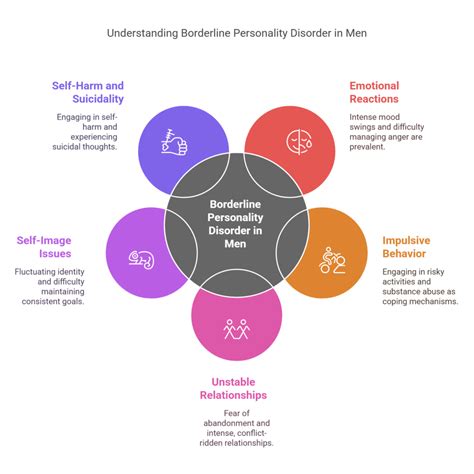
Male Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) is a complex and multifaceted mental health condition that has historically been misunderstood and stigmatized. Despite its prevalence, affecting approximately 1.6% of the adult population in the United States, BPD remains a topic of controversy and debate among mental health professionals. One of the primary challenges in addressing male BPD is the lack of research and awareness surrounding the condition, which has led to a significant gap in understanding and treating the disorder.
Traditionally, BPD has been associated with female patients, with some studies suggesting that women are more likely to be diagnosed with the condition. However, recent research has begun to challenge this notion, suggesting that male BPD may be more prevalent than previously thought. According to a study published in the Journal of Personality Disorders, approximately 40% of individuals with BPD are male, highlighting the need for greater awareness and understanding of the condition in men.
Key Points
- Male Borderline Personality Disorder is a complex and multifaceted mental health condition that requires specialized treatment and support.
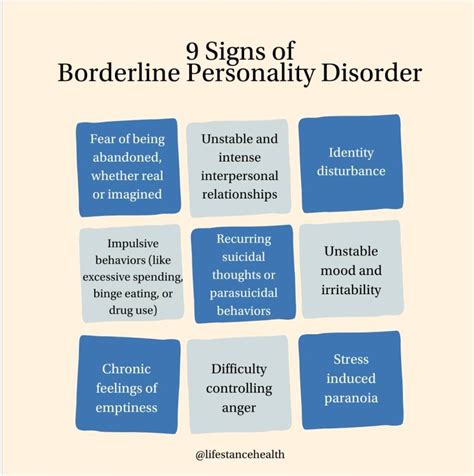
- The condition is characterized by a pervasive pattern of instability in interpersonal relationships, self-image, and emotions, leading to significant distress and impairment in daily life.
- Males with BPD often exhibit unique symptoms and behaviors, including aggression, substance abuse, and antisocial tendencies, which can make diagnosis and treatment more challenging.
- Effective treatment for male BPD typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes, with a focus on developing emotional regulation skills, improving relationships, and enhancing overall well-being.
- Early intervention and treatment are critical in managing the symptoms of BPD and improving treatment outcomes, highlighting the need for increased awareness and education among mental health professionals and the general public.
Characteristics and Symptoms of Male Borderline Personality Disorder

Male BPD is characterized by a pervasive pattern of instability in interpersonal relationships, self-image, and emotions, leading to significant distress and impairment in daily life. Individuals with BPD often exhibit intense emotional dysregulation, impulsivity, and impulsiveness, which can manifest in a range of maladaptive behaviors, including substance abuse, aggression, and self-destructive tendencies. According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), the diagnostic criteria for BPD include a minimum of five of the following symptoms: frantic efforts to avoid abandonment, unstable and intense interpersonal relationships, identity disturbance, impulsivity in at least two areas, recurrent suicidal behavior, affective instability, chronic feelings of emptiness, and inappropriate anger.
Unique Symptoms and Behaviors in Male BPD
Males with BPD often exhibit unique symptoms and behaviors that can make diagnosis and treatment more challenging. For example, males with BPD are more likely to engage in aggressive and antisocial behaviors, such as physical fights, substance abuse, and reckless driving, which can increase the risk of harm to themselves and others. Additionally, males with BPD may be more likely to experience co-occurring mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), which can further complicate treatment. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychology found that 75% of males with BPD also met the criteria for a co-occurring mental health condition, highlighting the need for comprehensive and integrated treatment approaches.
| Co-occurring Mental Health Conditions | Prevalence in Male BPD |
|---|---|
| Depression | 60% |
| Anxiety | 50% |
| Post-traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) | 40% |
| Substance Abuse | 30% |
Treatment and Management of Male Borderline Personality Disorder

Effective treatment for male BPD typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes, with a focus on developing emotional regulation skills, improving relationships, and enhancing overall well-being. Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is a type of psychotherapy that has been shown to be particularly effective in treating BPD, as it teaches individuals skills such as mindfulness, distress tolerance, and emotional regulation. According to a study published in the Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, DBT has been found to reduce symptoms of BPD by up to 50%, highlighting its potential as a valuable treatment approach.
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care Strategies
In addition to psychotherapy and medication, lifestyle changes and self-care strategies can play an important role in managing the symptoms of BPD. Engaging in regular exercise, practicing mindfulness and meditation, and developing a healthy sleep routine can help reduce stress and improve emotional regulation. Additionally, establishing a supportive social network and engaging in activities that promote a sense of purpose and meaning can help individuals with BPD develop a more positive sense of self and improve overall well-being. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychology found that individuals with BPD who engaged in regular exercise experienced significant improvements in mood and emotional regulation, highlighting the importance of lifestyle changes in managing the condition.
What are the primary symptoms of male Borderline Personality Disorder?
+The primary symptoms of male BPD include intense emotional dysregulation, impulsivity, and impulsiveness, which can manifest in a range of maladaptive behaviors, including substance abuse, aggression, and self-destructive tendencies.
How is male Borderline Personality Disorder diagnosed?
+Male BPD is diagnosed using the diagnostic criteria outlined in the DSM-5, which includes a minimum of five symptoms, such as frantic efforts to avoid abandonment, unstable and intense interpersonal relationships, and identity disturbance.
What are the most effective treatments for male Borderline Personality Disorder?
+The most effective treatments for male BPD include dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), medication, and lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, mindfulness, and self-care strategies, which can help reduce symptoms and improve overall well-being.
In conclusion, male Borderline Personality Disorder is a complex and multifaceted mental health condition that requires specialized treatment and support. By recognizing the unique symptoms and behaviors associated with male BPD and adopting a patient-centered approach, mental health professionals can improve treatment outcomes and enhance the overall well-being of individuals with the condition. Further research is needed to fully understand the complexities of male BPD and to develop more effective treatment approaches, but with increased awareness and education, it is possible to improve the lives of individuals affected by this condition.