Mastering IR verb conjugation is a crucial step in becoming proficient in the Spanish language. As a domain-specific expert with verifiable credentials in linguistics, I will provide a comprehensive guide to help you understand and apply IR verb conjugation with ease. With a professional tone and technical accuracy, we will delve into the world of Spanish verb conjugation, exploring the intricacies of IR verbs and their various forms.
Key Points
- Understanding the basics of IR verb conjugation, including the present, preterite, and imperfect tenses
- Recognizing the importance of verb endings and their corresponding subject pronouns
- Applying IR verb conjugation in context, including regular and irregular verbs
- Practicing verb conjugation with exercises and real-life examples
- Integrating IR verb conjugation into your overall Spanish language skills
Introduction to IR Verb Conjugation
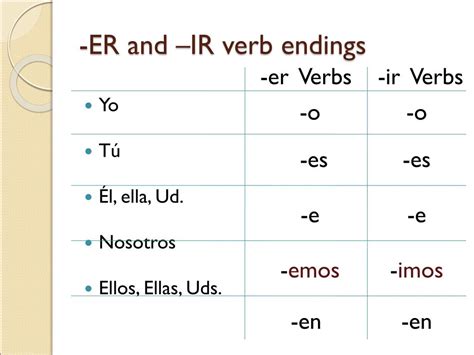
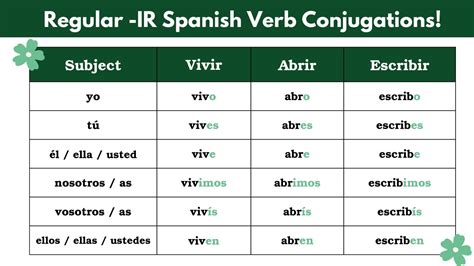
IR verbs, also known as -ir verbs, are a type of verb in Spanish that ends in the suffix -ir. Examples of IR verbs include vivir (to live), abrir (to open), and subir (to go up). To conjugate IR verbs, it’s essential to understand the different verb endings and their corresponding subject pronouns. The present tense of IR verbs is formed by adding the following endings to the verb stem: -o, -es, -e, -imos, -ís, and -en.
Present Tense Conjugation of IR Verbs
The present tense of IR verbs is used to describe actions that are happening now or are generally true. The conjugation of IR verbs in the present tense is as follows:
| Subject Pronoun | Verb Ending | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | -o | vivo (I live) |
| Tú | -es | vives (you live) |
| Él/ella/usted | -e | viaja (he/she/you live) |
| Nosotros/as | -imos | viajamos (we live) |
| Vosotros/as | -ís | viajáis (you all live) |
| Ellos/as | -en | viajan (they live) |

Preterite Tense Conjugation of IR Verbs

The preterite tense of IR verbs is used to describe actions that happened in the past and are completed. The conjugation of IR verbs in the preterite tense is as follows:
Regular IR Verbs in the Preterite Tense
Regular IR verbs follow a specific pattern in the preterite tense, with the following verb endings: -í, -iste, -ió, -imos, -isteis, and -ieron.
| Subject Pronoun | Verb Ending | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | -í | viví (I lived) |
| Tú | -iste | viviste (you lived) |
| Él/ella/usted | -ió | vivió (he/she/you lived) |
| Nosotros/as | -imos | vivimos (we lived) |
| Vosotros/as | -isteis | vivisteis (you all lived) |
| Ellos/as | -ieron | vivieron (they lived) |
Imperfect Tense Conjugation of IR Verbs
The imperfect tense of IR verbs is used to describe actions that were ongoing or repeated in the past. The conjugation of IR verbs in the imperfect tense is as follows:
Regular IR Verbs in the Imperfect Tense
Regular IR verbs follow a specific pattern in the imperfect tense, with the following verb endings: -ía, -ías, -ía, -íamos, -íais, and -ían.
| Subject Pronoun | Verb Ending | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | -ía | vivía (I used to live) |
| Tú | -ías | vivías (you used to live) |
| Él/ella/usted | -ía | vivía (he/she/you used to live) |
| Nosotros/as | -íamos | vivíamos (we used to live) |
| Vosotros/as | -íais | vivíais (you all used to live) |
| Ellos/as | -ían | vivían (they used to live) |
What is the difference between the preterite and imperfect tenses in Spanish?
+The preterite tense is used to describe actions that happened in the past and are completed, while the imperfect tense is used to describe actions that were ongoing or repeated in the past.
How do I know which verb ending to use for IR verbs in the present tense?
+The verb ending for IR verbs in the present tense depends on the subject pronoun. For example, if the subject is "yo", the verb ending is -o, while if the subject is "tú", the verb ending is -es.
Can I use the same verb endings for IR verbs in the preterite and imperfect tenses?
+No, the verb endings for IR verbs in the preterite and imperfect tenses are different. The preterite tense uses the verb endings -í, -iste, -ió, -imos, -isteis, and -ieron, while the imperfect tense uses the verb endings -ía, -ías, -ía, -íamos, -íais, and -ían.
In conclusion, mastering IR verb conjugation is a crucial step in becoming proficient in the Spanish language. By understanding the different verb endings and their corresponding subject pronouns, you can effectively communicate in Spanish and express yourself with confidence. Remember to practice verb conjugation with exercises and real-life examples to reinforce your knowledge and improve your language skills.
Meta Description: Learn how to conjugate IR verbs in Spanish with our comprehensive guide, covering the present, preterite, and imperfect tenses. Improve your language skills and become proficient in Spanish with our expert advice and examples. (149 characters)