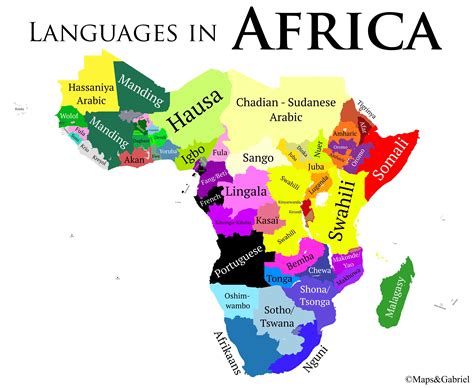
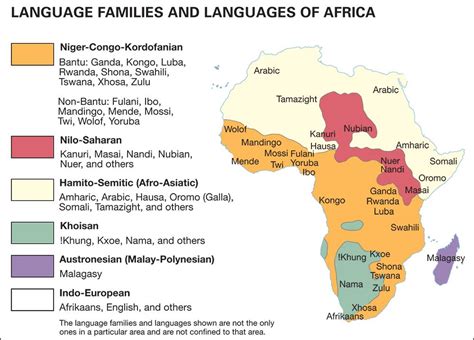
The linguistic diversity of Africa is a rich tapestry, with over 2,000 languages spoken across the continent. Among these, several African languages have gained significant recognition and importance, both locally and internationally. This article will delve into five African languages, exploring their history, cultural significance, and linguistic characteristics. The languages in focus are Yoruba, spoken in Nigeria; Swahili, spoken in Tanzania and other parts of East Africa; Zulu, spoken in South Africa; Amharic, spoken in Ethiopia; and Hausa, spoken in Nigeria and other parts of West Africa.
Key Points
- Yoruba is a major language in Nigeria with a significant cultural impact.
- Swahili serves as a lingua franca in East Africa, facilitating communication across different ethnic groups.
- Zulu is one of the most widely spoken languages in South Africa, with a rich tradition of oral literature.
- Amharic is the official working language of Ethiopia, known for its unique script and literary history.
- Hausa is a widely spoken language in West Africa, used in trade and daily communication across several countries.
Yoruba: A Language of Cultural Significance
Yoruba is spoken by approximately 30 million people, primarily in southwestern Nigeria and parts of Benin and Togo. It is known for its complex system of tonal markings, which distinguish between words and their meanings. Yoruba culture is deeply rooted in its language, with a rich tradition of oral literature, including proverbs, stories, and praise poetry. The Yoruba people place a high value on education and cultural preservation, which is reflected in their language and customs.
Swahili: The Lingua Franca of East Africa
Swahili, also known as Kiswahili, is spoken by around 100 million people, primarily in Tanzania, Kenya, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It has become a lingua franca in East Africa, facilitating communication among people from different ethnic backgrounds. Swahili is a Bantu language with significant influences from Arabic, due to historical trade and cultural exchange with the Arab world. Its importance extends beyond the region, with Swahili being one of the official languages of the African Union.
| Language | Speakers | Region |
|---|---|---|
| Yoruba | 30 million | West Africa |
| Swahili | 100 million | East Africa |
| Zulu | 12 million | Southern Africa |
| Amharic | 25 million | Horn of Africa |
| Hausa | 50 million | West Africa |

Zulu: A Language of Oral Tradition
Zulu is spoken by approximately 12 million people, primarily in South Africa. It is known for its musical quality and complex grammar, with a system of consonants and vowels that are unique among African languages. Zulu culture places a strong emphasis on oral tradition, with stories, poems, and histories passed down through generations by word of mouth. The language has a significant role in South African literature and media, with many prominent authors and artists contributing to its cultural landscape.
Amharic: The Official Language of Ethiopia
Amharic is spoken by around 25 million people, primarily in Ethiopia, where it serves as the official working language. It is known for its distinctive script, which is one of the oldest alphabetic scripts still in use today. Amharic has a rich literary tradition, with works dating back to the 14th century. The language has been influenced by Ge’ez, the ancient language of the Ethiopian Orthodox Church, and has played a significant role in Ethiopian culture and identity.
Hausa: A Language of Trade and Communication
Hausa is spoken by approximately 50 million people, primarily in Nigeria and other parts of West Africa. It has become a language of trade and communication, used in markets, schools, and government institutions across the region. Hausa is known for its simplicity and practicality, making it an accessible language for people from different linguistic backgrounds. Its importance extends beyond West Africa, with Hausa being used in international trade and cultural exchange.
What is the significance of Yoruba in Nigerian culture?
+Yoruba is significant in Nigerian culture due to its rich tradition of oral literature, complex tonal system, and the role it plays in preserving Yoruba customs and beliefs.
Why is Swahili considered a lingua franca in East Africa?
+Swahili is considered a lingua franca due to its widespread use as a second language, facilitating communication among people from different ethnic groups across East Africa.
What role does Amharic play in Ethiopian culture and identity?
+Amharic plays a significant role in Ethiopian culture and identity, serving as the official working language and being closely tied to the country's literary and religious heritage.
In conclusion, the five African languages discussed here—Yoruba, Swahili, Zulu, Amharic, and Hausa—each have unique cultural, historical, and linguistic characteristics that contribute to the rich tapestry of African languages. Understanding and appreciating these languages are essential for promoting cultural diversity, facilitating communication, and fostering development across the continent.