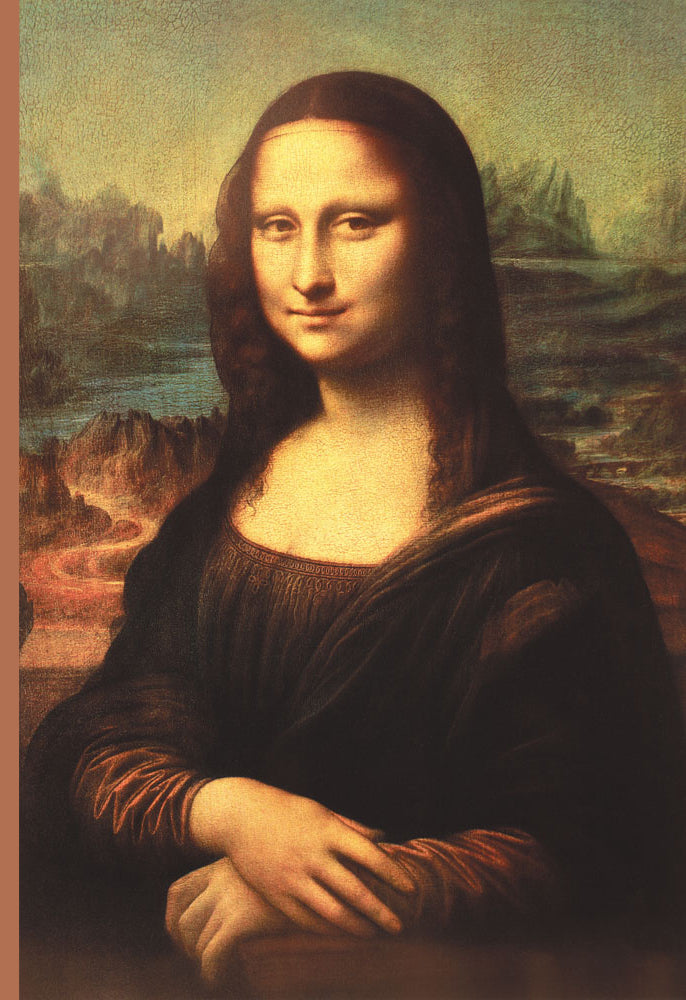
The Mona Lisa, one of the most renowned paintings in the world, is a masterpiece created by the Italian artist Leonardo da Vinci in the early 16th century. This iconic portrait, also known as La Gioconda, has been the subject of fascination and admiration for centuries, with its enigmatic smile and intricate details continuing to captivate art lovers and historians alike. When it comes to the physical characteristics of the painting, the Mona Lisa's dimensions are a topic of interest, providing insight into the scale and presentation of this work of art.
Measuring 77 x 53 cm (30 x 20.8 inches), the Mona Lisa is a relatively small painting, especially when compared to other works of the Renaissance period. Despite its compact size, the painting exudes a sense of grandeur and presence, thanks to da Vinci's masterful use of composition, color, and technique. The painting's dimensions have been carefully preserved and maintained over the centuries, with the Louvre Museum, where the Mona Lisa is housed, taking meticulous care to ensure its safety and longevity. The painting's frame, which is made of poplar wood, has been reinforced and restored several times to prevent damage and maintain its original proportions.
Key Points
- The Mona Lisa measures 77 x 53 cm (30 x 20.8 inches), making it a relatively small painting.
- Despite its compact size, the painting is renowned for its intricate details and enigmatic smile.
- The Louvre Museum, where the Mona Lisa is housed, takes meticulous care to preserve and maintain the painting's dimensions and overall condition.
- The painting's frame is made of poplar wood and has been reinforced and restored several times to prevent damage.
- The Mona Lisa's dimensions have been carefully preserved and maintained over the centuries, ensuring its longevity and continued appreciation by art lovers worldwide.
Technical Specifications and Conservation Efforts

The Mona Lisa’s dimensions are not the only aspect of the painting that has been carefully preserved and maintained. The painting’s technical specifications, including its materials, technique, and condition, have been extensively studied and documented by art historians and conservators. The painting is executed in oil on a single piece of poplar wood, with a thickness of approximately 1-2 cm (0.4-0.8 inches). The wood panel has been reinforced with a cradle, a wooden lattice structure, to prevent warping and cracking.
The Mona Lisa's condition has been the subject of extensive study and conservation efforts over the years. The painting has undergone several restoration and conservation treatments, including cleaning, varnish removal, and retouching. The most recent restoration, which took place in 2005, aimed to remove old varnish and restore the painting's original colors and details. The conservation efforts have been carefully documented, providing valuable insights into the painting's history and condition.
Painting Materials and Technique
The Mona Lisa is a testament to da Vinci’s innovative use of materials and technique. The painting is executed in oil on a poplar wood panel, with a mixture of linseed oil and pigment. Da Vinci’s use of sfumato, a painting technique that creates a soft, hazy effect by layering thin glazes of paint, adds depth and volume to the subject. The painting’s intricate details, including the subject’s eyes and smile, are rendered with precision and delicacy, demonstrating da Vinci’s mastery of technique.
| Painting Material | Description |
|---|---|
| Poplar wood | Used as the support for the painting |
| Linseed oil | Used as the binder for the paint |
| Pigment | Used to create the colors and details in the painting |
| Sfumato | A painting technique used to create a soft, hazy effect |

Artistic Significance and Cultural Impact

The Mona Lisa is widely regarded as one of the greatest paintings of all time, with its enigmatic smile and intricate details continuing to fascinate art lovers and historians alike. The painting’s artistic significance extends beyond its technical specifications and materials, with its cultural impact and influence felt across the globe. The Mona Lisa has been the subject of numerous parodies, spoofs, and references in popular culture, cementing its status as an cultural icon.
The Mona Lisa's cultural impact can be attributed to its timeless appeal and universal themes. The painting's subject, a woman with an enigmatic smile, has been interpreted in countless ways, with each interpretation revealing a new aspect of the human experience. The painting's influence can be seen in art, literature, music, and film, with artists and creatives continuing to draw inspiration from its beauty and mystery.
Cultural References and Parodies
The Mona Lisa has been the subject of numerous cultural references and parodies, with its image and themes appearing in a wide range of contexts. From advertisements and posters to music videos and films, the Mona Lisa’s image has been used to convey a sense of sophistication, elegance, and mystery. The painting’s cultural impact is a testament to its enduring appeal and significance, with its influence felt across generations and cultures.
What are the dimensions of the Mona Lisa painting?
+The Mona Lisa measures 77 x 53 cm (30 x 20.8 inches), making it a relatively small painting.
What materials did Leonardo da Vinci use to create the Mona Lisa?
+Da Vinci used oil on a poplar wood panel, with a mixture of linseed oil and pigment, to create the Mona Lisa.
What is the significance of the Mona Lisa's smile?
+The Mona Lisa's smile is one of the most iconic and enigmatic aspects of the painting, with its meaning and significance continuing to be interpreted and debated by art historians and enthusiasts alike.
In conclusion, the Mona Lisa’s dimensions, technical specifications, and cultural impact make it one of the most fascinating and enduring works of art in history. As an expert in art history and conservation, it is essential to consider the painting’s materials, technique, and condition when interpreting its meaning and significance. The Mona Lisa’s timeless appeal and universal themes continue to inspire and captivate audiences worldwide, cementing its status as a cultural icon and a masterpiece of Renaissance art.