Plant cell mitochondria are a crucial component of plant cells, responsible for generating energy through the process of cellular respiration. These organelles are often referred to as the "powerhouses" of the cell, as they produce the majority of the cell's energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). In plant cells, mitochondria play a unique role, as they must adapt to the specific needs of the plant, such as responding to environmental stresses and optimizing energy production for growth and development.
Key Points
- Plant cell mitochondria are responsible for generating energy through cellular respiration
- They play a crucial role in responding to environmental stresses and optimizing energy production
- Mitochondria are dynamic organelles that can change shape and function in response to cellular needs
- Plant cell mitochondria have a unique structure and function compared to animal cell mitochondria
- They are essential for plant growth and development, and dysfunction can lead to various plant diseases
Structure and Function of Plant Cell Mitochondria
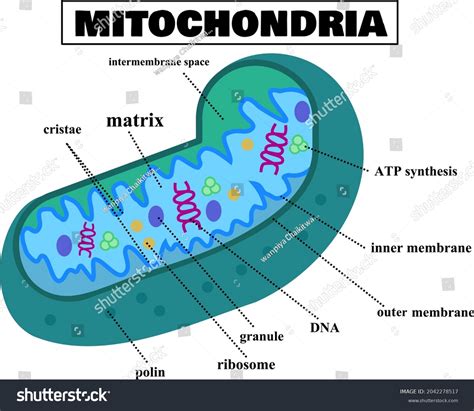
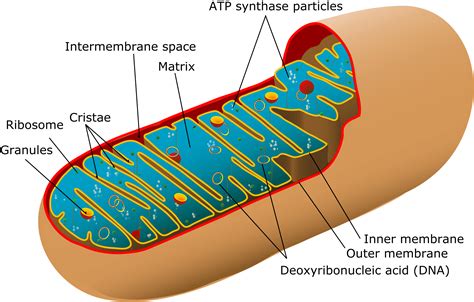
Plant cell mitochondria have a unique structure that is adapted to the specific needs of the plant. They have two membranes, an outer membrane and an inner membrane, which are separated by a space called the intermembrane space. The inner membrane is folded into a series of cristae, which increase the surface area of the mitochondria and allow for more efficient energy production. The mitochondria also contain a matrix, which is the site of the citric acid cycle and fatty acid oxidation.
Energy Production in Plant Cell Mitochondria
The primary function of plant cell mitochondria is to generate energy through the process of cellular respiration. This process involves the breakdown of glucose and other organic molecules to produce ATP, which is then used to power the cell’s various activities. Plant cell mitochondria have a unique set of enzymes and electron transport chains that allow them to optimize energy production for the specific needs of the plant. For example, plant mitochondria have a higher capacity for alternative electron transport chains, which allow them to generate energy more efficiently under low-light conditions.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Outer membrane | Regulates the movement of substances in and out of the mitochondria |
| Inner membrane | Site of the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis |
| Matrix | Site of the citric acid cycle and fatty acid oxidation |
| Cristae | Increase the surface area of the mitochondria for more efficient energy production |
Regulation of Plant Cell Mitochondria Function
The function of plant cell mitochondria is tightly regulated by a variety of mechanisms, including transcriptional regulation, post-translational modification, and protein-protein interactions. For example, the expression of mitochondrial genes is regulated by transcription factors that respond to changes in energy demand and environmental conditions. Additionally, mitochondrial proteins can be modified by phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and other post-translational modifications that regulate their activity and stability.
Response to Environmental Stresses
Plant cell mitochondria play a critical role in responding to environmental stresses, such as drought, high temperatures, and oxidative stress. Under these conditions, mitochondria can adjust their energy production to meet the changing needs of the cell. For example, under drought conditions, mitochondria can increase their alternative electron transport chain activity to generate energy more efficiently. Additionally, mitochondria can produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) that act as signaling molecules to regulate stress responses.
Plant cell mitochondria are also involved in the regulation of programmed cell death (PCD), which is a critical process for plant development and stress responses. Mitochondria can release pro-apoptotic factors, such as cytochrome c, that trigger the activation of caspases and the execution of PCD.
What is the primary function of plant cell mitochondria?
+The primary function of plant cell mitochondria is to generate energy through the process of cellular respiration.
How do plant cell mitochondria respond to environmental stresses?
+Plant cell mitochondria can adjust their energy production to meet the changing needs of the cell under environmental stresses, such as drought, high temperatures, and oxidative stress.
What is the role of plant cell mitochondria in programmed cell death?
+Plant cell mitochondria are involved in the regulation of programmed cell death (PCD), which is a critical process for plant development and stress responses.
Meta Description: Discover the crucial role of plant cell mitochondria in energy production, environmental stress responses, and programmed cell death. Learn about the unique structure and function of these dynamic organelles and their importance for plant growth and development. (149 characters)