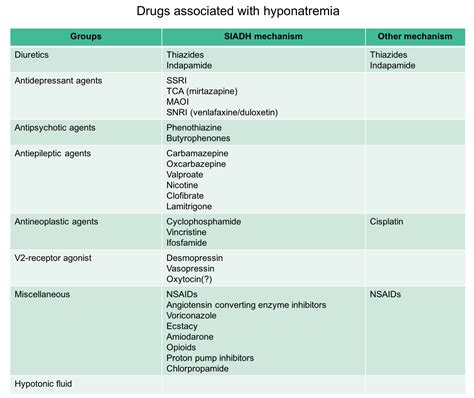
Hyponatremia, a condition characterized by low sodium levels in the blood, can be caused by a variety of factors, including certain medications. Sodium is an essential electrolyte that helps regulate the amount of water in the body, and its imbalance can lead to serious health complications. In this article, we will explore the medications that can cause hyponatremia, their mechanisms of action, and the clinical implications of this condition.
Key Points
- Hyponatremia is a condition characterized by low sodium levels in the blood, which can be caused by certain medications.
- Medications such as thiazide diuretics, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and antipsychotics can cause hyponatremia.
- The mechanisms of action of these medications can lead to an imbalance of sodium and water in the body, resulting in hyponatremia.
- Clinical implications of hyponatremia include neurological symptoms, seizures, and even death if left untreated.
- Early detection and treatment of hyponatremia are crucial to prevent long-term complications and improve patient outcomes.
Medications That Can Cause Hyponatremia
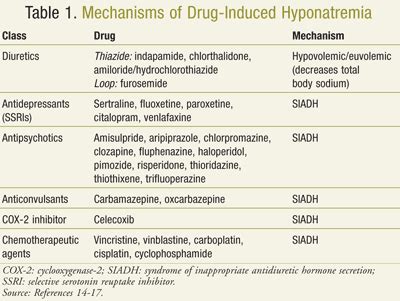
Several medications have been associated with the development of hyponatremia. These include:
- Thiazide diuretics: These medications, such as hydrochlorothiazide, are commonly used to treat hypertension and edema. They work by increasing the excretion of sodium and water in the urine, which can lead to hyponatremia if not monitored properly.
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): SSRIs, such as fluoxetine and sertraline, are used to treat depression and other mental health conditions. They can cause hyponatremia by increasing the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which leads to water retention and dilution of sodium in the blood.
- Antipsychotics: Certain antipsychotic medications, such as clozapine and olanzapine, can also cause hyponatremia. The exact mechanism is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to the medication's effect on ADH and the kidneys' ability to regulate sodium and water balance.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can cause hyponatremia by reducing the kidneys' ability to excrete sodium and water.
Mechanisms of Action
The medications listed above can cause hyponatremia through various mechanisms. Thiazide diuretics, for example, increase the excretion of sodium and water in the urine, leading to a decrease in sodium levels in the blood. SSRIs, on the other hand, increase the release of ADH, which leads to water retention and dilution of sodium in the blood. Antipsychotics and NSAIDs can also affect the kidneys’ ability to regulate sodium and water balance, leading to hyponatremia.
| Medication | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|
| Thiazide diuretics | Increased excretion of sodium and water in the urine |
| SSRIs | Increased release of ADH, leading to water retention and dilution of sodium in the blood |
| Antipsychotics | Affect the kidneys' ability to regulate sodium and water balance |
| NSAIDs | Reduce the kidneys' ability to excrete sodium and water |
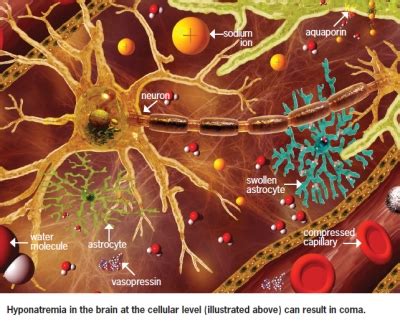
Clinical Implications

Hyponatremia can have serious clinical implications if left untreated. Severe hyponatremia can cause neurological symptoms, such as confusion, seizures, and even death. The condition can also lead to long-term complications, such as osteoporosis and falls, due to the imbalance of sodium and water in the body.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment of hyponatremia depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Mild cases may be treated with fluid restriction and monitoring of sodium levels, while more severe cases may require hospitalization and administration of hypertonic saline. Prevention of hyponatremia involves careful monitoring of patients taking medications that can cause the condition, as well as education on the importance of maintaining a balanced diet and staying hydrated.
What is the most common cause of hyponatremia in patients taking medications?
+The most common cause of hyponatremia in patients taking medications is the use of thiazide diuretics, which can lead to increased excretion of sodium and water in the urine.
How can hyponatremia be prevented in patients taking medications that can cause the condition?
+Hyponatremia can be prevented in patients taking medications that can cause the condition by careful monitoring of sodium levels, fluid restriction, and education on the importance of maintaining a balanced diet and staying hydrated.
What are the clinical implications of severe hyponatremia if left untreated?
+Severe hyponatremia can cause neurological symptoms, such as confusion, seizures, and even death if left untreated. It can also lead to long-term complications, such as osteoporosis and falls, due to the imbalance of sodium and water in the body.
In conclusion, medications such as thiazide diuretics, SSRIs, antipsychotics, and NSAIDs can cause hyponatremia, a condition characterized by low sodium levels in the blood. Understanding the mechanisms of action of these medications and the clinical implications of hyponatremia is essential for early detection and treatment. By monitoring patients taking these medications and educating them on the importance of maintaining a balanced diet and staying hydrated, healthcare providers can help prevent long-term complications and improve patient outcomes.