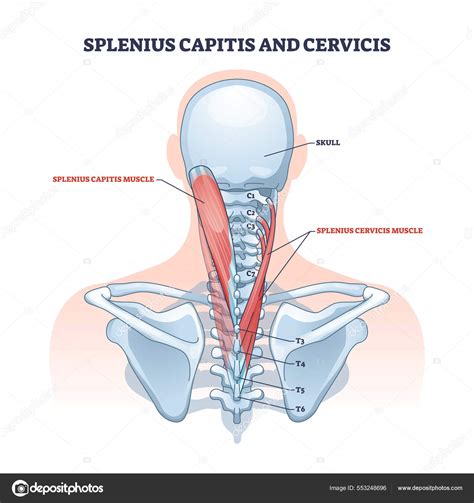
The splenius capitis and cervicis muscles are two deep muscles located in the posterior region of the neck, playing a crucial role in the movement and stability of the cervical spine. These muscles are part of the larger group of muscles known as the splenius muscles, which also include the splenius accessorius. The splenius capitis and cervicis muscles are named based on their attachments and functions, with "capitis" referring to the head and "cervicis" referring to the neck.
The splenius capitis muscle originates from the spinous processes of the lower cervical vertebrae (C7-T3) and the supraspinous ligament, and inserts into the lateral part of the occipital bone and the posterior aspect of the mastoid process of the temporal bone. This muscle acts to extend the head and rotate it to the same side. The splenius cervicis muscle, on the other hand, originates from the spinous processes of the upper thoracic vertebrae (T3-T6) and inserts into the posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the middle and lower cervical vertebrae (C2-C5). Its primary action is to extend the neck and rotate it to the same side.
Key Points
- The splenius capitis and cervicis muscles are crucial for cervical spine movement and stability.
- These muscles are named based on their attachments and functions, with the splenius capitis attaching to the head and the splenius cervicis attaching to the neck.
- The primary actions of the splenius capitis include extending the head and rotating it to the same side, while the splenius cervicis extends the neck and rotates it to the same side.
- Both muscles play a significant role in maintaining posture and facilitating movements such as turning the head or looking upwards.
- Dysfunction or injury to these muscles can lead to neck pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion.
Anatomy and Function
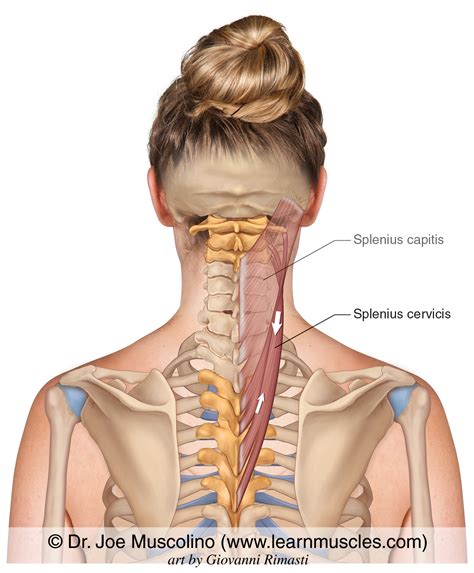
The anatomy of the splenius capitis and cervicis muscles is characterized by their deep location in the posterior neck, overlaying other muscles such as the semispinalis and multifidus. Their functions are closely related to the movements of the cervical spine, including extension, rotation, and lateral flexion. The muscles work in concert with other neck muscles to achieve these movements, highlighting the complexity and coordination of cervical spine function.
Biomechanical Analysis
A biomechanical analysis of the splenius capitis and cervicis muscles reveals that they are subjected to varying levels of stress and strain during different movements of the head and neck. This is due to their role in stabilizing the cervical spine and facilitating movements such as nodding, shaking the head, and turning to look over one’s shoulder. The muscles must work efficiently to balance the movements and maintain posture, making them susceptible to fatigue and injury if not properly conditioned or if subjected to repetitive strain.
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Splenius Capitis | Spinous processes of C7-T3 and supraspinous ligament | Lateral part of occipital bone and posterior aspect of mastoid process | Extends head, rotates to same side |
| Splenius Cervicis | Spinous processes of T3-T6 | Posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C2-C5 | Extends neck, rotates to same side |
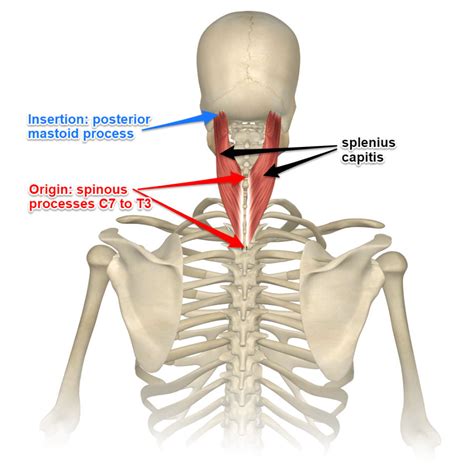
Clinical Significance
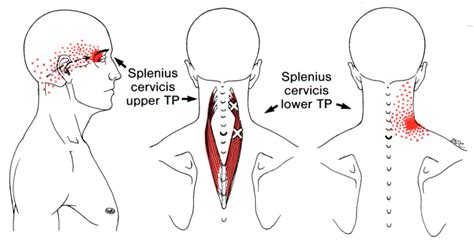
Clinically, the splenius capitis and cervicis muscles are important because they can be a source of pain and dysfunction in the neck and head. Strains or tears in these muscles, as well as imbalances in their strength and flexibility, can lead to symptoms such as stiffness, limited range of motion, and pain that radiates to the shoulders or head. Diagnostic techniques such as palpation, range of motion testing, and imaging studies can help identify issues with these muscles. Treatment may involve physical therapy, including exercises to strengthen and stretch the muscles, as well as modalities like heat, cold, or electrical stimulation to reduce pain and inflammation.
Treatment and Rehabilitation
Treatment and rehabilitation of the splenius capitis and cervicis muscles focus on restoring strength, flexibility, and proper function. This can involve a combination of exercises, manual therapy, and education on proper posture and body mechanics. Exercises may include isometric contractions to strengthen the muscles, as well as stretching exercises to improve flexibility. Manual therapy techniques such as massage and trigger point therapy can help reduce muscle tension and promote healing. Education on proper posture and body mechanics is crucial to prevent recurrence of injury and to promote long-term health of the cervical spine.
What are the primary actions of the splenius capitis muscle?
+The primary actions of the splenius capitis muscle include extending the head and rotating it to the same side.
How do the splenius capitis and cervicis muscles contribute to posture?
+Both muscles play a significant role in maintaining posture by facilitating movements such as extension and rotation of the head and neck, and by stabilizing the cervical spine.
What are common symptoms of dysfunction in the splenius capitis and cervicis muscles?
+Common symptoms include neck pain, stiffness, limited range of motion, and pain that radiates to the shoulders or head.
In conclusion, the splenius capitis and cervicis muscles are vital components of the posterior neck, contributing significantly to the movement, stability, and posture of the cervical spine. Their dysfunction can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to debilitating pain and limited mobility. Understanding the anatomy, function, and clinical significance of these muscles is essential for the diagnosis and treatment of cervical spine disorders, as well as for the development of effective rehabilitation strategies to restore function and alleviate pain.