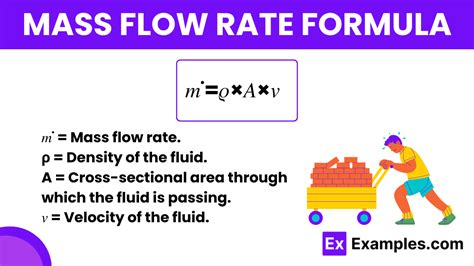
The concept of mass flow rate is fundamental in various fields of engineering, including chemical, mechanical, and aerospace engineering. It represents the rate at which mass flows through a given surface, and its calculation is crucial for designing and optimizing systems such as pipelines, ducts, and nozzles. The mass flow rate equation is a mathematical expression that relates the mass flow rate to other physical quantities such as density, velocity, and area. In this article, we will delve into the mass flow rate equation, its derivation, and its simplification, highlighting the key concepts and formulas involved.
Key Points
- The mass flow rate equation is given by m = ρAV, where m is the mass flow rate, ρ is the density, A is the cross-sectional area, and V is the velocity.
- The equation can be simplified for incompressible flows, where density is constant, to m = ρAV.
- For compressible flows, the equation of state and the conservation of mass principle must be considered, leading to more complex expressions.
- The mass flow rate is a critical parameter in the design and operation of various engineering systems, including pipelines, chemical reactors, and propulsion systems.
- Understanding the mass flow rate equation and its simplifications is essential for making accurate calculations and predictions in engineering applications.
Derivation of the Mass Flow Rate Equation
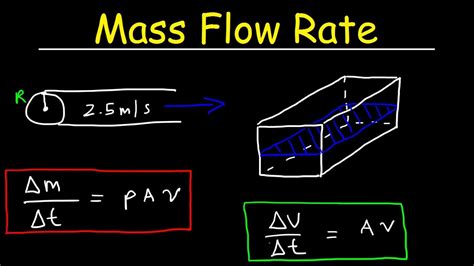
The mass flow rate equation can be derived by considering the conservation of mass principle. Imagine a control volume through which fluid flows. The mass flow rate into the control volume must equal the mass flow rate out of the control volume, assuming no mass is accumulated or depleted within the control volume. Mathematically, this can be expressed as the difference in mass flow rates between the inlet and outlet. However, for a steady-state flow, where the properties of the fluid do not change with time, the mass flow rate can be calculated using the formula m = ρAV, where m is the mass flow rate, ρ is the density of the fluid, A is the cross-sectional area of the flow, and V is the average velocity of the fluid.
Simplification for Incompressible Flows
For incompressible flows, where the density of the fluid is considered constant, the mass flow rate equation simplifies to m = ρAV. This simplification is valid for most liquids and for gases under conditions where the pressure and temperature changes are not significant enough to alter the density appreciably. The simplicity of this equation belies its power in calculating mass flow rates in a wide range of engineering applications, from water supply systems to chemical processing plants.
| Variable | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| m | Mass flow rate | kg/s |
| ρ | Density | kg/m³ |
| A | Cross-sectional area | m² |
| V | Average velocity | m/s |
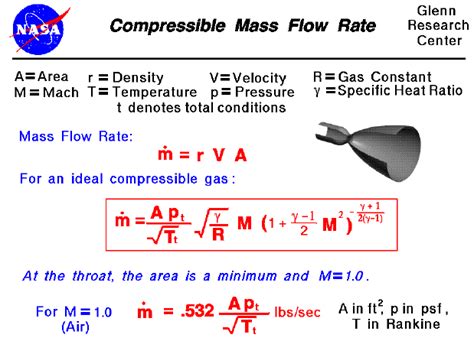
Compressible Flows and Complexity
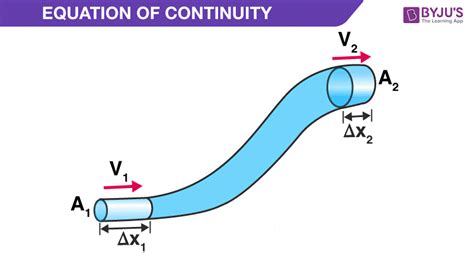
For compressible flows, where the density of the fluid can change due to pressure and temperature variations, the mass flow rate equation becomes more complex. The equation of state for the fluid, which relates density to pressure and temperature, must be considered. Additionally, the conservation of mass principle must be applied in a form that accounts for the changing density. This leads to equations that involve not just the velocity and area but also the pressure and temperature of the fluid, and potentially, the specific heat capacity and the gas constant, for gases. The complexity of these equations reflects the intricacies of compressible flow phenomena, which are critical in applications such as rocket propulsion and high-speed aerodynamics.
Practical Applications and Considerations
The mass flow rate equation, in its simplified or complex forms, has numerous practical applications. In the design of pipelines, for example, knowing the mass flow rate is crucial for determining the required diameter and material of the pipe, as well as the pumping power needed. In chemical engineering, mass flow rates are essential for calculating reactant and product quantities in chemical reactions. Furthermore, in the field of aerospace engineering, accurate calculations of mass flow rates are vital for the design of propulsion systems, where even small discrepancies can significantly impact performance and efficiency.
What is the primary factor that simplifies the mass flow rate equation for incompressible flows?
+The primary factor is the constant density of the fluid, which allows the equation to be expressed simply as m = ρAV.
Why is the mass flow rate equation more complex for compressible flows?
+The complexity arises from the need to account for changes in fluid density due to variations in pressure and temperature, requiring the incorporation of the equation of state and potentially other thermodynamic properties.
What are some key applications of the mass flow rate equation in engineering?
+The mass flow rate equation is crucial in the design and operation of pipelines, chemical reactors, propulsion systems, and other engineering systems where fluid flow is a key parameter.
In conclusion, the mass flow rate equation, whether in its simplified form for incompressible flows or its more complex versions for compressible flows, is a foundational concept in engineering. Its understanding and application are essential for the design, optimization, and operation of a wide range of systems and processes. By grasping the principles underlying the mass flow rate equation and its simplifications, engineers can make more accurate calculations, leading to more efficient and safer systems.