The concept of instantaneous rate of change is a fundamental idea in calculus, allowing us to understand how a function changes at a specific point. It is a measure of how fast the output of a function changes when one of its inputs changes. The instantaneous rate of change is calculated using the derivative of a function, which can be found using various rules and formulas. In this article, we will delve into the instantaneous rate of change formula, its significance, and how it is applied in different fields.
Key Points
- The instantaneous rate of change is calculated using the derivative of a function.
- The derivative of a function represents the rate of change of the function with respect to one of its variables.
- The instantaneous rate of change formula is f'(x) = lim(h → 0) [f(x + h) - f(x)]/h.
- The formula is used to find the derivative of a function, which can be used to determine the instantaneous rate of change at a specific point.
- The instantaneous rate of change has numerous applications in physics, engineering, economics, and other fields.
Understanding the Instantaneous Rate of Change Formula
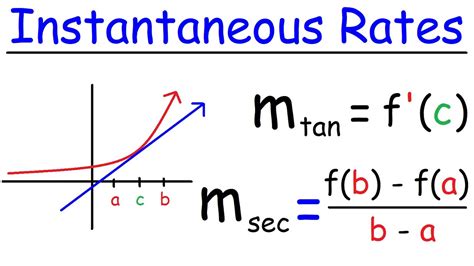
The instantaneous rate of change formula is based on the concept of limits, which is a fundamental idea in calculus. The formula is f’(x) = lim(h → 0) [f(x + h) - f(x)]/h, where f’(x) represents the derivative of the function f(x) at point x. The limit represents the behavior of the function as the change in the input h approaches zero. This formula allows us to calculate the instantaneous rate of change of a function at a specific point.
Derivative Rules and Formulas
There are various rules and formulas used to find the derivative of a function, including the power rule, product rule, quotient rule, and chain rule. These rules enable us to differentiate complex functions and calculate their instantaneous rates of change. For example, the power rule states that if f(x) = x^n, then f’(x) = nx^(n-1). The product rule states that if f(x) = u(x)v(x), then f’(x) = u’(x)v(x) + u(x)v’(x).
| Derivative Rule | Formula |
|---|---|
| Power Rule | f'(x) = nx^(n-1) |
| Product Rule | f'(x) = u'(x)v(x) + u(x)v'(x) |
| Quotient Rule | f'(x) = (u'(x)v(x) - u(x)v'(x)) / v(x)^2 |
| Chain Rule | f'(x) = f'(u(x)) \* u'(x) |
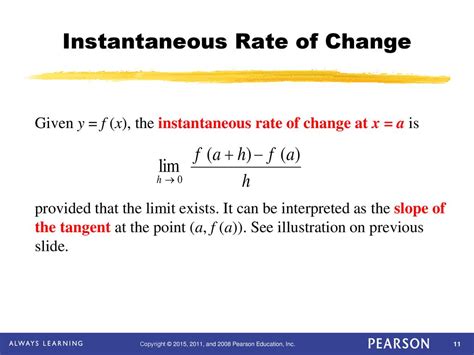
Applications of Instantaneous Rate of Change

The instantaneous rate of change has numerous applications in physics, engineering, economics, and other fields. In physics, it is used to describe the motion of objects, including velocity and acceleration. In engineering, it is used to design and optimize systems, such as electronic circuits and mechanical systems. In economics, it is used to analyze the behavior of economic systems, including the supply and demand of goods and services.
Real-World Examples
For example, in physics, the instantaneous rate of change of an object’s position is its velocity. The instantaneous rate of change of an object’s velocity is its acceleration. In engineering, the instantaneous rate of change of a circuit’s voltage is its current. In economics, the instantaneous rate of change of a company’s revenue is its marginal revenue.
What is the instantaneous rate of change formula?
+The instantaneous rate of change formula is f'(x) = lim(h → 0) [f(x + h) - f(x)]/h, where f'(x) represents the derivative of the function f(x) at point x.
What are the applications of instantaneous rate of change?
+The instantaneous rate of change has numerous applications in physics, engineering, economics, and other fields, including describing the motion of objects, designing and optimizing systems, and analyzing economic behavior.
How is the instantaneous rate of change calculated?
+The instantaneous rate of change is calculated using the derivative of a function, which can be found using various rules and formulas, including the power rule, product rule, quotient rule, and chain rule.
In conclusion, the instantaneous rate of change formula is a powerful tool for analyzing functions and understanding their behavior. By applying the derivative rules and formulas, we can calculate the instantaneous rate of change of a function at a specific point, which has numerous applications in various fields. The concept of instantaneous rate of change is essential in calculus and has far-reaching implications in physics, engineering, economics, and other fields.


