Mexico, a country known for its rich cultural diversity, is home to a significant population of indigenous people. With over 20 million individuals identifying as indigenous, they make up approximately 20% of the country's total population. The indigenous people of Mexico are comprised of numerous ethnic groups, each with their unique language, customs, and traditions. This article will delve into the history, culture, and current state of the indigenous people of Mexico, highlighting their struggles, achievements, and contributions to the country's rich cultural heritage.
History and Pre-Columbian Era

The history of indigenous people in Mexico dates back to the pre-Columbian era, with evidence of human habitation in the region as far back as 30,000 years ago. The Aztecs, Mayans, and Olmecs are just a few of the many civilizations that flourished in Mexico before the arrival of the Spanish conquistadors in the 16th century. These civilizations made significant contributions to the development of writing, astronomy, mathematics, and architecture, leaving behind a legacy of impressive ruins and artifacts. The Aztecs, in particular, are renowned for their advanced knowledge of astronomy, with their calendar being one of the most accurate in the world at the time.
Colonization and its Impact
The arrival of the Spanish conquistadors had a devastating impact on the indigenous population of Mexico. The conquest led to the loss of land, culture, and lives, as many indigenous people were forced to adopt European customs, language, and religion. The indigenous population was also subjected to forced labor, enslavement, and violence, leading to a significant decline in their numbers. According to historical records, the indigenous population of Mexico declined from an estimated 25 million in 1519 to just 1 million by the early 17th century. This drastic decline was due to a combination of factors, including disease, violence, and forced assimilation.
Key Points
- The indigenous people of Mexico are comprised of over 60 ethnic groups, each with their unique language and customs.
- The Aztecs, Mayans, and Olmecs are some of the most well-known pre-Columbian civilizations in Mexico.
- The arrival of the Spanish conquistadors had a devastating impact on the indigenous population, leading to the loss of land, culture, and lives.
- Today, indigenous people in Mexico continue to face significant challenges, including poverty, lack of access to education and healthcare, and discrimination.
- Efforts are being made to preserve and promote indigenous languages, customs, and traditions, including the development of bilingual education programs and cultural festivals.
Current State and Challenges
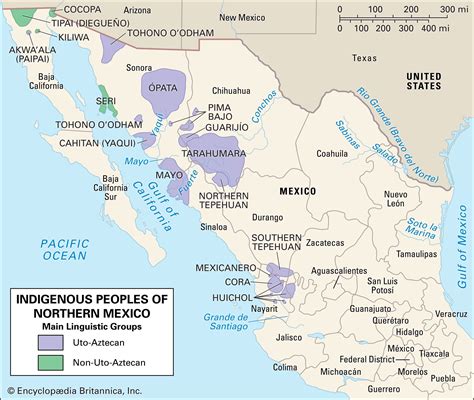
Today, indigenous people in Mexico continue to face significant challenges, including poverty, lack of access to education and healthcare, and discrimination. According to data from the National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI), in 2020, 73.4% of indigenous people lived in poverty, compared to 43.6% of the non-indigenous population. Additionally, indigenous people have limited access to education and healthcare, with many communities lacking basic services such as clean water, sanitation, and electricity. The lack of access to education and healthcare is particularly concerning, as it perpetuates the cycle of poverty and limits opportunities for social mobility.
Preservation of Indigenous Languages and Cultures
Despite the challenges they face, indigenous people in Mexico are working to preserve and promote their languages, customs, and traditions. Efforts include the development of bilingual education programs, cultural festivals, and language documentation projects. For example, the Mexican government has established the National Institute of Indigenous Languages (INALI), which aims to promote and preserve indigenous languages through language documentation, education, and cultural activities. Additionally, many indigenous communities are working to revitalize their languages and cultures, including the development of language and culture classes, traditional dance and music performances, and cultural festivals.
| Indigenous Group | Population | Language |
|---|---|---|
| Nahua | 2.4 million | Nahuatl |
| Maya | 800,000 | Mayan languages |
| Zapotec | 700,000 | Zapotec languages |
| Mixtec | 500,000 | Mixtec languages |
| Tzotzil | 400,000 | Tzotzil |

Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the indigenous people of Mexico are a vital part of the country’s cultural heritage, with a rich history, diverse languages, and unique customs. Despite the challenges they face, indigenous people are working to preserve and promote their languages, customs, and traditions. It is essential that we recognize the importance of preserving indigenous languages and cultures and support efforts to promote and protect the rights of indigenous people. By working together, we can help to ensure a brighter future for the indigenous people of Mexico and preserve the country’s rich cultural diversity for generations to come.
What is the current state of indigenous languages in Mexico?
+According to the Mexican government, there are currently 68 recognized indigenous languages in Mexico, with many more dialects and variations. However, many of these languages are considered endangered, with some having as few as 100 speakers.
What efforts are being made to preserve indigenous languages and cultures in Mexico?
+Efforts include the development of bilingual education programs, cultural festivals, and language documentation projects. Additionally, many indigenous communities are working to revitalize their languages and cultures, including the development of language and culture classes, traditional dance and music performances, and cultural festivals.
What can be done to support the indigenous people of Mexico?
+Supporting efforts to preserve and promote indigenous languages and cultures is essential. This can include advocating for the rights of indigenous people, supporting organizations that work with indigenous communities, and promoting cultural awareness and understanding. Additionally, supporting indigenous-led initiatives and projects can help to ensure that the needs and priorities of indigenous communities are being addressed.