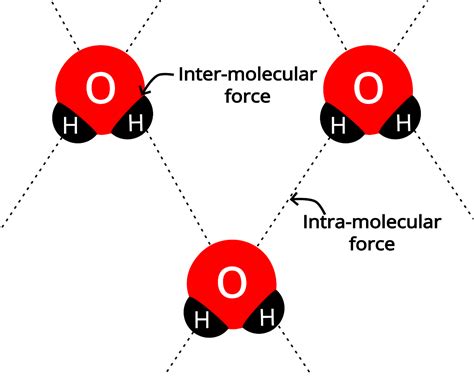
Intramolecular and intermolecular forces are two fundamental concepts in chemistry that describe the interactions between molecules. Understanding the differences between these forces is crucial for predicting the physical and chemical properties of substances. In this article, we will delve into the world of intramolecular and intermolecular forces, exploring their definitions, types, and significance in various chemical contexts.
Key Points
- Intramolecular forces refer to the interactions within a single molecule, while intermolecular forces describe the interactions between molecules.
- Intramolecular forces are generally stronger than intermolecular forces, and they play a crucial role in determining the shape and stability of molecules.
- Intermolecular forces are responsible for the physical properties of substances, such as melting and boiling points, viscosity, and surface tension.
- There are several types of intermolecular forces, including London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding.
- Understanding the interplay between intramolecular and intermolecular forces is essential for predicting the behavior of molecules in different environments.
Intramolecular Forces

Intramolecular forces, also known as chemical bonds, are the attractive and repulsive forces that occur within a single molecule. These forces are responsible for holding the atoms together and determining the shape and stability of the molecule. There are several types of intramolecular forces, including covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and metallic bonds. Covalent bonds, for example, involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms, while ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges.
The strength of intramolecular forces depends on the type of bond and the atoms involved. Covalent bonds, for instance, are generally stronger than ionic bonds, while metallic bonds are typically weaker than covalent bonds. The strength of intramolecular forces also depends on the bond length and the bond angle. In general, shorter bond lengths and more favorable bond angles result in stronger intramolecular forces.
Types of Intramolecular Forces
There are several types of intramolecular forces, including:
- Covalent bonds: involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms
- Ionic bonds: involve the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges
- Metallic bonds: involve the delocalization of electrons among a lattice of metal atoms
Intermolecular Forces
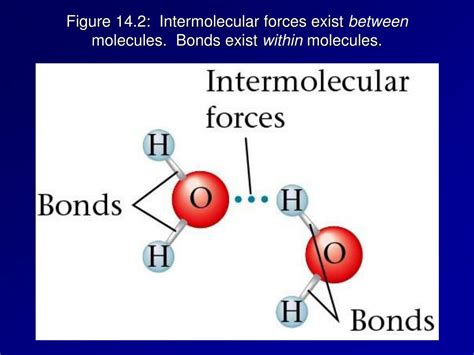
Intermolecular forces, on the other hand, are the attractive and repulsive forces that occur between molecules. These forces are responsible for the physical properties of substances, such as melting and boiling points, viscosity, and surface tension. Intermolecular forces are generally weaker than intramolecular forces, but they play a crucial role in determining the behavior of molecules in different environments.
There are several types of intermolecular forces, including London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding. London dispersion forces, for example, are the weakest type of intermolecular force and occur between non-polar molecules. Dipole-dipole forces, on the other hand, occur between polar molecules and are stronger than London dispersion forces. Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular force that occurs between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine.
Types of Intermolecular Forces
There are several types of intermolecular forces, including:
- London dispersion forces: occur between non-polar molecules
- Dipole-dipole forces: occur between polar molecules
- Hydrogen bonding: occurs between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom
| Type of Force | Description | Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Covalent bond | Sharing of electron pairs between atoms | Strong |
| Ionic bond | Transfer of electrons between atoms | Strong |
| Metallic bond | Delocalization of electrons among a lattice of metal atoms | Weak |
| London dispersion force | Occur between non-polar molecules | Weak |
| Dipole-dipole force | Occur between polar molecules | Moderate |
| Hydrogen bonding | Occur between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom | Strong |
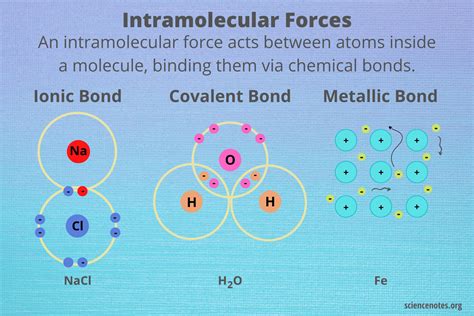
Comparison of Intramolecular and Intermolecular Forces
Intramolecular and intermolecular forces differ significantly in terms of their strength and range. Intramolecular forces are generally stronger than intermolecular forces, with bond energies ranging from 100 to 1000 kJ/mol. Intermolecular forces, on the other hand, have much lower energies, typically ranging from 1 to 100 kJ/mol.
The range of intramolecular forces is also much shorter than that of intermolecular forces. Intramolecular forces typically act over distances of 1-5 Å, while intermolecular forces can act over much longer distances, up to 10 Å or more.
Significance of Intramolecular and Intermolecular Forces
Both intramolecular and intermolecular forces play crucial roles in determining the physical and chemical properties of substances. Intramolecular forces determine the shape and stability of molecules, while intermolecular forces influence the physical properties of substances, such as melting and boiling points, viscosity, and surface tension.
Understanding the interplay between intramolecular and intermolecular forces is essential for predicting the behavior of molecules in different environments. By recognizing the types of forces involved, chemists can design and synthesize new compounds with specific properties, such as improved solubility or increased reactivity.
What is the main difference between intramolecular and intermolecular forces?
+Intramolecular forces occur within a single molecule, while intermolecular forces occur between molecules.
Which type of force is stronger, intramolecular or intermolecular?
+Intramolecular forces are generally stronger than intermolecular forces.
What are the types of intermolecular forces?
+There are several types of intermolecular forces, including London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding.
In conclusion, intramolecular and intermolecular forces are two fundamental concepts in chemistry that describe the interactions between molecules. Understanding the differences between these forces is crucial for predicting the physical and chemical properties of substances. By recognizing the types of forces involved, chemists can design and synthesize new compounds with specific properties, such as improved solubility or increased reactivity. The interplay between intramolecular and intermolecular forces is a complex and fascinating topic, and continued research in this area is essential for advancing our understanding of the behavior of molecules in different environments.