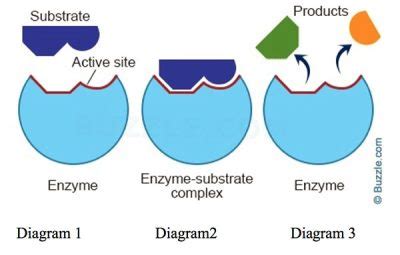
The addition of enzymes to chemical reactions has been a long-standing practice in various fields, including biochemistry, pharmaceuticals, and food production. Enzymes, biological molecules typically proteins, act as catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. The concept of enzyme addition to boost reaction rates is rooted in the understanding of enzyme kinetics and the role of enzymes in facilitating chemical transformations. For instance, in the production of biofuels, enzymes such as cellulases are used to break down cellulose into fermentable sugars, significantly increasing the efficiency of the process. By grasping the fundamental principles of enzyme action and their application in different contexts, it becomes clear why enzyme addition is a crucial strategy for enhancing reaction rates and efficiency.
Key Points
- Enzymes act as biological catalysts, accelerating chemical reactions without being consumed.
- The addition of enzymes can significantly boost reaction rates, enhancing efficiency in various industrial processes.
- Understanding enzyme kinetics is crucial for optimizing enzyme performance in different reaction conditions.
- Enzyme specificity and substrate affinity are key factors influencing the effectiveness of enzyme addition in reaction rate enhancement.
- Enzyme immobilization techniques can improve enzyme stability and reusability, further optimizing reaction processes.
Enzyme Kinetics and Reaction Rate Enhancement

The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions is complex, involving several steps including substrate binding, conversion to product, and release of the product. The rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is influenced by several factors, including enzyme concentration, substrate concentration, temperature, and pH. By optimizing these conditions, the reaction rate can be significantly enhanced. For example, increasing the enzyme concentration can boost the reaction rate up to a point where the enzyme becomes saturated with substrate, at which point further increases in enzyme concentration will not result in proportional increases in reaction rate. This understanding is critical for applying enzymes in industrial processes, where maximizing efficiency and minimizing costs are paramount.
Specificity and Affinity in Enzyme-Substrate Interactions
The specificity of an enzyme for its substrate and the affinity between them play crucial roles in determining the effectiveness of enzyme addition in enhancing reaction rates. Enzymes are highly specific, meaning they can only catalyze specific reactions or types of reactions. This specificity is due to the unique shape and chemical properties of the enzyme’s active site, which is complementary to the substrate. The affinity of an enzyme for its substrate, often measured by the Michaelis constant (Km), indicates how tightly the enzyme binds to the substrate. High affinity (low Km) means the enzyme can effectively catalyze the reaction at lower substrate concentrations, which can be advantageous in reactions where substrate availability is limited.
| Enzyme Property | Description | Impact on Reaction Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Specificity | Determines the types of reactions an enzyme can catalyze | Ensures that the enzyme only catalyzes the desired reaction, reducing unwanted side reactions |
| Affinity (Km) | Measures how tightly the enzyme binds to the substrate | Influences the concentration of substrate required for the reaction to proceed at a significant rate |
| Turnover Number (kcat) | Indicates how many substrate molecules an enzyme can convert to product per unit time | Affects the overall rate of the reaction, with higher kcat values corresponding to faster reaction rates |
Applications of Enzyme Addition in Industrial Processes

The addition of enzymes has found widespread application in various industrial sectors, including food production, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and biofuel production. In the food industry, enzymes such as amylases and proteases are used to break down starches and proteins, respectively, improving the texture and nutritional value of food products. In pharmaceutical manufacturing, enzymes are used in the synthesis of complex molecules, offering a more efficient and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional chemical synthesis methods. The use of enzymes in biofuel production, such as the conversion of biomass into fermentable sugars, represents a significant step towards sustainable energy solutions.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the numerous benefits of enzyme addition in boosting reaction rates, there are challenges associated with their use, including enzyme stability, cost, and the potential for enzyme inhibition. Enzyme immobilization techniques, which involve attaching enzymes to solid supports, can improve enzyme stability and reusability, addressing some of these challenges. Furthermore, advances in enzyme engineering and the discovery of new enzymes with improved properties are expected to expand the range of applications for enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The integration of biotechnology and nanotechnology may also provide novel solutions for enhancing enzyme performance and stability.
What is the primary role of enzymes in chemical reactions?
+Enzymes act as catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They lower the activation energy required for the reaction to occur, making it more efficient.
How does enzyme specificity influence the reaction rate?
+Enzyme specificity ensures that the enzyme only catalyzes the desired reaction, reducing unwanted side reactions and improving the overall efficiency of the process.
What are the potential challenges associated with the use of enzymes in industrial processes?
+Challenges include enzyme stability, cost, and the potential for enzyme inhibition. However, techniques such as enzyme immobilization and advances in enzyme engineering are addressing these challenges.
In conclusion, the addition of enzymes to chemical reactions offers a powerful strategy for boosting reaction rates and enhancing efficiency in various industrial processes. By understanding the principles of enzyme kinetics, specificity, and affinity, and addressing the challenges associated with enzyme use, the full potential of enzyme-catalyzed reactions can be realized, contributing to more sustainable and efficient industrial practices.