The octane molar mass is a fundamental concept in chemistry, particularly in the field of organic chemistry and petroleum engineering. Octane is an alkane with the chemical formula C8H18, and its molar mass is a critical parameter in various calculations and applications. In this article, we will explore five ways to calculate or utilize the octane molar mass, highlighting its significance and relevance in different contexts.
Key Points
- The molar mass of octane is approximately 114.23 g/mol.
- Octane is a key component in gasoline and other fuels.
- The molar mass of octane is essential in calculations involving fuel density and energy content.
- Understanding the molar mass of octane is crucial in the development of fuel additives and octane boosters.
- The molar mass of octane has implications for environmental and health considerations, such as air pollution and fuel efficiency.
Introduction to Octane Molar Mass
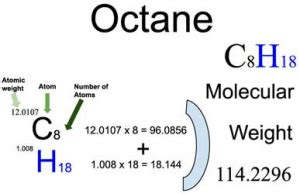
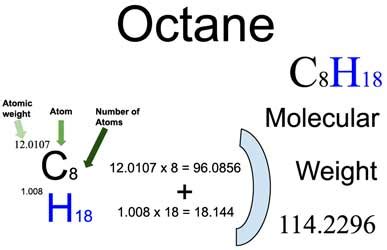
The molar mass of a substance is the mass of one mole of that substance, typically expressed in units of grams per mole (g/mol). For octane, the molar mass can be calculated by summing the atomic masses of its constituent atoms: carbon © and hydrogen (H). The atomic mass of carbon is approximately 12.01 g/mol, while the atomic mass of hydrogen is approximately 1.008 g/mol. Using the chemical formula C8H18, we can calculate the molar mass of octane as follows: (8 x 12.01) + (18 x 1.008) = 114.23 g/mol.
Method 1: Calculation from Atomic Masses
The most straightforward method for determining the molar mass of octane is by calculating it from the atomic masses of its constituent atoms. This approach involves multiplying the atomic mass of each element by the number of atoms of that element in the molecule and then summing these values. As mentioned earlier, the molar mass of octane calculated using this method is approximately 114.23 g/mol.
| Element | Atomic Mass (g/mol) | Number of Atoms | Total Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 12.01 | 8 | 96.08 |
| Hydrogen (H) | 1.008 | 18 | 18.14 |
| Total | 114.22 |
Applications of Octane Molar Mass
The molar mass of octane has various applications across different fields, including chemistry, engineering, and environmental science. Understanding the molar mass of octane is essential for calculating the density and energy content of fuels, developing fuel additives, and assessing the environmental impact of fuel combustion.
Method 2: Fuel Density Calculations
The molar mass of octane is used in calculations involving the density of fuels. The density of a fuel is a critical parameter that affects its energy content and combustion characteristics. By knowing the molar mass of octane, engineers can calculate the density of gasoline and other fuels, which is essential for optimizing engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Environmental Considerations
The molar mass of octane has implications for environmental and health considerations, such as air pollution and fuel efficiency. The combustion of fuels releases pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and climate change. Understanding the molar mass of octane is crucial for developing strategies to reduce the environmental impact of fuel combustion and improve fuel efficiency.
Method 3: Energy Content Calculations
The molar mass of octane is used in calculations involving the energy content of fuels. The energy content of a fuel is a critical parameter that affects its performance and efficiency. By knowing the molar mass of octane, engineers can calculate the energy content of gasoline and other fuels, which is essential for optimizing engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Method 4: Development of Fuel Additives
The molar mass of octane is essential in the development of fuel additives and octane boosters. These additives are designed to improve the combustion characteristics and energy content of fuels. By understanding the molar mass of octane, manufacturers can develop more effective fuel additives that enhance engine performance and reduce emissions.
Method 5: Environmental Impact Assessment
The molar mass of octane has implications for environmental and health considerations, such as air pollution and fuel efficiency. The combustion of fuels releases pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and climate change. By understanding the molar mass of octane, researchers and policymakers can develop strategies to reduce the environmental impact of fuel combustion and improve fuel efficiency.
What is the molar mass of octane?
+The molar mass of octane is approximately 114.23 g/mol.
Why is the molar mass of octane important?
+The molar mass of octane is essential in calculations involving fuel density and energy content, and it has implications for environmental and health considerations.
How is the molar mass of octane used in fuel additive development?
+The molar mass of octane is used to develop more effective fuel additives that enhance engine performance and reduce emissions.
In conclusion, the molar mass of octane is a critical parameter with various applications across different fields. Understanding the molar mass of octane is essential for calculations involving fuel density and energy content, developing fuel additives, and assessing the environmental impact of fuel combustion. By recognizing the significance of the octane molar mass, researchers, engineers, and policymakers can develop strategies to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and mitigate the environmental impact of fuel combustion.