Lisinopril and losartan are two commonly prescribed medications used to treat high blood pressure and other cardiovascular conditions. While both drugs are effective in managing hypertension, they belong to different classes of medications and have distinct mechanisms of action. In this article, we will delve into the similarities and differences between lisinopril and losartan, exploring their pharmacological profiles, therapeutic uses, and potential side effects.
Introduction to Lisinopril and Losartan
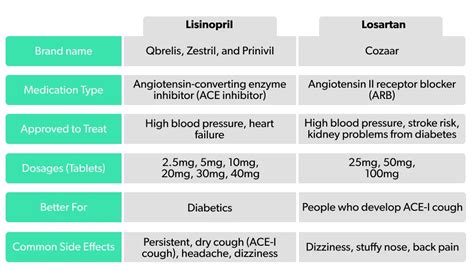
Lisinopril is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, which works by blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor. This action leads to vasodilation, reducing blood pressure and increasing cardiac output. Losartan, on the other hand, is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist (ARB), which directly blocks the action of angiotensin II on its receptors, resulting in decreased vasoconstriction and reduced blood pressure.
Pharmacological Profiles
Lisinopril is available in oral tablet form, with dosages ranging from 2.5 to 40 mg per day. It is typically administered once daily, with peak plasma concentrations achieved within 6-8 hours. Losartan is also available in oral tablet form, with dosages ranging from 25 to 100 mg per day. It is usually administered once or twice daily, with peak plasma concentrations achieved within 1-3 hours. Both medications have a long duration of action, allowing for once-daily dosing in most cases.
| Medication | Class | Dosage Range | Peak Plasma Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lisinopril | ACE Inhibitor | 2.5-40 mg/day | 6-8 hours |
| Losartan | ARB | 25-100 mg/day | 1-3 hours |
Therapeutic Uses and Efficacy

Both lisinopril and losartan are indicated for the treatment of hypertension, either as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive agents. Lisinopril is also approved for the treatment of heart failure, while losartan is approved for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Clinical trials have demonstrated that both medications are effective in reducing blood pressure and improving cardiovascular outcomes. The Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension (LIFE) study showed that losartan was superior to atenolol in reducing the risk of stroke, myocardial infarction, and cardiovascular mortality. Similarly, the Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (HOPE) study demonstrated that lisinopril reduced the risk of cardiovascular events, including myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular death.
Key Points
- Lisinopril and losartan are both effective in reducing blood pressure and improving cardiovascular outcomes.
- Lisinopril is an ACE inhibitor, while losartan is an ARB.
- Both medications have different pharmacological profiles and therapeutic uses.
- The choice between lisinopril and losartan depends on individual patient factors, such as comorbidities and potential side effects.
- Both medications have been shown to be effective in reducing the risk of cardiovascular events, including myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions
Both lisinopril and losartan are generally well-tolerated, but they can cause side effects, such as dizziness, headache, and cough. Lisinopril is more likely to cause cough, while losartan is more likely to cause hyperkalemia (elevated potassium levels). Both medications can interact with other drugs, such as diuretics, potassium supplements, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It’s essential to monitor patients closely for potential side effects and interactions, especially when initiating or adjusting therapy.
What is the primary difference between lisinopril and losartan?
+Lisinopril is an ACE inhibitor, while losartan is an ARB. This difference in mechanism of action can affect how each medication interacts with other drugs and how they are tolerated by individual patients.
Can lisinopril and losartan be used together?
+While both medications can be used together in certain cases, such as in patients with resistant hypertension, it's essential to monitor patients closely for potential side effects and interactions, especially hyperkalemia.
What are the potential benefits of using lisinopril over losartan?
+Lisinopril may be preferred in patients with heart failure or those who require a medication with a longer duration of action. Additionally, lisinopril may be more effective in reducing proteinuria (excess protein in the urine) in patients with diabetic nephropathy.
In conclusion, lisinopril and losartan are both effective medications for the treatment of hypertension and other cardiovascular conditions. While they share some similarities, they also have distinct differences in their pharmacological profiles, therapeutic uses, and potential side effects. By understanding these differences, healthcare providers can make informed decisions when selecting the most appropriate medication for individual patients. Ultimately, the choice between lisinopril and losartan depends on a thorough evaluation of each patient's unique needs and medical history.
Meta description suggestion: “Lisinopril vs losartan: Compare the differences between these two blood pressure medications, including their mechanisms of action, therapeutic uses, and potential side effects.” (149 characters)