vocabulary and practice in spelling words can help to reinforce the rule and its exceptions.
Another strategy is to learn the exceptions to the rule, rather than relying solely on the rule itself. By recognizing common exception patterns, such as words with a single "e" sound or words with silent letters, learners can improve their spelling accuracy and develop a more nuanced understanding of the English language.
What is the primary exception to the "I before E" rule?
+The primary exception to the rule involves words with a single "e" sound, where "E" often appears before "I" despite the letters being sounded separately.
How can I improve my spelling accuracy with the "I before E" rule?
+Improving spelling accuracy with the "I before E" rule requires a combination of practice, familiarity with English vocabulary, and a nuanced understanding of the rule's limitations and exceptions. Focus on learning the exceptions, recognizing common patterns, and developing a phonetic and linguistic awareness of the words in question.
In conclusion, the “I before E” rule is a complex and multifaceted guideline that requires a nuanced understanding of its limitations and exceptions. By recognizing the rule’s shortcomings and developing a more informed approach to spelling words with “I” and “E”, learners and language users can improve their accuracy and mastery of the English language. As with any aspect of language learning, practice, patience, and persistence are essential for achieving proficiency and confidence in spelling words with the “I before E” pattern.