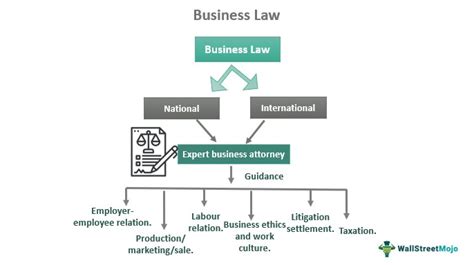
Business laws are a complex and multifaceted set of regulations that govern the operation of companies, partnerships, and sole proprietorships. These laws are designed to protect the rights of businesses, consumers, and employees, and to promote fair competition and ethical practices. In this article, we will provide an in-depth explanation of business laws, including their history, types, and applications.
Business laws have evolved over time, with the first commercial laws dating back to ancient civilizations such as the Babylonians and Romans. However, it was not until the 20th century that business laws began to take shape as we know them today. The passage of landmark legislation such as the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 in the United States marked a significant turning point in the development of modern business laws. Today, business laws are an essential part of the global economy, with countries around the world establishing their own unique regulatory frameworks.
Key Points
- Business laws govern the operation of companies, partnerships, and sole proprietorships
- These laws protect the rights of businesses, consumers, and employees
- Business laws promote fair competition and ethical practices
- The history of business laws dates back to ancient civilizations
- Modern business laws have evolved over the 20th century with landmark legislation
Types of Business Laws

There are several types of business laws, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types of business laws include contract law, tort law, property law, and employment law. Contract law governs the formation and enforcement of contracts between businesses and individuals, while tort law provides remedies for individuals who have been harmed by the actions of businesses. Property law regulates the ownership and use of property, including real estate and intellectual property. Employment law, on the other hand, governs the relationships between employers and employees, including issues such as wages, hours, and working conditions.
Contract Law
Contract law is a critical component of business laws, as it provides a framework for businesses to enter into agreements with suppliers, customers, and partners. A contract is a legally binding agreement between two or more parties, and it can be either written or oral. However, written contracts are generally preferred, as they provide a clear and tangible record of the agreement. Contract law governs the formation, performance, and enforcement of contracts, and it provides remedies for parties who have been harmed by breaches of contract.
| Type of Contract | Description |
|---|---|
| Express Contract | A contract that is explicitly stated, either in writing or orally |
| Implied Contract | A contract that is implied by the actions of the parties, rather than explicitly stated |
| Unilateral Contract | A contract in which one party makes a promise or offer, and the other party accepts by performing a specific action |
| Bilateral Contract | A contract in which both parties make promises or offers to each other |

Employment Law

Employment law is another critical component of business laws, as it governs the relationships between employers and employees. Employment law regulates issues such as wages, hours, and working conditions, and it provides protections for employees against discrimination and harassment. Employment law also governs the formation and termination of employment contracts, and it provides remedies for employees who have been wrongfully terminated or discriminated against.
Types of Employment
There are several types of employment, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types of employment include at-will employment, contract employment, and temporary employment. At-will employment is a type of employment in which the employer has the right to terminate the employee at any time, with or without cause. Contract employment, on the other hand, is a type of employment in which the employee is hired for a specific period of time, and the employer is required to provide the employee with a certain level of compensation and benefits. Temporary employment is a type of employment in which the employee is hired for a short period of time, often to fill a specific need or to complete a specific project.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the number of temporary employees in the United States has increased significantly over the past decade, with approximately 3 million temporary employees working in the country as of 2022. This trend is expected to continue, as businesses seek to increase their flexibility and reduce their labor costs.
What is the difference between a contract employee and a temporary employee?
+A contract employee is an employee who is hired for a specific period of time, and is required to provide a certain level of services or work product. A temporary employee, on the other hand, is an employee who is hired for a short period of time, often to fill a specific need or to complete a specific project.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of at-will employment?
+The advantages of at-will employment include the flexibility to terminate employees at any time, and the ability to make quick decisions about staffing needs. The disadvantages of at-will employment include the potential for unfair treatment of employees, and the lack of job security.
How do I know if I am an employee or an independent contractor?
+To determine whether you are an employee or an independent contractor, you should consider the level of control that your employer has over your work, the amount of independence you have in your work, and the level of benefits and compensation you receive. If you are unsure, you should consult with an attorney or a qualified human resources professional.
In conclusion, business laws are a complex and multifaceted set of regulations that govern the operation of companies, partnerships, and sole proprietorships. By understanding the different types of business laws, including contract law and employment law, businesses can protect their interests and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. As a business owner, it is essential to work with a qualified attorney to ensure that your business is in compliance with all applicable laws and regulations.
Business laws are constantly evolving, and it is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest developments and trends. By doing so, businesses can ensure that they are operating in a fair and ethical manner, and that they are providing a safe and healthy work environment for their employees. Ultimately, the goal of business laws is to promote fair competition, protect the rights of businesses and individuals, and ensure that businesses are operating in a responsible and sustainable manner.